Loran-C is a hyperbolic radio navigation system that allows a receiver to determine its position by listening to low frequency radio signals that are transmitted by fixed land-based radio beacons. Loran-C combined two different techniques to provide a signal that was both long-range and highly accurate, features that had been incompatible. Its disadvantage was the expense of the equipment needed to interpret the signals, which meant that Loran-C was used primarily by militaries after it was introduced in 1957.

Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, marine navigation, aeronautic navigation, and space navigation.

Radio navigation or radionavigation is the application of radio frequencies to determine a position of an object on the Earth, either the vessel or an obstruction. Like radiolocation, it is a type of radiodetermination.

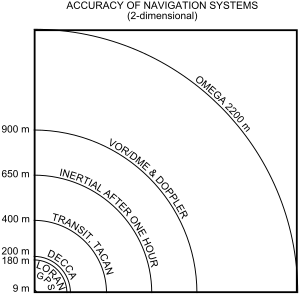
OMEGA was the first global-range radio navigation system, operated by the United States in cooperation with six partner nations. It was a hyperbolic navigation system, enabling ships and aircraft to determine their position by receiving very low frequency (VLF) radio signals in the range 10 to 14 kHz, transmitted by a global network of eight fixed terrestrial radio beacons, using a navigation receiver unit. It became operational around 1971 and was shut down in 1997 in favour of the Global Positioning System.
A non-directional beacon (NDB) or non-directional radio beacon is a radio beacon which does not include inherent directional information. Radio beacons are radio transmitters at a known location, used as an aviation or marine navigational aid. NDB are in contrast to directional radio beacons and other navigational aids, such as low-frequency radio range, VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) and tactical air navigation system (TACAN).

Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range Station (VOR) is a type of short-range radio navigation system for aircraft, enabling aircraft with a receiving unit to determine its position and stay on course by receiving radio signals transmitted by a network of fixed ground radio beacons. It uses frequencies in the very high frequency (VHF) band from 108.00 to 117.95 MHz. Developed in the United States beginning in 1937 and deployed by 1946, VOR became the standard air navigational system in the world, used by both commercial and general aviation, until supplanted by satellite navigation systems such as GPS in the early 21st century. As such, VOR stations are being gradually decommissioned. In 2000 there were about 3,000 VOR stations operating around the world, including 1,033 in the US, but by 2013 the number in the US had been reduced to 967. The United States is decommissioning approximately half of its VOR stations and other legacy navigation aids as part of a move to performance-based navigation, while still retaining a "Minimum Operational Network" of VOR stations as a backup to GPS. In 2015, the UK planned to reduce the number of stations from 44 to 19 by 2020.

Gee, sometimes written GEE, was a radio navigation system used by the Royal Air Force during World War II. It measured the time delay between two radio signals to produce a fix, with accuracy on the order of a few hundred metres at ranges up to about 350 miles (560 km). It was the first hyperbolic navigation system to be used operationally, entering service with RAF Bomber Command in 1942.

In aviation, distance measuring equipment (DME) is a radio navigation technology that measures the slant range (distance) between an aircraft and a ground station by timing the propagation delay of radio signals in the frequency band between 960 and 1215 megahertz (MHz). Line-of-visibility between the aircraft and ground station is required. An interrogator (airborne) initiates an exchange by transmitting a pulse pair, on an assigned 'channel', to the transponder ground station. The channel assignment specifies the carrier frequency and the spacing between the pulses. After a known delay, the transponder replies by transmitting a pulse pair on a frequency that is offset from the interrogation frequency by 63 MHz and having specified separation.

Direction finding (DF), or radio direction finding (RDF), is the use of radio waves to determine the direction to a radio wave source. The source may be a cooperating radio transmitter or may be an inadvertant source, a naturally-occurring radio source, or an illicit or enemy system. Radio direction finding differs from radar in that only the direction is determined by any one receiver; a radar system usually also gives a distance to the object of interest, as well as direction. By triangulation, the location of a radio source can be determined by measuring its direction from two or more locations. Radio direction finding is used in radio navigation for ships and aircraft, to locate emergency transmitters for search and rescue, for tracking wildlife, and to locate illegal or interfering transmitters. During the Second World War, radio direction finding was used by both sides to locate and direct aircraft, surface ships, and submarines.

