
Cyan is a greenish-blue color. It is evoked by light with a predominant wavelength of between 490–520 nm, between the wavelengths of green and blue.

The CMYK color model is a subtractive color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. CMYK refers to the four inks used in some color printing: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key.

Optical character recognition or optical character reader, often abbreviated as OCR, is the mechanical or electronic conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene-photo or from subtitle text superimposed on an image.

Inkjet printing is a type of computer printing that recreates a digital image by propelling droplets of ink onto paper, plastic, or other substrates. Inkjet printers are the most commonly used type of printer, and range from small inexpensive consumer models to expensive professional machines.

An image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner, although the term is ambiguous out of context —is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting or an object and converts it to a digital image. Commonly used in offices are variations of the desktop flatbed scanner where the document is placed on a glass window for scanning. Hand-held scanners, where the device is moved by hand, have evolved from text scanning "wands" to 3D scanners used for industrial design, reverse engineering, test and measurement, orthotics, gaming and other applications. Mechanically driven scanners that move the document are typically used for large-format documents, where a flatbed design would be impractical.
Optical mark recognition is the process of capturing human-marked data from document forms such as surveys and tests. They are used to read questionnaires, multiple choice examination paper in the form of lines or shady areas.

Scanner Access Now Easy (SANE) is an application programming interface (API) that provides standardized access to any raster image scanner hardware.

Paper marbling is a method of aqueous surface design, which can produce patterns similar to smooth marble or other kinds of stone. The patterns are the result of color floated on either plain water or a viscous solution known as size, and then carefully transferred to an absorbent surface, such as paper or fabric. Through several centuries, people have applied marbled materials to a variety of surfaces. It is often employed as a writing surface for calligraphy, and especially book covers and endpapers in bookbinding and stationery. Part of its appeal is that each print is a unique monotype.
Color printing or colour printing is the reproduction of an image or text in color. Any natural scene or color photograph can be optically and physiologically dissected into three primary colors, red, green and blue, roughly equal amounts of which give rise to the perception of white, and different proportions of which give rise to the visual sensations of all other colors. The additive combination of any two primary colors in roughly equal proportion gives rise to the perception of a secondary color. For example, red and green yields yellow, red and blue yields magenta, and green and blue yield cyan. Only yellow is counter-intuitive.
Yellow, cyan and magenta are merely the "basic" secondary colors: unequal mixtures of the primaries give rise to perception of many other colors all of which may be considered "tertiary."

A data entry clerk is a member of staff employed to enter or update data into a computer system. Data is often entered into a computer from paper documents using a keyboard. The keyboards used can often have special keys and multiple colors to help in the task and speed up the work. Proper ergonomics at the workstation is a common topic considered.
The aim of color calibration is to measure and/or adjust the color response of a device to a known state. In International Color Consortium (ICC) terms, this is the basis for an additional color characterization of the device and later profiling. In non-ICC workflows, calibration refers sometimes to establishing a known relationship to a standard color space in one go. The device that is to be calibrated is sometimes known as a calibration source; the color space that serves as a standard is sometimes known as a calibration target. Color calibration is a requirement for all devices taking an active part of a color-managed workflow, and is used by many industries, such as television production, gaming, photography, engineering, chemistry, medicine and more.

Optically variable ink (OVI) also called color shifting ink is an anti-counterfeiting measure used on many major modern banknotes, as well as on other official documents.

In digital photography and digital video, clipping is a result of capturing or processing an image where the intensity in a certain area falls outside the minimum and maximum intensity which can be represented. It is an instance of signal clipping in the image domain. The clipped area of the image will typically appear as a uniform area of the minimum or maximum brightness, losing any image detail. The amount by which values were clipped, and the extent of the clipped area, affect the degree to which the clipping is visually noticeable or undesirable in the resulting image.
A paperless office is a work environment in which the use of paper is eliminated or greatly reduced. This is done by converting documents and other papers into digital form, a process known as digitization. Proponents claim that "going paperless" can save money, boost productivity, save space, make documentation and information sharing easier, keep personal information more secure, and help the environment. The concept can be extended to communications outside the office as well.
CuneiForm Cognitive OpenOCR is a freely distributed open source OCR system developed by Russian software company Cognitive Technologies.

OCR-A is a font that arose in the early days of computer optical character recognition when there was a need for a font that could be recognized not only by the computers of that day, but also by humans. OCR-A uses simple, thick strokes to form recognizable characters.
The font is monospaced (fixed-width), with the printer required to place glyphs 0.254 cm apart, and the reader required to accept any spacing between 0.2286 cm and 0.4572 cm.
This comparison of optical character recognition software includes:
Image translation is a term related to machine translation. Image translation refers to a technology where the user can translate the text on images or pictures taken of printed text .This is done by applying optical character recognition (OCR) technology to an image to extract any text contained in the image, and then have this text translated into a language of their choice, and the applying Digital image processing on the original image to get the translated image with a new language.
Forms processing is a process by which one can capture information entered into data fields and convert it into an electronic format. This can be done manually or automatically, but the general process is that hard copy data is filled out by humans and then "captured" from their respective fields and entered into a database or other electronic format.
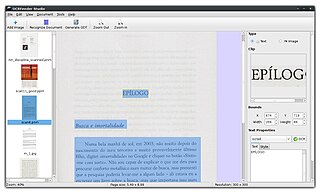
OCRFeeder is an optical character recognition suite for GNOME, which also supports virtually any command-line OCR engine, such as CuneiForm, GOCR, Ocrad and Tesseract. It converts paper documents to digital document files and can serve to make them accessible to visually impaired users.










