The Portable Document Format (PDF) is a file format developed by Adobe in the 1990s to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. Based on the PostScript language, each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a fixed-layout flat document, including the text, fonts, vector graphics, raster images and other information needed to display it. PDF was standardized as an open format, ISO 32000, in 2008, and no longer requires any royalties for its implementation.
In computing, a core dump, crash dump, memory dump, or system dump consists of the recorded state of the working memory of a computer program at a specific time, generally when the program has crashed or otherwise terminated abnormally. In practice, other key pieces of program state are usually dumped at the same time, including the processor registers, which may include the program counter and stack pointer, memory management information, and other processor and operating system flags and information. A snapshot dump is a memory dump requested by the computer operator or by the running program, after which the program is able to continue. Core dumps are often used to assist in diagnosing and debugging errors in computer programs.
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the presentation layer is layer 6 and serves as the data translator for the network. It is sometimes called the syntax layer.
An application layer is an abstraction layer that specifies the shared communications protocols and interface methods used by hosts in a communications network. The application layer abstraction is used in both of the standard models of computer networking: the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) and the OSI model. Although both models use the same term for their respective highest level layer, the detailed definitions and purposes are different.
In computer networking, Server Message Block (SMB), one version of which was also known as Common Internet File System, operates as an application-layer network protocol mainly used for providing shared access to files, printers, and serial ports and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides an authenticated inter-process communication mechanism. Most usage of SMB involves computers running Microsoft Windows, where it was known as "Microsoft Windows Network" before the introduction of Active Directory. Corresponding Windows services are LAN Manager Server and LAN Manager Workstation.
External Data Representation (XDR) is a standard data serialization format, for uses such as computer network protocols. It allows data to be transferred between different kinds of computer systems. Converting from the local representation to XDR is called encoding. Converting from XDR to the local representation is called decoding. XDR is implemented as a software library of functions which is portable between different operating systems and is also independent of the transport layer.

A timestamp is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second. The term derives from rubber stamps used in offices to stamp the current date, and sometimes time, in ink on paper documents, to record when the document was received. Common examples of this type of timestamp are a postmark on a letter or the "in" and "out" times on a time card.

In computing, a file system or filesystem controls how data is stored and retrieved. Without a file system, information placed in a storage medium would be one large body of data with no way to tell where one piece of information stops and the next begins. By separating the data into pieces and giving each piece a name, the information is easily isolated and identified. Taking its name from the way paper-based information systems are named, each group of data is called a "file". The structure and logic rules used to manage the groups of information and their names is called a "file system".
On Microsoft Windows operating systems, starting with the IE4 Desktop Update for Win95/98, a thumbnail cache is used to store thumbnail images for Windows Explorer's thumbnail view. This speeds up the display of images as these smaller images do not need to be recalculated every time the user views the folder.
Windows XP introduced many features not found in previous versions of Windows.
COM Structured Storage is a technology developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows operating system for storing hierarchical data within a single file. Strictly speaking, the term structured storage refers to a set of COM interfaces that a conforming implementation must provide, and not to a specific implementation, nor to a specific file format. In addition to providing a hierarchical structure for data, structured storage may also provide a limited form of transactional support for data access. Microsoft provides an implementation that supports transactions, as well as one that does not.
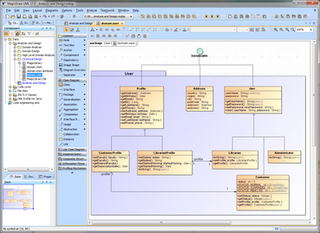
MagicDraw is a visual UML, SysML, BPMN, and UPDM modeling tool with team collaboration support. Designed for business analysts, software analysts, programmers, and QA engineers, this dynamic and versatile development tool facilitates analysis and design of object oriented (OO) systems and databases. It provides the code engineering mechanism, as well as database schema modeling, DDL generation and reverse engineering facilities.
An NTFS reparse point is a type of NTFS file system object. It is available with the NTFS v3.0 found in Windows 2000 or later versions. Reparse points provide a way to extend the NTFS filesystem. A reparse point contains a reparse tag and data that are interpreted by a filesystem filter identified by the tag. Microsoft includes several default tags including NTFS symbolic links, directory junction points, volume mount points and Unix domain sockets. Also, reparse points are used as placeholders for files moved by Windows 2000's Remote Storage hierarchical storage system. They also can act as hard links, but aren't limited to point to files on the same volume: they can point to directories on any local volume.
In computing, a shared resource, or network share, is a computer resource made available from one host to other hosts on a computer network. It is a device or piece of information on a computer that can be remotely accessed from another computer, typically via a local area network or an enterprise intranet, transparently as if it were a resource in the local machine.
Network sharing is made possible by inter-process communication over the network.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of the "Windows Setup" process, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista.
A clustered file system is a file system which is shared by being simultaneously mounted on multiple servers. There are several approaches to clustering, most of which do not employ a clustered file system. Clustered file systems can provide features like location-independent addressing and redundancy which improve reliability or reduce the complexity of the other parts of the cluster. Parallel file systems are a type of clustered file system that spread data across multiple storage nodes, usually for redundancy or performance.
Mobile document access (MDA) is a methodology by which a mobile computer such as a cell phone or PDA, can retrieve, store, and otherwise access electronic documents and/or images of paper documents not specifically created for a mobile computing device. The term has some overlap with the concepts of Mobile content, Content Management Systems and Data conversion, and sometimes utilize the Mobile Web.
NTFS volume mount points are specialized NTFS filesystem objects which are used to mount and provide an entry point to other volumes. Mount points can be created in a directory on an NTFS file system, which gives a reference to the root directory of the mounted volume. Any empty directory can be converted to a mount point. The mounted volume is not limited to the NTFS filesystem but can be formatted with any file system supported by Microsoft Windows. Volume Mount Points are supported from NTFS 3.0, which was introduced with Windows 2000.

Distributed Data Management Architecture (DDM) is IBM's open, published software architecture for creating, managing and accessing data on a remote computer. DDM was initially designed to support record-oriented files; it was extended to support hierarchical directories, stream-oriented files, queues, and system command processing; it was further extended to be the base of IBM's Distributed Relational Database Architecture (DRDA); and finally, it was extended to support data description and conversion. Defined in the period from 1980 to 1993, DDM specifies necessary components, messages, and protocols, all based on the principles of object-orientation. DDM is not, in itself, a piece of software; the implementation of DDM takes the form of client and server products. As an open architecture, products can implement subsets of DDM architecture and products can extend DDM to meet additional requirements. Taken together, DDM products implement a distributed file system.




