This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Theaceae is a family of flowering plants, composed of shrubs and trees, including the camellias. It can be described as having from seven to 40 genera, depending on the source and the method of circumscription used. The family Ternstroemiaceae has been included within Theaceae; however, the APG III system of 2009 places it instead in Pentaphylacaceae.

Franklinia is a monotypic genus in the tea plant family, Theaceae. The sole species in this genus is a flowering tree, Franklinia alatamaha, commonly called the Franklin tree, and native to the Altamaha River valley in Georgia in the southeastern United States. It has been extinct in the wild since the early 19th century, but survives as a cultivated ornamental tree.
A Zionist youth movement is an organization formed for Jewish children and adolescents for educational, social, and ideological development, including a belief in Jewish nationalism as represented in the State of Israel. Youth leaders in modern youth movements use informal education approaches to educate toward the movement's ideological goals.

Urim is a kibbutz in the Negev desert in southern Israel. Located near the border of the Gaza Strip and about 30 kilometers west of Beersheba, the kibbutz falls under the jurisdiction of Eshkol Regional Council. In 2017 it had a population of 475.
Gordonia curtyana is a species of plant in the Theaceae family. It is endemic to Cuba. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Neve Yam is a kibbutz in northern Israel. Located around twenty kilometres south of Haifa, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hof HaCarmel Regional Council. In 2017 it had a population of 241.

The gordonia darkwing is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in North America, from North Carolina to Mississippi and Florida. The food plant occurs in Alabama and Mississippi and the moth could be expected from these areas as well.
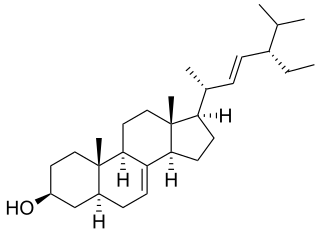
α-Spinasterol is a phytosterol found in a variety of plant sources such as spinach, from which it gets its name.
Gordonia alkaliphila is a Gram-positive, aerobic and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Gordonia which has been isolated from tidal flat sediments from the Yellow Sea in Korea.
Gordonia caeni is a Gram-positive, strictly aerobic, short-rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Gordonia which has been isolated from sludge from a sewage disposal plant in Daejeon in Korea.
Gordonia cholesterolivorans is a bacterium from the genus of Gordonia which has been isolated from sewage sludge from a sewage treatment plant in Ciudad Real in Spain. Gordonia cholesterolivorans has the ability to degrade cholesterol.
Gordonia effusa is a bacterium from the genus of Gordonia which has been isolate from human sputum in Japan.
Gordonia hirsuta is a bacterium from the genus of Gordonia which has been isolated from a biofilter of an animal rendering plant in Germany.
Gordonia malaquae is a bacterium from the genus of Gordonia which has been isolated from sludge from a wastewater treatment plant in Taiwan.
Gordonia rhizosphera is a bacterium from the genus of Gordonia which has been isolated from rhizosphere soil from a mangrove plant in Japan.

Polyspora axillaris is a species of evergreen trees or shrubs that can grow up to 9 m tall. It has been given the name "Fried Egg Plant" for its white and yellow flower.
P. axillaris is found in Southern China, including Hong Kong, Hainan and Taiwan. Is also grows in the wild in Vietnam, and is a garden tree all over the world.









