
An adiabatic process occurs without transfer of heat or mass of substances between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings. In an adiabatic process, energy is transferred to the surroundings only as work. The adiabatic process provides a rigorous conceptual basis for the theory used to expound the first law of thermodynamics, and as such it is a key concept in thermodynamics.

Caelum is a faint constellation in the southern sky, introduced in the 1750s by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille and counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name means “chisel” in Latin, and it was formerly known as Caelum Scalptorium ; It is a rare word, unrelated to the far more common Latin caelum, meaning “sky, heaven, atmosphere”. It is the eighth-smallest constellation, and subtends a solid angle of around 0.038 steradians, just less than that of Corona Australis.

The Cauchy distribution, named after Augustin Cauchy, is a continuous probability distribution. It is also known, especially among physicists, as the Lorentz distribution, Cauchy–Lorentz distribution, Lorentz(ian) function, or Breit–Wigner distribution. The Cauchy distribution
is the distribution of the x-intercept of a ray issuing from
with a uniformly distributed angle. It is also the distribution of the ratio of two independent normally distributed random variables if the denominator distribution has mean zero.
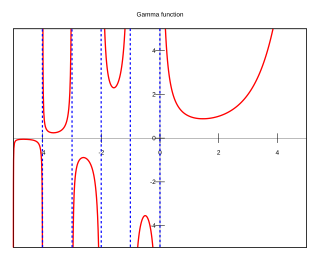
In mathematics, the gamma function is one of the extensions of the factorial function with its argument shifted down by 1, to real and complex numbers. Derived by Daniel Bernoulli, if n is a positive integer,
In mathematics, a curve is, generally speaking, an object similar to a line but that need not be straight. Thus, a curve is a generalization of a line, in that its curvature need not be zero.
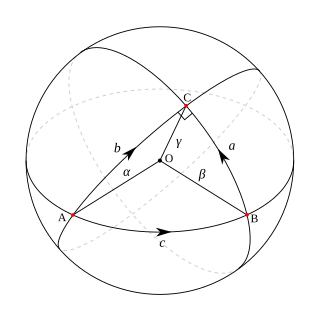
In differential geometry, a geodesic is a generalization of the notion of a "straight line" to "curved spaces". The term "geodesic" comes from geodesy, the science of measuring the size and shape of Earth; in the original sense, a geodesic was the shortest route between two points on the Earth's surface, namely, a segment of a great circle. The term has been generalized to include measurements in much more general mathematical spaces; for example, in graph theory, one might consider a geodesic between two vertices/nodes of a graph.

Queen of Heaven is a title given to Mary, mother of Jesus, by Christians mainly of the Roman Catholic Church, and also, to some extent, in Anglicanism, some Lutheran churches such as the Church of Sweden and Eastern Orthodoxy. The title is a consequence of the First Council of Ephesus in the fifth century, in which Mary was proclaimed "Theotokos", a title rendered in Latin as Mater Dei, in English "Mother of God".
The Lorentz factor or Lorentz term is the factor by which time, length, and relativistic mass change for an object while that object is moving. The expression appears in several equations in special relativity, and it arises in derivations of the Lorentz transformations. The name originates from its earlier appearance in Lorentzian electrodynamics – named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz.

The Regina Cæli or Regina Cœli is an ancient Latin Marian Hymn of the Christian Church.
In mathematical physics, the gamma matrices,
, also known as the Dirac matrices, are a set of conventional matrices with specific anticommutation relations that ensure they generate a matrix representation of the Clifford algebra Cℓ1,3(R). It is also possible to define higher-dimensional gamma matrices. When interpreted as the matrices of the action of a set of orthogonal basis vectors for contravariant vectors in Minkowski space, the column vectors on which the matrices act become a space of spinors, on which the Clifford algebra of spacetime acts. This in turn makes it possible to represent infinitesimal spatial rotations and Lorentz boosts. Spinors facilitate spacetime computations in general, and in particular are fundamental to the Dirac equation for relativistic spin-½ particles.

Gamma1 Caeli, Latinized from γ1 Caeli, is a double star in the constellation Caelum. It is approximately 185 light years from Earth. The brighter component is an orange K-type giant with an apparent magnitude of +4.55. The companion is an eighth magnitude star located 3.1 arcseconds away.
Queen of Angels Academy was a Roman Catholic high school for girls in Compton, California. It was established in 1995 through the merger of two all-girl schools, St. Michael's High School in Los Angeles, and Regina Caeli High School. The academy occupied the campus of the former Regina Caeli High School, a school with a 99% minority student body, administered by the Sisters of the Holy Family, a congregation of African-American Religious Sisters.
RV Caeli is a red giant star in the constellation Caelum. Located approximately 365 parsecs (1,190 ly) distant, Hipparcos has found it to vary between its photometric values of 6.44 and 6.56, which roughly corresponds with the magnitude as seen with the naked eye.

Ad Caeli Reginam is an encyclical of Pope Pius XII, given at Rome, from St. Peter's Basilica, on the feast of the Maternity of the Blessed Virgin Mary, the eleventh day of October, 1954, in the sixteenth year of his Pontificate. The encyclical is an important element of the Mariology of Pope Pius XII. It established the feast Queenship of Mary.
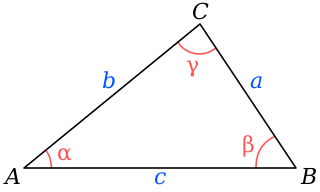
In trigonometry, the law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. Using notation as in Fig. 1, the law of cosines states
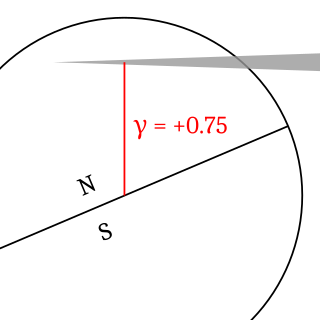
Gamma of an eclipse describes how centrally the shadow of the Moon or Earth strikes the other body. This distance, measured at the moment when the axis of the shadow cone passes closest to the center of the Earth or Moon, is stated as a fraction of the equatorial radius of the Earth or Moon.

Alien Legacy is a sci-fi strategy game developed by Ybarra Productions and published by Sierra On-Line in 1994 for MS-DOS.
RR Caeli is a double star in the constellation Caelum. It is approximately 66 light years from Earth. It was first noted to be a high-proper motion star in 1955 by Jacob Luyten, and given the name LFT 349. Discovered to be an eclipsing binary in 1979, it has a baseline magnitude of 14.36, dimming markedly every 7.2 hours for an interval of around 10 minutes, due to the total eclipse of the brighter star by the fainter one. Its variability in brightness led to its being given the variable star designation RR Caeli in 1984. This star system consists of a red dwarf of spectral type M6 and a white dwarf that orbit each other every seven hours; the former is 18% as massive as the Sun, while the latter has 44% of the Sun's mass. The red dwarf is tidally locked with the white dwarf, meaning it displays the same side to the heavier star. The system is also a post-common-envelope binary, and the red dwarf star is transferring material onto the white dwarf. In approximately 9–20 billion years, RR Caeli will likely become a cataclysmic variable star due to the period's gradual shortening, leading to increasing rates of transfer of hydrogen to the surface of the white dwarf.

C/1881 K1 is a long-period comet discovered by John Tebbutt on 22 May 1881 at Windsor, New South Wales. It is called a great comet because of its brightness at its last apparition.















