
Puerto Rico, officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico and briefly called Porto Rico, is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the northeast Caribbean Sea, approximately 1,000 miles (1,600 km) southeast of Miami, Florida.

The geography of Puerto Rico consists of an archipelago located between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of the Virgin Islands. The main island of Puerto Rico is the smallest and most eastern of the Greater Antilles. With an area of 3,515 square miles (9,104 km2), it is the third largest island in the United States and the 82nd largest island in the world. Various smaller islands and cays, including Vieques, Culebra, Mona, Desecheo, and Caja de Muertos comprise the remainder of the archipelago with only Culebra and Vieques being inhabited year-round. Mona is uninhabited through large parts of the year except for employees of the Puerto Rico Department of Natural Resources.

The Virgin Islands are geologically and biogeographically the easternmost part of the Greater Antilles, the northern islands belonging to the Puerto Rican Bank and St. Croix being a displaced part of the same geologic structure. Politically, the British Virgin Islands have been governed as the western island group of the Leeward Islands, which are the northern part of the Lesser Antilles, and form the border between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The archipelago is separated from the true Lesser Antilles by the Anegada Passage and from the main island of Puerto Rico by the Virgin Passage.

Isla Culebra is an island-municipality of Puerto Rico and geographically part of the Virgin Islands. It is located approximately 17 miles (27 km) east of the Puerto Rican mainland, 12 miles (19 km) west of St. Thomas and 9 miles (14 km) north of Vieques. Culebra is spread over 5 wards and Culebra Pueblo (Dewey), the downtown area and the administrative center of the city. Residents of the island are known as Culebrenses. With a population of 1,818 as of the latest census, it is Puerto Rico's least populous municipality.

Fajardo is a town and municipality in Puerto Rico (U.S.) located in the east region of the island, bordering the Atlantic Ocean, north of Ceiba and east of Luquillo. Fajardo is spread over 7 wards and Downtown Fajardo, which serves as the administrative center. It is both a principal part of the Fajardo Metropolitan Statistical Area and the San Juan-Caguas-Fajardo Combined Statistical Area.
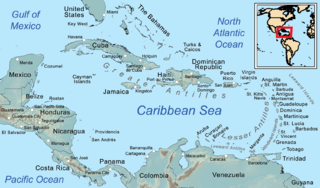
The Leeward Islands are a group of islands situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. Starting with the Virgin Islands east of Puerto Rico, they extend southeast to Guadeloupe and its dependencies. In English, the term Leeward Islands refers to the northern islands of the Lesser Antilles chain. The more southerly part of this chain, starting with Dominica, is called the Windward Islands. Dominica was originally considered part of the Leeward Islands, but was transferred from the British Leeward Islands to the British Windward Islands in 1940.

Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government. They differ from U.S. states and Native American tribes, which have limited sovereignty. The territories are classified by incorporation and whether they have an "organized" government through an organic act passed by Congress.

The Puerto Rico Trench is located on the boundary between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The oceanic trench is associated with a complex transition between the Lesser Antilles subduction zone to the south and the major transform fault zone or plate boundary, which extends west between Cuba and Hispaniola through the Cayman Trough to the coast of Central America. The trench is 800 kilometres (497 mi) long and has a maximum depth of 8,376 metres (27,480 ft) or 5.20 miles in the Brownson Deep, which is the deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean and the deepest point not in the Pacific Ocean. On December 19, 2018, its deepest point was identified by the DSSV Pressure Drop using a state-of-the-art Kongsberg EM124 multibeam sonar and then directly visited and its depth verified by the manned submersible DSV Limiting Factor.

Caja de Muertos is an uninhabited island off the southern coast of Puerto Rico, in the municipality of Ponce. The island is protected by the Reserva Natural Caja de Muertos natural reserve, because of its native turtle traffic. Hikers and beachgoers are often seen in the island, which can be reached by ferry from the La Guancha Boardwalk sector of Ponce Playa. Together with Cardona, Ratones, Morrillito, Isla del Frio, Gatas, and Isla de Jueyes, Caja de Muertos is one of seven islands ascribed to the municipality of Ponce.
"Dead Man's Chest" is a fictional sea song, originally from Robert Louis Stevenson's novel Treasure Island (1883). It was expanded in a poem, titled "Derelict" by Young E. Allison, published in the Louisville Courier-Journal in 1891. It has since been used in many later works of art in various forms.
Centennial Communications and its subsidiaries provided wireless and broadband telecommunications services to wireless telephone subscribers in the United States, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. On March 13, 2007 Centennial Communications completed the sale of Centennial Dominicana to Trilogy International Partners for approximately $80 million in cash.

The history of Puerto Ricans of African descent begins with free African men, known as libertos, who accompanied the Spanish Conquistadors in the invasion of the island. The Spaniards enslaved the Taínos, many of whom died as a result of new infectious diseases and the Spaniards' oppressive colonization efforts. Spain's royal government needed laborers and began to rely on slavery to staff their mining and fort-building operations. The Crown authorized importing enslaved West Africans. As a result, the majority of the African peoples who entered Puerto Rico were part of the forced migration of the Atlantic slave trade, and came from many different cultures and peoples of the African continent.
Dead Man's Chest may refer to:

The Spanish Virgin Islands, formerly called the Passage Islands and also known as the Puerto Rican Virgin Islands, primarily consisting of the islands of Culebra and Vieques, are part of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and are located east of the main island of Puerto Rico in the Caribbean.

Piracy in the British Virgin Islands was prevalent during the so-called "Golden Age of Piracy", mainly during the age of 1690-1730. Privateering was also widely practised in the jurisdiction throughout frequent colonial wars, not least by emancipated slaves who, with in preference to back-breaking labour in the fields for pitiful wages, took enormous risks to capture fortunes on the seas with the sanction of the Crown. In 1808, Patrick Colquhoun, a prize agent for the Territory spoke of "the most daring outrages which are frequently committed by people of colour."

The green-throated carib is a species of hummingbird in the genus Eulampis, which contains one other species. It has two subspecies, holosericeus and chlorolaemus, the former occurring in Puerto Rico and the latter in Grenada.

Sabal causiarum, commonly known as the Puerto Rico palmetto or Puerto Rican hat palm, is a species of palm which is native to Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, the United States Virgin Islands, and the British Virgin Islands. As its common and scientific names suggest, its leaves are used in the manufacture of "straw" hats.

This is an English language bibliography of United States Virgin Islands and its geography, history, inhabitants, culture, biota, etc.