A tactical air navigation system, commonly referred to by the acronym TACAN, is a navigation system used by military aircraft. It provides the user with bearing and distance to a ground or ship-borne station. It is a more accurate version of the VOR/DME system that provides bearing and range information for civil aviation. The DME portion of the TACAN system is available for civil use; at VORTAC facilities where a VOR is combined with a TACAN, civil aircraft can receive VOR/DME readings. Aircraft equipped with TACAN avionics can use this system for en route navigation as well as non-precision approaches to landing fields. The Space Shuttle is one such vehicle that was designed to use TACAN navigation but later upgraded with GPS as a replacement.
Gee-H, sometimes written G-H or GEE-H, was a radio navigation system developed by Britain during World War II to aid RAF Bomber Command. The name refers to the system's use of the earlier Gee equipment, as well as its use of the "H principle" or "twin-range principle" of location determination. Its official name was AMES Type 100.

Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPSs) supplement and enhance the positional data available from global navigation satellite systems (GNSSs). A DGPS for GPS can increase accuracy by about a thousandfold, from approximately 15 metres (49 ft) to 1–3 centimetres.

The microwave landing system (MLS) is an all-weather, precision radio guidance system intended to be installed at large airports to assist aircraft in landing, including 'blind landings'. MLS enables an approaching aircraft to determine when it is aligned with the destination runway and on the correct glidepath for a safe landing. MLS was intended to replace or supplement the instrument landing systems (ILS). MLS has a number of operational advantages over ILS, including a wider selection of channels to avoid interference with nearby installations, excellent performance in all weather, a small "footprint" at the airports, and wide vertical and horizontal "capture" angles that allowed approaches from wider areas around the airport.
Pseudo-range multilateration, often simply multilateration (MLAT) when in context, is a technique for determining the position of an unknown point, such as a vehicle, based on measurement of the times of arrival (TOAs) of energy waves traveling between the unknown point and multiple stations at known locations. When the waves are transmitted by the vehicle, MLAT is used for surveillance; when the waves are transmitted by the stations, MLAT is used for navigation. In either case, the stations' clocks are assumed synchronized but the vehicle's clock is not.

Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. Radio is widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications.

In radio navigation, a VOR/DME is a radio beacon that combines a VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) with a distance-measuring equipment (DME). The VOR allows the receiver to measure its bearing to or from the beacon, while the DME provides the slant distance between the receiver and the station. Together, the two measurements allow the receiver to compute a position fix.

The low-frequency radio range, also known as the four-course radio range, LF/MF four-course radio range, A-N radio range, Adcock radio range, or commonly "the range", was the main navigation system used by aircraft for instrument flying in the 1930s and 1940s, until the advent of the VHF omnidirectional range (VOR), beginning in the late 1940s. It was used for en route navigation as well as instrument approaches and holds.

Hyperbolic navigation is a class of radio navigation systems in which a navigation receiver instrument is used to determine location based on the difference in timing of radio waves received from radio navigation beacon transmitters.
Sonne was a radio navigation system developed in Germany during World War II. It was developed from an earlier experimental system known as Elektra, and therefore the system is also known as Elektra-sonnen. When the British learned of the system they started using it as well, under the name Consol, meaning "by the sun".

LORAN, short for long range navigation, was a hyperbolic radio navigation system developed in the United States during World War II. It was similar to the UK's Gee system but operated at lower frequencies in order to provide an improved range up to 1,500 miles (2,400 km) with an accuracy of tens of miles. It was first used for ship convoys crossing the Atlantic Ocean, and then by long-range patrol aircraft, but found its main use on the ships and aircraft operating in the Pacific theater during World War II.