A craft or trade is a pastime or a profession that requires particular skills and knowledge of skilled work. In a historical sense, particularly the Middle Ages and earlier, the term is usually applied to people occupied in small-scale production of goods, or their maintenance, for example by tinkers. The traditional term craftsman is nowadays often replaced by artisan and rarely by craftsperson (craftspeople).

Art glass is an item that is made, generally as an artwork for decoration but often also for utility, from glass, sometimes combined with other materials. Techniques include stained glass windows, leaded lights, glass that has been placed into a kiln so that it will mould into a shape, glassblowing, sandblasted glass, and copper-foil glasswork. In general the term is restricted to relatively modern pieces made by people who see themselves as artists who have chosen to work in the medium of glass and both design and make their own pieces as fine art, rather than traditional glassworker craftsmen, who often produce pieces designed by others, though their pieces certainly may form part of art. Studio glass is another term often used for modern glass made for artistic purposes. Art glass has grown in popularity in recent years with many artists becoming famous for their work; and, as a result, more colleges are offering courses in glass work.

Studio glass is the modern use of glass as an artistic medium to produce sculptures or three-dimensional artworks. The glass objects created are intended to make a sculptural or decorative statement. Their prices may range from a few hundred to hundreds of thousands of dollars (US). For the largest installations, the prices are in the millions.

The Worshipful Company of Glaziers and Painters of Glass is one of the Livery Companies of the City of London. The Guild of Glaziers, or makers of Glass, the Company's forerunner, existed as early as 1328. It received a Royal Charter of incorporation in 1638. It is no longer a trade association of glass craftsmen, instead existing, along with a majority of Livery Companies, as a charitable body.

The Compagnie des Cristalleries de Saint Louis is a corporation, founded in 1767 in Münzthal in Lorraine. It is the oldest glass manufacturer in France with roots dating back to 1586 and the first crystal glass manufacturer in continental Europe (1781).
A vase is an open container. It can be made from a number of materials, such as ceramics, glass, non-rusting metals, such as aluminium, brass, bronze or stainless steel. Even wood has been used to make vases, either by using tree species that naturally resist rot, such as teak, or by applying a protective coating to conventional wood. Vases are often decorated, and they are often used to hold cut flowers. Vases come in different sizes to support whatever flower its holding or keeping in place.

Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion, making them resistant to thermal shock, more so than any other common glass. Such glass is less subject to thermal stress and is commonly used for the construction of reagent bottles. Borosilicate glass is sold under such trade names as Borcam, Borosil, DURAN, Suprax, Simax, BSA 60, BSC 51, Heatex, Endural, Schott, Refmex, Kimble, MG(India) and some items sold under different trade names.

According to the Venetians, Venetian glass has been made for over 1,500 years, and production has been concentrated on the Venetian island of Murano since the 13th century. Today Murano is known for its art glass, but it has a long history of innovations in glassmaking in addition to its artistic fame—and was Europe's first major glassmaking center. During the 15th century, Murano glassmakers created cristallo—which was almost transparent and considered the finest glass in the world. Murano glassmakers also developed a white-colored glass that looked like porcelain. They later became Europe's finest makers of mirrors.

John Adams, pioneer American glass manufacturer, and the founder of Adams Glass was born in Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania in 1823. He began working in glass manufacture at the age of 14.

Lino Tagliapietra is a Venetian glass artist who has also worked extensively in the United States. As a teacher and mentor, he has played a key role in the international exchange of glassblowing processes and techniques between the principal American centers and his native Murano, "but his influence is also apparent in China, Japan, and Australia—and filters far beyond any political or geographic boundaries."

Dante Marioni is an American glass artist.
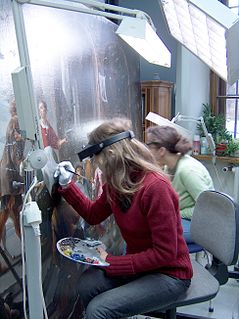
A conservator-restorer is a professional responsible for the preservation of artistic and cultural artifacts, also known as cultural heritage. Conservators possess the expertise to preserve cultural heritage in a way that retains the integrity of the object, building or site, including its historical significance, context and aesthetic or visual aspects. This kind of preservation is done by analyzing and assessing the condition of cultural property, understanding processes and evidence of deterioration, planning collections care or site management strategies that prevent damage, carrying out conservation treatments, and conducting research. A conservator's job is to ensure that the objects in a museum's collection are kept in the best possible condition, as well as to serve the museum's mission to bring art before the public.

Liuli Gongfang or Liuligongfang is Taiwan's only contemporary glass studio devoted to artistic Chinese glassware. Since its establishment in 1987 Liuligongfang has become known in Asia and abroad for its outstanding artistic endeavours and its high standard of craftsmanship.

Dracula is a soundtrack performed by the Kronos Quartet, with music composed by Philip Glass, for the 1931 film Dracula.

Mary Lowndes (1857–1929) was a British stained-glass artist who co-founded the stained glass studio and workshop, Lowndes and Drury in 1897. She was an influential leader in the Arts and Crafts Movement, not only for her stained glass work and successful studio-workshop, but also for opening doors for other women stained glass artists. She was an active participant in the suffragette movement, acting as Chair of the Artists' Suffrage League, and creating poster art to assist the movement.

Glass art refers to individual works of art that are substantially or wholly made of glass. It ranges in size from monumental works and installation pieces, to wall hangings and windows, to works of art made in studios and factories, including glass jewelry and tableware.
Andy Segal, nicknamed "the Magic Man", is a trick-shot pool champion from Huntington, New York. He began as a professional nine-ball player in the 1990s, and was a regular on the Camel Pro Billiard Tour before switching to trick-shot competition in 2002. A full-time pro player since 2007, Segal holds three world records in artistic billiards. He is known for his television competition appearances on ESPN, and has won many such events, including Trick Shot Magic, the World Cup of Trick Shots, the WPA World Artistic Pool Championship, and the Masters Artistic Pool Championship. Segal also performs trick shot exhibitions all over the world, and in films and television.
Tomasz Urbanowicz is an architect and a designer of artistic architectural glass. He finished studies at the architecture department of the Wroclaw University of Technology (1978–85). He took glass-window studies at the Fine Arts Academy of Nicolaus Copernicus University in Torun, Poland (1982–85) and worked as an assistant in the Painting and Sculpture Establishment at the Architecture Department of Wroclaw Institute. In 1987, together with his wife, architect Beata Urbanowicz, he established his own studio, Archiglass.

Flavio Poli (1900-1984) was an Italian artist, known for his designs in glass.