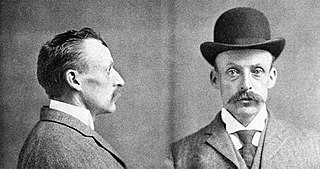Osteichthyes, popularly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse taxonomic group of fish that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue, as opposed to cartilage. The vast majority of fish are members of Osteichthyes, which is an extremely diverse and abundant group consisting of 45 orders, and over 435 families and 28,000 species. It is the largest class of vertebrates in existence today. The group Osteichthyes is divided into the ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii) and lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii). The oldest known fossils of bony fish are about 420 million years old, which are also transitional fossils, showing a tooth pattern that is in between the tooth rows of sharks and bony fishes.

Seafood is any form of sea life regarded as food by humans, prominently including fish and shellfish. Shellfish include various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Historically, marine mammals such as cetaceans as well as seals have been eaten as food, though that happens to a lesser extent in modern times. Edible sea plants such as some seaweeds and microalgae are widely eaten as sea vegetables around the world, especially in Asia. In North America, although not generally in the United Kingdom, the term "seafood" is extended to fresh water organisms eaten by humans, so all edible aquatic life may be referred to as "seafood". For the sake of completeness, this article is inclusive of all edible aquatic life.

Sushi is a Japanese dish of prepared vinegared rice, usually with some sugar and salt, accompanying a variety of ingredients, such as seafood, vegetables, and occasionally tropical fruits. Styles of sushi and its presentation vary widely, but the one key ingredient is "sushi rice", also referred to as shari (しゃり), or sumeshi (酢飯).

Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are normally caught in the wild. Techniques for catching fish include hand gathering, spearing, netting, angling and trapping. “Fishing” may include catching aquatic animals other than fish, such as molluscs, cephalopods, crustaceans, and echinoderms. The term is not normally applied to catching farmed fish, or to aquatic mammals, such as whales where the term whaling is more appropriate. In addition to being caught to be eaten, fish are caught as recreational pastimes. Fishing tournaments are held, and caught fish are sometimes kept as preserved or living trophies. When bioblitzes occur, fish are typically caught, identified, and then released.

Salmon is the common name for several species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. Other fish in the same family include trout, char, grayling and whitefish. Salmon are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic and Pacific Ocean. Many species of salmon have been introduced into non-native environments such as the Great Lakes of North America and Patagonia in South America. Salmon are intensively farmed in many parts of the world.

Fish and chips is a hot dish of English origin consisting of fried fish in batter served with chips. It is a common take-away food in the United Kingdom and an early example of culinary fusion. Fish and chips first appeared in the UK in the 1860s. By 1910 there were more than 25,000 fish and chip shops across the UK, and by the 1930s there were over 35,000, falling to about 10,000 by 2009. The British government safeguarded the supply of fish and chips during World War I and World War II; it was one of the few foods in the UK not subject to rationing. Fish and chips is a staple meal in numerous countries, particularly in English-speaking and Commonwealth countries.

Fish sauce is a liquid condiment made from fish or krill that have been coated in salt and fermented for up to two years. It is used as a staple seasoning in East Asian cuisine and Southeast Asian cuisine, particularly Burma, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Philippines, Taiwan, Thailand, and Vietnam.

Trout is the common name for a number of species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera Oncorhynchus, Salmo and Salvelinus, all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word trout is also used as part of the name of some non-salmonid fish such as Cynoscion nebulosus, the spotted seatrout or speckled trout.

Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores, and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, Vandellia cirrhosa. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels. Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus Corydoras, are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, but others are crepuscular or diurnal.

Clupeidae is a family of ray-finned fishes, comprising, for instance, the herrings, shads, sardines, hilsa, and menhadens. The clupeoids include many of the most important food fishes in the world, and are also commonly caught for production of fish oil and fish meal. Many members of the family have a body protected with shiny cycloid scales, a single dorsal fin, and a fusiform body for quick, evasive swimming and pursuit of prey composed of small planktonic animals. Due to their small size and position in the lower trophic level of many marine food webs, the levels of methylmercury they bioaccumulate are very low, reducing the risk of mercury poisoning when consumed.

Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family Clupeidae.

Tilapia is the common name for nearly a hundred species of cichlid fish from the tilapiine cichlid tribe. Tilapia are mainly freshwater fish inhabiting shallow streams, ponds, rivers, and lakes, and less commonly found living in brackish water. Historically, they have been of major importance in artisanal fishing in Africa, and they are of increasing importance in aquaculture and aquaponics. Tilapia can become a problematic invasive species in new warm-water habitats such as Australia, whether deliberately or accidentally introduced, but generally not in temperate climates due to their inability to survive in cold water.
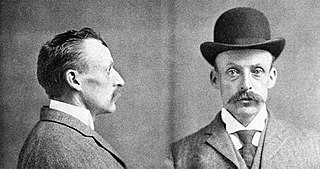
Hamilton Howard "Albert" Fish was an American serial killer, child rapist and cannibal. He was also known as the Gray Man, the Werewolf of Wysteria, the Brooklyn Vampire, the Moon Maniac, and The Boogey Man. Fish once boasted that he "had children in every state", and at one time stated his number of victims was about 100. However, it is not known whether he was referring to rapes or cannibalization, nor is it known if the statement was truthful. Fish was a suspect in at least five murders during his lifetime. Fish confessed to three murders that police were able to trace to a known homicide, and he confessed to stabbing at least two other people. He was put on trial for the kidnapping and murder of Grace Budd, and was convicted and executed by electric chair. His crimes were dramatized in the 2007 film The Gray Man, starring Patrick Bauchau as Fish.

Fish farming or pisciculture involves raising fish commercially in tanks or enclosures such as fish ponds, usually for food. It is the principal form of aquaculture, while other methods may fall under mariculture. A facility that releases juvenile fish into the wild for recreational fishing or to supplement a species' natural numbers is generally referred to as a fish hatchery. Worldwide, the most important fish species produced in fish farming are carp, tilapia, salmon, and catfish.
FishBase is a global species database of fish species. It is the largest and most extensively accessed online database on adult finfish on the web. Over time it has "evolved into a dynamic and versatile ecological tool" that is widely cited in scholarly publications.

Generally, a fishery is an entity engaged in raising or harvesting fish which is determined by some authority to be a fishery. According to the FAO, a fishery is typically defined in terms of the "people involved, species or type of fish, area of water or seabed, method of fishing, class of boats, purpose of the activities or a combination of the foregoing features". The definition often includes a combination of fish and fishers in a region, the latter fishing for similar species with similar gear types.

Pisces (♓️) is the twelfth astrological sign in the Zodiac. It is a negative mutable sign. It spans 330° to 360° of celestial longitude. Under the tropical zodiac, the sun transits this area between February 19 and March 20. In Sidereal astrology, the Sun currently transits the constellation of Pisces from approximately March 12 to April 18. In classical interpretations, the symbol of the fish is derived from the ichthyocentaurs, who aided Aphrodite when she was born from the sea.

Fish are gill-bearing aquatic craniate animals that lack limbs with digits. They form a sister group to the tunicates, together forming the olfactores. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Tetrapods emerged within lobe-finned fishes, so cladistically they are fish as well. However, traditionally fish are rendered paraphyletic by excluding the tetrapods. Because in this manner the term "fish" is defined negatively as a paraphyletic group, it is not considered a formal taxonomic grouping in systematic biology, unless it is used in the cladistic sense, including tetrapods. The traditional term pisces is considered a typological, but not a phylogenetic classification.

Pescetarianism or pescatarianism is the practice of adhering to a diet that incorporates seafood as the only source of meat in an otherwise vegetarian diet. Most pescetarians are ovo-lacto vegetarians who eat seafood along with dairy products and eggs, often colloquially defined as "fish but no other meat". Vegetarian groups have had to clarify that pescetarian diets fall outside of the range of vegetarianism.

The Day's round herring is a relative of the herring that is endemic to southwestern India. It is the only species in its genus. It is named after Francis Day who described the species in 1873.