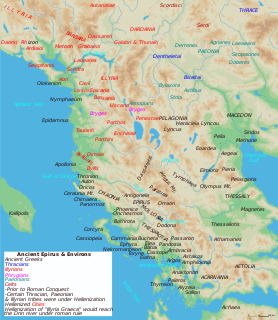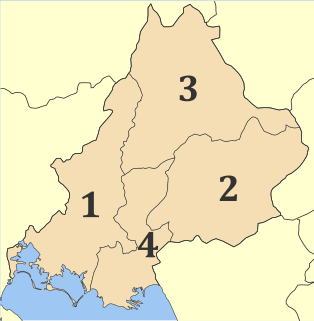
Arta is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the Epirus region. Its capital is the town of Arta.
Cypselus was the first tyrant of Corinth in the 7th century BC.
Alexander V of Macedon was the third and youngest son of Cassander and Thessalonica of Macedon, who was a half-sister of Alexander the Great. He ruled as King of Macedon along with his brother Antipater from 297 to 294 BC.
Marcus Fulvius Nobilior, Roman general, a member of one of the most important families of the plebeian Fulvia gens.

The Ambracian Gulf, also known as the Gulf of Arta or the Gulf of Actium, and in some official documents as the Amvrakikos Gulf, is a gulf of the Ionian Sea in northwestern Greece. About 40 km (25 mi) long and 15 km (9 mi) wide, it is one of the largest enclosed gulfs in Greece. The towns of Preveza, Amphilochia, and Vonitsa lie on its shores.

Arta is a city in northwestern Greece, capital of the regional unit of Arta, which is part of Epirus region. The city was known in ancient times as Ambracia. Arta is known for the medieval bridge over the Arachthos River. Arta is also known for its ancient sites from the era of Pyrrhus of Epirus and its well-preserved 13th-century castle. Arta's Byzantine history is reflected in its many Byzantine churches; perhaps the best known is the Panagia Paregoretissa, built about 1290 by Despot Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas. The city is the seat of the Technological Educational Institute of Epirus.
A siege hook is a weapon used to pull stones from a wall during a siege. The method used was to penetrate the protective wall with the hook and then retract it, pulling away some of the wall with it.
An epigonion was an ancient stringed instrument mentioned in Athenaeus, probably a psaltery.
In Greek mythology, Melaneus was the founder of Oechalia (Oikhalia), variously located in Thessaly, Messenia or Euboea and also king of the Dryopes.

In Greek mythology, Phorbas, or Phorbaceus, may refer to:

Gomfoi is a village and a former municipality in the Trikala regional unit, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Pyli, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 58.482 km2. Population 4,782 (2011). The seat of the municipality was in Lygaria. Gomfoi is located in Thessalian Plain, near the river Pamisos. It is 5 km northeast of Mouzaki, and 12 km southwest of the city of Trikala. A town existed on the site of present Gomfoi in ancient times, which was renamed Philippoupolis during the reign of Philip II of Macedon. The area joined Greece in 1881.
Dexamenus was a name attributed to at least three characters in Greek mythology.
Epicrates of Ambracia, was an Ambraciote who lived in Athens, a comic poet of the Middle Comedy, according to the testimony of Athenaeus. This is confirmed by extant fragments of his plays, in which he ridicules Plato and his disciples, Speusippus and Menedemus, and in which he refers to the courtesan Lais of Corinth, as being now far advanced in years. From these indications, Augustus Meineke infers that he flourished between the 101st and 108th Olympiads.

Epigonus is a genus of fish in the family Epigonidae found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean.

The Archaeological Museum of Arta is a museum in Arta, Greece. It was established in 1973 as the Archaeological collection of Arta, and used to be housed in the 13th-century Paregoretissa church. The collection has now been moved to a brand new, purpose-built museum building which opened in 2009. The new museum building is located by the river, close to the historical bridge.

In Greek mythology, Cragaleus was a son of Dryops who dwelt in the land Dryopis next to a spring which was believed to have appeared at a place where Heracles hit the earth with his club. He was renowned as just and wise, and was one day visited by Apollo, Artemis, and Heracles who asked him to act as an arbiter in their argument as to which of the three should become patron of Ambracia, Epirus. Apollo argued that the city should belong to him on account of the fact that Epirus was once conquered by his son Melaneus, and that he assisted the Ambraciotes in the war against the natives of Epirus, and brought law and order to Ambracia. Artemis reminded that it was she who saved the Ambraciotes from the tyrant Phalecus, having sent a lioness to kill him. Finally, Heracles brought up the fact that it was he who destroyed the many non-Greek peoples of Epirus for trying to steal the kine of Geryon from him, and that the Corinthians, who later came to Epirus and founded Ambracia, were his descendants. Cragaleus considered Heracles' argument the most convincing and declared him the winner. Apollo was enraged and turned Cragaleus into stone. Since then, the Ambraciotes sacrificed to Apollo the Saviour, but believed their city to belong to Heracles and the Heracleidae, and honored Cragaleus with sacrifices as well.
Cleombrotus is a young man mentioned in Plato's Phaedo as one of two young men notably absent when Socrates drank the hemlock. This is his only mention in Plato, but a later tradition added that he was from Ambracia; Callimachus explains that Cleombrotus committed suicide in a way that caused a debate still held in the time of Michel de Montaigne—whether his suicide, leaping into the ocean to enter the life of the spirits after reading the Phaedo, was foolish or not. Callimachus's epigram, as translated by H.W. Tytler reads,
Epigonus is the Latinized form of epigonos. It can refer to:
Athenaeus of Naucratis was a Greek rhetorician and grammarian, flourishing about the end of the 2nd and beginning of the 3rd century AD. The Suda says only that he lived in the times of Marcus Aurelius, but the contempt with which he speaks of Commodus, who died in 192, shows that he survived that emperor. He was a contemporary of Adrantus.
Andrew Dennison Barker, is a British classicist and academic, specialising in ancient Greek music and the intersection between musical theory and philosophy. He was Professor of Classics at the University of Birmingham from 1998 to 2008, and had previously taught at the University of Warwick, University of Cambridge, and Selwyn College, Cambridge.