This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
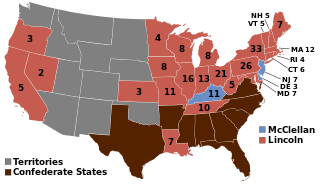
The United States presidential election of 1864, the 20th quadrennial presidential election, was held on Tuesday, November 8, 1864. In the midst of the American Civil War, incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 221-21 electoral votes, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats.

Jefferson , commonly known as Thomas Jefferson University, is a private university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was formed in 2017 through the merger of Philadelphia University and Thomas Jefferson University.
A Secular Humanist Declaration was an argument for and statement of support for democratic secular humanism. The document was issued in 1980 by the Council for Democratic and Secular Humanism (CODESH), now the Council for Secular Humanism (CSH). Compiled by Paul Kurtz, it is largely a restatement of the content of the American Humanist Association's 1973 Humanist Manifesto II, of which he was co-author with Edwin H. Wilson. Both Wilson and Kurtz had served as editors of The Humanist, from which Kurtz departed in 1979 and thereafter set about establishing his own movement and his own periodical. His Secular Humanist Declaration was the starting point for these enterprises.
McClellan is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:

A fireboat is a specialized watercraft with pumps and nozzles designed for fighting shoreline and shipboard fires. The first fireboats, dating to the late 18th century, were tugboats, retrofitted with firefighting equipment.
Older designs derived from tugboats and modern fireboats more closely resembling seafaring ships can both be found in service today. Some departments would give their multi-purpose craft the title of "fireboat" also.

Neal D. Barnard, M.D., F.A.C.C., is an American author, clinical researcher, and founding president of the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine (PCRM).
Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, colloquially known as P&S and formerly Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, is the graduate professional medical school of Columbia University. Located at the Columbia University Irving Medical Center in the Washington Heights neighborhood of Manhattan with its affiliate New York-Presbyterian Hospital. Founded in 1767 by Samuel Bard as the medical department of King's College, the College of Physicians and Surgeons was the first medical school in the thirteen colonies and hence, the United States, to award the Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) degree. Beginning in 1993, P&S also was the first U.S. medical school to hold a white coat ceremony.
George Williams may refer to:

The Faculty of Medicine is one of the constituent faculties of McGill University. It was established in 1829 after the Montreal Medical Institution was incorporated into McGill College as the College's first faculty; it was the first medical faculty to be established in Canada. The Faculty awarded McGill's first degree, and Canada's first medical degree to William Leslie Logie in 1833. His dissertation, "Medical inaugural dissertation on Cynanche trachealis" can be found in the McGill Library institutional repository, eScholarship@McGill.
The 1864 Democratic National Convention was held at The Amphitheatre in Chicago, Illinois.

Austin Flint II was an American physician. He carried out extensive experimental investigations in human physiology and made several important discoveries. He assisted in establishing the glycogenic function of the liver; showed that one of the functions of the liver is to separate from the blood the cholesterin, which is a product of the nervous system. and which, becoming a constituent of the bile, is afterward converted into what he named "stercorin", the odorous principle of feces.

John D. McKean is a fireboat that served the New York City Fire Department as Marine Company 1. She is named after John D. Mckean, who died in a 1953 steam explosion while trying to save a predecessor fireboat, the George B. McClellan.

The George B. McClellan was a fireboat operated by the FDNY from 1904 to 1954. She was designed by Harry deBerkley Parsons, as were other FDNY fireboats built at the time.

The 1864 United States presidential election in New York took place on November 8, 1864, as part of the 1864 United States presidential election. Voters chose 33 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1864 United States presidential election in New Jersey took place on November 8, 1864, as part of the 1864 United States presidential election. Voters chose seven representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.













