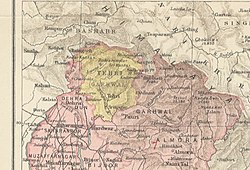
Kumaon is a revenue and administrative division in the Indian State of Uttarakhand. It spans over the eastern half of the state and is bounded on the north by Tibet, on the east by Nepal, on the south by the state of Uttar Pradesh, and on the west by Garhwal. Kumaon comprises six districts of the state: Almora, Bageshwar, Champawat, Nainital, Pithoragarh and Udham Singh Nagar.

Garhwal is one of the two administrative divisions of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Lying in the Himalayas, it is bounded on the north by Tibet, on the east by Kumaon, on the south by Uttar Pradesh state, and on the northwest by Himachal Pradesh state. It includes the districts of Chamoli, Dehradun, Haridwar, Pauri Garhwal, Rudraprayag, Tehri Garhwal, and Uttarkashi. The people of Garhwal are known as Garhwali and speak the Garhwali language. The administrative center for Garhwal division is the town of Pauri. The Divisional Commissioner is the administrative head of the Division, and is a senior Indian Administrative Service officer. As the administrative head of the division, the Commissioner is overall incharge of the 7 districts in the Garhwal region of Uttarakhand, and is aided in his duties by an additional commissioner and the district magistrates. Sushil Kumar is the divisional commissioner of the Garhwal Division since December 2021.

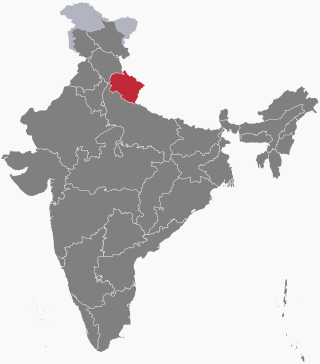
Uttarakhand, formerly known as Uttaranchal, is a state in northern India. The state is divided into two divisions, Garhwal and Kumaon, with a total of 13 districts. The winter capital and largest city of the state is Dehradun, which is also a railhead. On 5 March 2020, Bhararisain, a town in the Gairsain Tehsil of the Chamoli district, was declared as the summer capital of Uttarakhand. The High Court of the state is located in Nainital, but is to be moved to Haldwani in future.
The Panwar dynasty ruled the Garhwal Kingdom. The dynasty independently ruled Garhwal from the ninth to nineteenth century until the Kingdom of Nepal attacked the Kumaon Kingdom in 1791 and Garhwal in 1804. With the help of the British troops, Garhwal and Kumaon gained independence from Nepal. Unable to pay the military cost of British-ruled India, the then-Garhwali king gave part of his territory to the Raj and ruled until 1949. The last king of Garhwal, Manabendra Shah, decided to join India after it became independent. Garhwal and Kumaon became part of India as the then-state of Uttar Pradesh, which is now Uttarakhand.
Gairsain is a town in Chamoli district of the Indian state of Uttarakhand near state's summer capital Bhararisain. A town and Nagar Panchayat, Gairsain is situated at the eastern edge of the vast Dudhatoli mountain range, and is located in Chamoli district almost at the centre of the state, at a distance of approximately 250 kilometres from Dehradun. It is easily accessible from both the Garhwal and the Kumaon divisions, and in a way, acts as the bridge between the two regions. It is being considered as the future Permanent capital of Uttarakhand.

Pauri Garhwal is a district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Its headquarters is in the town of Pauri. It is sometimes referred to simply as Garhwal district, though it should not be confused with the larger Garhwal region of which it is only a part of.

Tehri Garhwal is a district in the hill state of Uttarakhand, India. Its administrative headquarters is at New Tehri. The district has a population of 618, 931, a 2.35% increase over the previous decade. It is surrounded by Rudraprayag District in the east, Dehradun District in the west, Uttarkashi District in the north, and Pauri Garhwal District in the south. Tehri Garhwal is a part of the Himalayas.

Uttarkashi District is a district of Garhwal division of the Uttarakhand state in northern India, and has its headquarters at Uttarkashi city. It has six Tehsils namely Barkot, Dunda, Bhatwadi, Chinyalisaur, Purola and Mori.
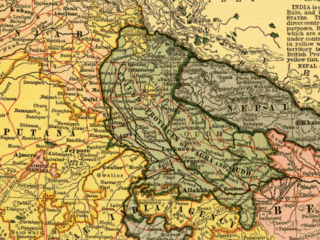
Garhwal District is a former district in Kumaon of British India of the United Provinces, and had an area of 5,629 sq mi (14,580 km2). It later became a part of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, today it is part of the Indian state Uttarakhand.

Gauchar is a Hill Town sort of a valley town located in Karnaprayag tehsil within Chamoli district of Uttarakhand state in India. Gauchar is situated on the left bank of river Alaknanda and is en route to the celebrated holy destination of Badrinath. It is well known for being one of the cleanest place in country. It has previously topped Swachta sarvekshan best ganga town award. Situated at an altitude of 800 metres (2,620 ft) above the sea level, Gauchar is surrounded by seven mountains. Gauchar is well known for its historic trade fair and airstrip. Gauchar town known for its great work to curb loss of lives in 2013 flood disaster of Uttarakhand. This town is unique in terms of its geographical location and topography. Gauchar is located on one of the largest pieces of flatland in this mountainous region of Uttarakhand. Education institution in Gauchar includes a beautiful Kendriya Vidyalaya adjacent to the main playground.

Narendranagar is a town and a municipal board in Tehri Garhwal district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
Lt. Col. Maharaja Manabendra Shah was a member of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 10th, 11th, 12th, 13th and 14th Lok Sabha of India. He represented the Tehri Garhwal constituency of Uttarakhand and was a member of the Indian National Congress before joining the Bharatiya Jan Sangh and later the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) political party. He became one of the BJP's longest-serving members. Shah was ambassador to Ireland from 1980 to 1983.
Fateh Shah was the Hindu Rajput king of Garhwal, a small kingdom in North India, from 1684 to 1716.

Uttarakhand is a Himalayan state in North India, nestled between the Tibetan Plateau and the Indo-Gangetic Plains. The name, which means "northern land" or "section" or "northern part" in Sanskrit was made popular in the 80s as part of the wider statehood struggle within the region.

The Garhwali people are an Indian ethnolinguistic group native to the Garhwal, in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, who speak Garhwali, an Indo-Aryan language.

Kumaon Kingdom was an independent Himalayan kingdom in Kumaon, a region located in the eastern part of the present-day Uttarakhand state of India. It was established around 7th century and remained an independent and sovereign kingdom until 1791.
The Uttarakhand movement refers to the events of statehood activism within the undivided state of Uttar Pradesh which ultimately resulted in the formation of Uttarakhand, India as a separate state.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Uttarakhand:
Battle of Khurbura or Battle of Khudbuda also known as Gorkha-Garhwal War occurred in May 1804 near modern-day village of Dehradun, Khurbura 30.3256°N 78.0267°E. The battle is regarded as the first major attack in the history of Garhwal Kingdom that triggered between Kingdom of Nepal forces and Maharaja Pradyumna Shah, and continued for 13 days until the Garhwal king was defeated. It is chiefly regarded the only defeat of Pradyumna Shah's life and the victory of Gorkhali forces under Kingdom of Nepal.
Maharaja Pradyumna Shah or Pradyuman Shah, also known as Pradyumna Chand, was the last and 54th ruler of Garhwal dynasty until the kingdom was independent. He reigned over the state territories from 1785 to 14 May 1804, and later the kingdom was defeated by the Gurkha forces after the Battle of Khurbura occurred near Dehradun.