In electrical engineering, the power factor of an AC electrical power system is defined as the ratio of the real power absorbed by the load to the apparent power flowing in the circuit, and is a dimensionless number in the closed interval of −1 to 1. A power factor of less than one indicates the voltage and current are not in phase, reducing the instantaneous product of the two. Real power is the instantaneous product of voltage and current and represents the capacity of the electricity for performing work. Apparent power is the average product of current and voltage. Due to energy stored in the load and returned to the source, or due to a non-linear load that distorts the wave shape of the current drawn from the source, the apparent power may be greater than the real power. A negative power factor occurs when the device generates power, which then flows back towards the source.
In electric power transmission and distribution, volt-ampere reactive (var) is a unit of measurement of reactive power. Reactive power exists in an AC circuit when the current and voltage are not in phase. The term var was proposed by the Romanian electrical engineer Constantin Budeanu and introduced in 1930 by the IEC in Stockholm, which has adopted it as the unit for reactive power.

A high-voltage, direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system uses direct current for the bulk transmission of electrical power, in contrast with the more common alternating current (AC) systems. For long-distance transmission, HVDC systems may be less expensive and has lower electrical losses. For underwater power cables, HVDC avoids the heavy currents required to charge and discharge the cable capacitance each cycle. For shorter distances, the higher cost of DC conversion equipment compared to an AC system may still be justified, due to other benefits of direct current links. HVDC currently uses voltages between 100 kV and 800 kV, with an 1,100 kV link in China due to become operational in 2019.
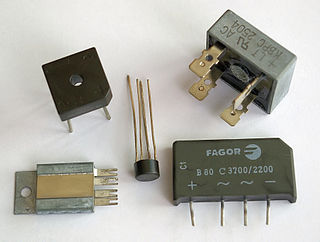
A diode bridge is an arrangement of four diodes in a bridge circuit configuration that provides the same polarity of output for either polarity of input.
In power engineering, the power-flow study, or load-flow study, is a numerical analysis of the flow of electric power in an interconnected system. A power-flow study usually uses simplified notations such as a one-line diagram and per-unit system, and focuses on various aspects of AC power parameters, such as voltages, voltage angles, real power and reactive power. It analyzes the power systems in normal steady-state operation.
In electrical engineering and mechanical engineering, the power rating of equipment is the highest power input allowed to flow through particular equipment. According to the particular discipline, the term "power" may refer to the electrical or mechanical power. A power rating can also involve average and maximum power, which may vary depending on the kind of equipment and its application.
Electric power quality, or simply power quality, involves voltage, frequency, and waveform. Good power quality can be defined as a steady supply voltage that stays within the prescribed range, steady a.c. frequency close to the rated value, and smooth voltage curve waveform. In general, it is useful to consider power quality as the compatibility between what comes out of an electric outlet and the load that is plugged into it. The term is used to describe electric power that drives an electrical load and the load's ability to function properly. Without the proper power, an electrical device may malfunction, fail prematurely or not operate at all. There are many ways in which electric power can be of poor quality and many more causes of such poor quality power.

Power in an electric circuit is the rate of flow of energy past a given point of the circuit. In alternating current circuits, energy storage elements such as inductors and capacitors may result in periodic reversals of the direction of energy flow.

Electric power is the rate, per unit time, at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second.

In electrical engineering, a synchronous condenser is a DC-excited synchronous motor, whose shaft is not connected to anything but spins freely. Its purpose is not to convert electric power to mechanical power or vice versa, but to adjust conditions on the electric power transmission grid. Its field is controlled by a voltage regulator to either generate or absorb reactive power as needed to adjust the grid's voltage, or to improve power factor. The condenser’s installation and operation are identical to large electric motors and generators.

A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
Doubly-fed electric machines also slip-ring generators are electric motors or electric generators, where both the field magnet windings and armature windings are separately connected to equipment outside the machine.
An induction generator or asynchronous generator is a type of alternating current (AC) electrical generator that uses the principles of induction motors to produce electric power. Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their rotors faster than synchronous speed. A regular AC induction motor usually can be used as a generator, without any internal modifications. Induction generators are useful in applications such as mini hydro power plants, wind turbines, or in reducing high-pressure gas streams to lower pressure, because they can recover energy with relatively simple controls.
An electric power system is a network of electrical components deployed to supply, transfer, and use electric power. An example of an electric power system is the grid that provides power to an extended area. An electrical grid power system can be broadly divided into the generators that supply the power, the transmission system that carries the power from the generating centres to the load centres, and the distribution system that feeds the power to nearby homes and industries. Smaller power systems are also found in industry, hospitals, commercial buildings and homes. The majority of these systems rely upon three-phase AC power—the standard for large-scale power transmission and distribution across the modern world. Specialised power systems that do not always rely upon three-phase AC power are found in aircraft, electric rail systems, ocean liners and automobiles.

Active rectification, or synchronous rectification, is a technique for improving the efficiency of rectification by replacing diodes with actively controlled switches such as transistors, usually power MOSFETs or power BJTs. Whereas normal semiconductor diodes have a roughly fixed voltage drop of around 0.5-1 volts, active rectifiers behave as resistances, and can have arbitrarily low voltage drop.
In an electric power system, a harmonic is a voltage or current at a multiple of the fundamental frequency of the system, produced by the action of non-linear loads such as rectifiers, discharge lighting, or saturated magnetic devices. Harmonic frequencies in the power grid are a frequent cause of power quality problems. Harmonics in power systems result in increased heating in the equipment and conductors, misfiring in variable speed drives, and torque pulsations in motors.
A permanent magnet synchronous generator is a generator where the excitation field is provided by a permanent magnet instead of a coil. The term synchronous refers here to the fact that the rotor and magnetic field rotate with the same speed, because the magnetic field is generated through a shaft mounted permanent magnet mechanism and current is induced into the stationary armature.
Most of the terms listed in Wikipedia glossaries are already defined and explained within Wikipedia itself. However, glossaries like this one are useful for looking up, comparing and reviewing large numbers of terms together. You can help enhance this page by adding new terms or writing definitions for existing ones.










