A bus stop is a designated place where buses stop for passengers to board or alight from a bus. The construction of bus stops tends to reflect the level of usage, where stops at busy locations may have shelters, seating, and possibly electronic passenger information systems; less busy stops may use a simple pole and flag to mark the location. Bus stops are, in some locations, clustered together into transport hubs allowing interchange between routes from nearby stops and with other public transport modes to maximise convenience.

Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to improve capacity and reliability relative to a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes roadways that are dedicated to buses, and gives priority to buses at intersections where buses may interact with other traffic; alongside design features to reduce delays caused by passengers boarding or leaving buses, or purchasing fares. BRT aims to combine the capacity and speed of a metro with the flexibility, lower cost and simplicity of a bus system.

The Oyster card is a form of electronic ticket used on public transport in Greater London in the United Kingdom. It is promoted by Transport for London and is valid on travel modes across London including London Underground, London Buses, the Docklands Light Railway (DLR), London Overground, Tramlink, some river boat services, and most National Rail services within the London fare zones. Since its introduction in June 2003, more than 86 million cards have been used.

The Strathclyde Partnership for Transport (SPT) is a passenger transport executive responsible for planning and coordinating regional transport, especially the public transport system, in the Strathclyde area of western Scotland. This includes responsibility for operating Glasgow's Subway, the third oldest in the world.

The São Paulo Metro, commonly called the Metro or Companhia do Metropolitano de São Paulo (CMSP), is one of the rapid transit companies that serves the city of São Paulo, alongside São Paulo Metropolitan Trains Company (CPTM) and ViaQuatro, forming the largest metropolitan rail transport network of Latin America. The six main lines in the metro system operate on 96.0 kilometres (59.7 mi) of route, serving 84 stations. The sixth line, Line 15, is a monorail line that partially opened for service in 2014 and it is the first high capacity monorail line of Brazil. In 2016, the five lines operated by CMSP achieved an average weekday ridership of 4.3 million, and provided 1,107 billion rides over the course of 2016.
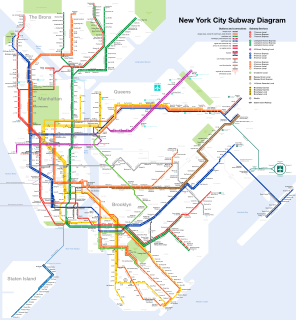
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system that serves four of the five boroughs of New York City, New York: the Bronx, Brooklyn, Manhattan, and Queens. Its operator is the New York City Transit Authority, which is itself controlled by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority of New York. In 2015, an average of 5.65 million passengers used the system daily, making it the busiest rapid transit system in the United States and the seventh busiest in the world.
For the diesel multiple unit that operated in the United Kingdom, see British Rail Class 101.

The Société de transport de Montréal (STM) is a public transport agency that operates transit bus, and rapid transit services in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Established in 1861 as Montreal City Passenger Railway Company, it has grown to comprise four subway lines with a total of 68 stations, as well as over 186 bus routes and 23 night routes.
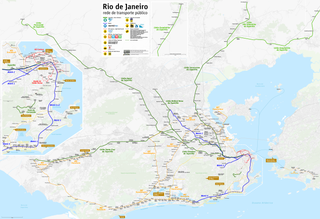
The Rio de Janeiro Metro is a mass-transit underground railway network that serves the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The Metrô was inaugurated on March 5, 1979 and consisted of five stations operating on a single line. The system currently covers a total of 58 kilometres (36 mi), serving 41 stations, divided into three lines: Line 1 ; Line 2, which together travel over a shared stretch of line that covers 10 stations of an approximate distance of 5 kilometers; and Line 4. Metrô Rio has the second highest passenger volume of the metro systems in Brazil, after the São Paulo Metro.

Ponta Grossa is a municipality in the state of Paraná, southern Brazil. The estimated population for 2018 is 348,043, according to official data from the institute in charge in the country, it is the 4th most populous city in Paraná. It is too the largest city in the state around Greater Curitiba, within a radius of 186 miles (300 km). It is known as Princesa dos Campos and Capital Cívica do Paraná. Its settlement is connected to the Caminho das Tropas, being one of the points of landing of tropeiros in the middle of a high hill inside a grassy vegetation. The city is considered of average size appearing of a central hill, its most accelerated growth occurred in the second half of the twentieth century with the weakening of the primary economy.
The Public Transport Council is an independent regulatory statutory board under the Ministry of Transport of Singapore, established on 14 August 1987 by the Public Transport Council Act of 1987. PTC regulates the public bus and rapid transit network in areas such as fares and service standards.
The London Underground metro system of London, England uses a mix of paper and electronic smart-card ticketing.
Transperth is the brand name of the public transport system serving the city and suburban areas of Perth, the state capital of Western Australia. It is operated by the Public Transport Authority.
A transit pass or travel card, often referred to as a bus pass or train pass etc., is a ticket that allows a passenger of the service to take either a certain number of pre-purchased trips or unlimited trips within a fixed period of time.
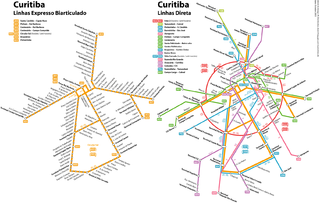
The North–South Trunk Line is a Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) service that runs from Santa Cândida Transit Center, in northeast Curitiba, to Pinheirinho Transit Center, in south side Curitiba. Two express routes run through this line and it is supplemented by a limited route that serves only certain stops. It is part of Curitiba's Rede Integrada de Transporte transportation system.

The RioCard is a smartcard system used in the transport system of Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. The card is contactless and uses MIFARE technology. It is a form of electronic payment produced and distributed by the Fetranspor company, in cooperation with Itaú bank. Its installation was seen as strengthening Brazil's connection with the Open Standard for Public Transport (OSPT) Alliance.
BRT creep comprises several types of gradual erosions in service that sometimes affect a bus rapid transit (BRT) system, resulting in a service that is not up to the standards promised by BRT advocates. In its ideal form, BRT aims to combine the capacity and speed of a light rail system with the flexibility, cost and simplicity of a bus system. BRT creep occurs when a system that promises these features instead acts more like a standard, non-rapid bus system.
The São Mateus–Jabaquara metropolitan corridor, also called ABD Corridor is a bus rapid transit line in Brazil, linking the city of São Paulo to three neighboring cities, Diadema, São Bernardo do Campo and Santo André, as well as (indirectly) Mauá. Operations started in 1988. Its other name references one letter per city, the same way the ABC region in Greater São Paulo is named.