A record, recording or records may refer to:
Data transmission is the transfer of data over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibers, wireless communication channels, storage media and computer buses. The data are represented as an electromagnetic signal, such as an electrical voltage, radiowave, microwave, or infrared signal.

Digital audio is sound that has been recorded in, or converted into, digital form. In digital audio, the sound wave of the audio signal is encoded as numerical samples in continuous sequence. For example, in CD audio, samples are taken 44100 times per second each with 16 bit sample depth. Digital audio is also the name for the entire technology of sound recording and reproduction using audio signals that have been encoded in digital form. Following significant advances in digital audio technology during the 1970s, it gradually replaced analog audio technology in many areas of audio engineering and telecommunications in the 1990s and 2000s.
Dolby Digital is the name for audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. Originally named Dolby Stereo Digital until 1994, except for Dolby TrueHD, the audio compression is lossy. The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35mm film prints; today, it is now also used for other applications such as TV broadcast, radio broadcast via satellite, digital video streaming, DVDs, Blu-ray discs and game consoles.
Artifact, or artefact, may refer to:
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation.

In telecommunications, transmission is the process of sending and propagating an analogue or digital information signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint transmission medium, either wired, optical fiber or wireless.
Remaster refers to changing the quality of the sound or of the image, or both, of previously created recordings, either audiophonic, cinematic, or videographic.
Analogue electronics are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal. The word analogue is derived from the Greek word ανάλογος (analogos) meaning "proportional".

Digital access carrier system (DACS) is the name used by British Telecom in the United Kingdom for a 0+2 pair gain system.
System Y is an electronic switching system and digital telephone exchange used by British Telecom, the operator of the telephone network in the United Kingdom.
A standard test image is a digital image file used across different institutions to test image processing and image compression algorithms. By using the same standard test images, different labs are able to compare results, both visually and quantitatively.

The history of sound recording - which has progressed in waves, driven by the invention and commercial introduction of new technologies — can be roughly divided into four main periods:
Digital UK is a British company owned by the BBC, ITV, Channel 4 and Arqiva which supports Freeview viewers and channels. It provides people with information about their options for receiving terrestrial TV and advice on reception and equipment. The company also handles day-to-day technical management of the Freeview Electronic Programme Guide (EPG), allocates channel numbers and manages the launch of new services and multiplexes onto the platform. Digital UK has been licensed by Ofcom as an EPG provider.
DTMB is the TV standard for mobile and fixed terminals used in the People's Republic of China, Cuba, Hong Kong and Macau.
An intelligent sensor is a sensor that takes some predefined action when it senses the appropriate input.

Offset Press Inc., Also known as OPI, is an Iranian corporation that develops, manufactures, and distributes analogue and digital products and systems for the making, processing, and reproduction of images.
The Florence Declaration – Recommendations for the Preservation of Analogue Photo Archives is an initiative of the Photo Library of the Kunsthistorisches Institut in Florenz.
A digital sensor is an electronic or electrochemical sensor, where data is digitally converted and transmitted. Sensors are often used for analytical measurements, e.g. the measurement of chemical and physical properties of liquids. Typical measured parameters are pH value, conductivity, oxygen, redox potentials, and others. Such measurements are used in the industrialized world and give vital input for process control.
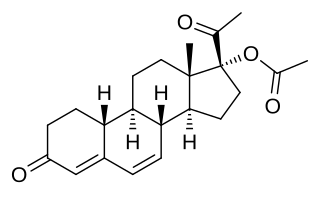
Gestadienol acetate an orally active progestin which was described in the literature in 1967 and was never marketed. It has no androgenic or estrogenic effects. The effects of gestadienol acetate on the endometrium and its general pharmacology were studied in a clinical trial in women. It has also been studied in a clinical trial for benign prostatic hyperplasia in men, but was ineffective.