
The Andes or Andean Mountains are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. This range is about 7,000 km (4,300 mi) long, about 200 to 700 km wide, and of an average height of about 4,000 m (13,000 ft). The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile and Argentina.

La Paz, officially known as Nuestra Señora de La Paz, also named Chuqi Yapu (Chuquiago) in Aymara, is the seat of government and the de facto national capital of the Plurinational State of Bolivia. With an estimated 789,541 residents as of 2015, La Paz is the third-most populous city in Bolivia. Its metropolitan area, which is formed by La Paz, El Alto and Viacha, makes up the most populous urban area in Bolivia, with a population of 2.3 million. It is also the capital of the La Paz Department.

Sucre is the constitutional capital of Bolivia, the capital of the Chuquisaca Department and the 6th most populated city in Bolivia. Located in the south-central part of the country, Sucre lies at an elevation of 2,810 meters. This relatively high altitude gives the city a cool temperate climate year-round.

The Chaco War was fought between Bolivia and Paraguay over control of the northern part of the Gran Chaco region of South America, which was thought to be rich in oil. It is also referred to as La Guerra de la Sed in literary circles, for being fought in the semi-arid Chaco. It was the bloodiest military conflict fought in South America during the 20th century, between two of its poorest countries, both having previously lost territory to neighbors in 19th-century wars.

The economy of Bolivia is the 95th largest economy in the world in nominal terms and the 87th economy in terms of purchasing power parity. It is classified by the World Bank to be a lower middle income country. With a Human Development Index of 0.675, it is ranked 119th.

The President of Bolivia officially known as the President of the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is head of state and head of government of Bolivia. According to the current Constitution, the president is elected by popular vote to a five-year term, renewable once. In 2016, in a referendum the country voted to maintain term limits. Since 2009, if no candidate wins a majority, the top two candidates advance to a runoff election. Prior to 2009, if no candidate won half the popular vote, the president was chosen by a vote in a joint legislative session from among the top two candidates.

The Aymara or Aimara people are an indigenous nation in the Andes and Altiplano regions of South America; about 1 million live in Bolivia, Peru and Chile. Their ancestors lived in the region for many centuries before becoming a subject people of the Inca in the late 15th or early 16th century, and later of the Spanish in the 16th century. With the Spanish American Wars of Independence (1810–25), the Aymaras became subjects of the new nations of Bolivia and Peru. After the War of the Pacific (1879–83), Chile acquired territory occupied by the Aymaras.
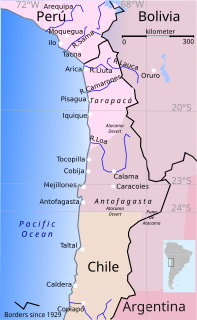
The War of the Pacific, also known as the Saltpeter War and by multiple other names was a war between Chile and a Bolivian-Peruvian alliance. It lasted from 1879 to 1884, and was fought over Chilean claims on coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert. The war ended with victory for Chile, which gained a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia. Chile's army took Bolivia's nitrate rich coastal region and Peru was defeated by Chile's navy.

Juan Evo Morales Ayma, commonly known as Evo Morales, is a Bolivian politician and cocalero activist who has served as President of Bolivia since 2006. Widely regarded as the country's first president to come from the indigenous population, his administration has focused on the implementation of leftist policies, poverty reduction, and combating the influence of the United States and multinational corporations in Bolivia. A socialist, he is the head of the Movement for Socialism (MAS) party.

Bolivia is a unitary state consisting of nine departments. Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia, and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the federal Plurinational Legislative Assembly—a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Each department is represented by four Senators, while Deputies are awarded to each state in proportion to their total population.

The La Paz Department of Bolivia comprises 133,985 square kilometres (51,732 sq mi) with a 2012 census population of 2,706,359 inhabitants. It is situated at the western border of Bolivia, sharing Lake Titicaca with adjacent Peru. It contains the Cordillera Real, which reaches altitudes of 6.6 kilometers (4.1 mi). Northeast of the Cordillera Real are the Yungas, the steep eastern slopes of the Andes Mountains that make the transition to the Amazon River basin to the northeast. The capital of the department is the city of La Paz and is the administrative city and seat of government/national capital of Bolivia.

Cochabamba is a city and municipality in central Bolivia in a valley in the Andes mountain range. It is the capital of the Cochabamba Department and the fourth largest city in Bolivia, with a population of 630,587 according to the 2012 Bolivian census. Its name is from a compound of the Quechua words qucha "lake" and pampa, "open plain." Residents of the city and the surrounding areas are commonly referred to as cochalas or, more formally, cochabambinos.

The Bolivia national football team, also known as La Verde or Los Sin Mar, has represented Bolivia in international football since 1926. Organized by the Bolivian Football Federation (FBF), it is one of the 10 members of FIFA's South American Football Confederation (CONMEBOL).

The Bolivian Football Federation is the governing body of football in Bolivia. It was founded in 1925, making it the eighth oldest South American federation. It affiliated to CONMEBOL and FIFA in 1926 and is in charge of Bolivia national football team.
Miss Bolivia is a national beauty pageant in Bolivia.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to South America.

Bolivian cuisine stems from the combination of Spanish cuisine with indigenous ingredients and Aymara traditions, among others, with later influences from Germans, Italians, French, and Arabs due to the arrival of immigrants from those countries. The traditional staples of Bolivian cuisine are corn, potatoes, quinoa and beans. These ingredients have been combined with a number of staples brought by the Spanish, such as rice, wheat, and meat, including beef, pork, and chicken.

Citizens of specific countries and territories are eligible to visit Bolivia for tourism or business purposes without having to obtain a visa.















