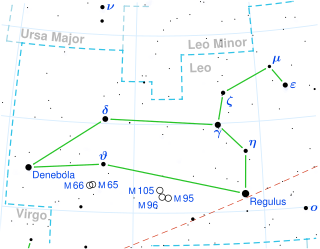
Leo is one of the constellations of the zodiac, lying between Cancer the crab to the west and Virgo the maiden to the east. Its name is Latin for lion, and to the ancient Greeks represented the Nemean Lion killed by the mythical Greek hero Heracles meaning 'Glory of Hera' as one of his twelve labors. Its symbol is . One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, Leo remains one of the 88 modern constellations today, and one of the most easily recognizable due to its many bright stars and a distinctive shape that is reminiscent of the crouching lion it depicts. The lion's mane and shoulders also form an asterism known as "The Sickle," which to modern observers may resemble a backwards "question mark."

Newport News Shipbuilding (NNS), a division of Huntington Ingalls Industries, is the largest industrial employer in Virginia, and sole designer, builder and refueler of United States Navy aircraft carriers and one of two providers of U.S. Navy submarines. Founded as the Chesapeake Dry Dock and Construction Co. in 1886, Newport News Shipbuilding has built more than 800 ships, including both naval and commercial ships. Located in the city of Newport News, their facilities span more than 550 acres (2.2 km2), strategically positioned in one of the great harbors of the East Coast.

The Victory ship was a class of cargo ship produced in large numbers by North American shipyards during World War II to replace losses caused by German submarines. They were a more modern design compared to the earlier Liberty ship, were slightly larger and had more powerful steam turbine engines giving higher speed to allow participation in high speed convoys and make them more difficult targets for German U-boats. A total of 531 Victory ships were built.

The New York Shipbuilding Corporation was an American shipbuilding company that operated from 1899 to 1968, ultimately completing more than 500 vessels for the U.S. Navy, the United States Merchant Marine, the United States Coast Guard, and other maritime concerns. At its peak during World War II, NYSB was the largest and most productive shipyard in the world. Its best-known vessels include the destroyer USS Reuben James (DD-245), the cruiser USS Indianapolis (CA-35), the aircraft carrier USS Kitty Hawk (CV-63), the nuclear-powered cargo ship NS Savannah, and a quartet of cargo-passenger liners nicknamed the Four Aces.
USS Leonis (AK-128) was a Crater-class cargo ship in service with the US Navy in World War II. It was the only ship of the Navy to have borne this name, the Latin form of the northern constellation Leo.
USS Deimos (AK-78) was a Crater-class cargo ship in the service of US Navy in World War II. It was the first ship of the Navy to have borne the name Deimos, after one of the moons of Mars.

The Algol-class vehicle cargo ships, also known as Fast Sealift Ships (FSS) or SL-7s, are currently the fastest cargo ships in the world, capable of speeds in excess of 33 knots (61 km/h). Originally built in 1972 and 1973 as high-speed container ships known as SL-7's for Sea-Land Services, Inc., the ships' high operating costs limited their profitability. All eight ships were acquired by the US Navy in 1981 and 1982, with the last ship converted, delivered to and placed in service with Military Sealift Command in 1986. The conversion entailed the installation of four cranes, addition of roll on/roll off capability and a redesign of the cargo hold to better facilitate storage of vehicles. Due largely to their high cost of operation, all fast sealift ships are kept in Reduced Operating Status, but can be activated and ready to sail in 96 hours. All ships are named after bright stars in the night sky.

USS Mizar (AF-12) was a United Fruit Company cargo and passenger liner that served as a United States Navy Mizar-class stores ship in World War II.

USS Denebola (AF-56) was a Denebola-class stores ship acquired by the U.S. Navy. She was built as the SS Hibbing Victory as a type VC2-S-AP2 Victory ship built by Oregon Shipbuilding Corporation of Portland, Oregon, under a Maritime Commission. The Maritime Administration cargo ship was the 113h ship built. Its keel was laid on May 2, 1944. The ship was christened on June 30, 1944. She was built at the Oregon Shipbuilding yards in just 59 days, under the Emergency Shipbuilding program for World War II. The 10,600 ton ship was constructed for the Maritime Commission. She was operated by the (Pacific-Atlantic SS Company under the United States Merchant Marine act for the War Shipping Administration. USS Denebolatask was to carry stores, refrigerated items, and equipment to ships in the fleet, and to remote stations and staging areas.

USS Regulus (AF-57) was a Denebola-class stores ship acquired by the United States Navy. Her task was to carry stores, refrigerated items, and equipment to ships in the fleet, and to remote stations and staging areas.

The Windsor-class attack transport was a class of nine US Navy attack transports. Ships of the class saw service in World War II.
USS Marengo (AK-194) was an Alamosa-class cargo ship that was constructed by the US Navy during the closing period of World War II. She was declared excess-to-needs and returned to the US Maritime Commission shortly after commissioning.

The Altair class destroyer tender was a class of three United States Navy destroyer tenders. These ships were built in Skinner & Eddy's Seattle shipyard as commercial cargo ships during World War I, and acquired by the Navy when the shipyard closed in 1921. All three served through World War II, and were decommissioned and scrapped shortly after the war.

The Type R ship is a United States Maritime Administration (MARAD) designation for World War II refrigerated cargo ship, also called a reefer ship. The R type ship was used in World War II, Korean War, Vietnam War and the Cold War. Type R ships were used to transport perishable commodities which require temperature-controlled transportation, such as fruit, meat, fish, vegetables, dairy products and other foods. The US Maritime Commission ordered 41 new refrigerated ships for the US Navy. Because of the difficulty of building refrigerated ships only two were delivered in 1944, and just 26 were delivered in 1945 and the remainder in 1946–48. The 41 R type ships were built in four groups. Two of design types were modified type C1 ships and two were modified type C2 ships. The United Fruit Company operated many of the R type ships in World War II. The type R2-S-BV1 became the US Navy Alstede-class stores ship and the type R1-M-AV3 became the US Navy Adria-class stores ship.
Deneb is a supergiant star in the Cygnus constellation, also known as α Cygni.
The following index is provided as an overview of and topical guide to recreational dive sites: