
The celiac plexus or coeliac plexus, also known as the solar plexus because of its radiating nerve fibers, is a complex network of nerves located in the abdomen, near where the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, and renal arteries branch from the abdominal aorta. It is behind the stomach and the omental bursa, and in front of the crura of the diaphragm, on the level of the first lumbar vertebra.

The abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.

The superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine. At its termination behind the neck of the pancreas, the SMV combines with the splenic vein to form the hepatic portal vein. The SMV lies to the right of the similarly named artery, the superior mesenteric artery, which originates from the abdominal aorta.

The lesser omentum is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach and the first part of the duodenum.

The hepatic artery proper is the artery that supplies the liver and gallbladder. It raises from the common hepatic artery, a branch of the celiac artery.
The left gastroepiploic vein receives branches from the antero-superior and postero-inferior surfaces of the stomach and from the greater omentum; it runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach and ends in the commencement of the splenic vein.

The right gastroepiploic artery is one of the two terminal branches of the gastroduodenal artery. It runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, anastomosing with the left gastroepiploic artery, a branch of the splenic artery.

The left gastroepiploic artery, the largest branch of the splenic artery, runs from left to right about a finger’s breadth or more from the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, and anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic.

The greater omentum is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, passing in front of the small intestines and doubles back to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. The greater omentum is larger than the lesser omentum, which hangs down from the liver to the lesser curvature. The common anatomical term "epiploic" derives from "epiploon", from the Greek epipleein, meaning to float or sail on, since the greater omentum appears to float on the surface of the intestines. It is the first structure observed when the abdominal cavity is opened anteriorly.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

The left gastric vein is a vein carrying deoxygenated blood that derives from tributaries draining both surfaces of the stomach; it runs from right to left along the lesser curvature of the stomach, between the two layers of the lesser omentum, to the esophageal opening of the stomach, where it receives some esophageal veins.

The curvatures of the stomach refer to the greater and lesser curvatures. The greater curvature of the stomach is four or five times as long as the lesser curvature.
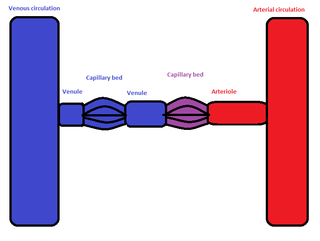
In the circulatory system of animals, a portal venous system occurs when a capillary bed pools into another capillary bed through veins, without first going through the heart. Both capillary beds and the blood vessels that connect them are considered part of the portal venous system.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
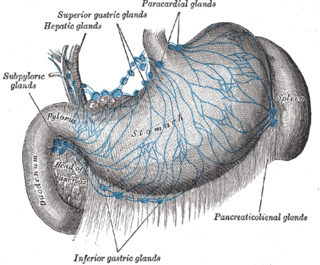
The gastric lymph nodes consist of two sets, superior and inferior.
Gastro- is a common English-language prefix derived from the ancient Greek γαστήρ gastēr ("stomach").
Gastro-omental artery may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.













