Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia (Somali: Jamhuuriyadda Federaalka Soomaaliya; Arabic: جمهورية الصومال الفيدرالية, translit. Jumhūrīyah aṣ-Ṣūmāl al-Fīdirālīyah, is a country with its territory located in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti and Somaliland to the northwest, the Gulf of Aden to the north, the Guardafui Channel and Somali Sea to the east, and Kenya to the southwest. It is separated from Socotra by the Guardafui Channel in the northeast and from the Seychelles by the Somali Sea. Somalia has the longest coastline on Africa's mainland, and its terrain consists mainly of plateaus, plains and highlands. Climatically, hot conditions prevail year-round, with periodic monsoon winds and irregular rainfall.

Somaliland, officially the Republic of Somaliland, is a self-declared state, internationally considered to be an autonomous region of Somalia.

Mogadishu, locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and most populous city of Somalia. Located in the coastal Banadir region on the Somali Sea, the city has served as an important port for millennia. As of 2017, it had a population of 2,425,000 residents. Mogadishu is the nearest foreign mainland city to Seychelles, at a distance of 835 mi (1,344 km) over the Somali Sea.

Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, or Saxe-Coburg-Gotha, was an Ernestine duchy ruled by a branch of the House of Wettin, consisting of territories in the present-day states of Bavaria and Thuringia in Germany. It lasted from 1826 to 1918. In November 1918, Charles Edward, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, was forced to abdicate. Saxe (Gotha) was subsequently merged into Thuringia whereas Coburg merged into Bavaria.
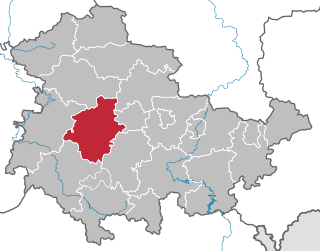
Gotha is a Kreis (district) in western central Thuringia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis, Sömmerda, the Kreis-free city Erfurt, Ilm-Kreis, Schmalkalden-Meiningen and the Wartburgkreis.

Gothaer Waggonfabrik was a German manufacturer of rolling stock established in the late nineteenth century at Gotha. During the two world wars, the company expanded into aircraft building.

Somali is an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic branch. It is spoken as a mother tongue by Somalis in Greater Somalia and the Somali diaspora. Somali is an official language of Somalia, a national language in Djibouti, and a working language in the Somali Region of Ethiopia. It is used as an adoptive language by a few neighboring ethnic minority groups and individuals. The Somali language is written officially with the Latin alphabet.

The House of Wettin is a dynasty of German counts, dukes, prince-electors and kings that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany.
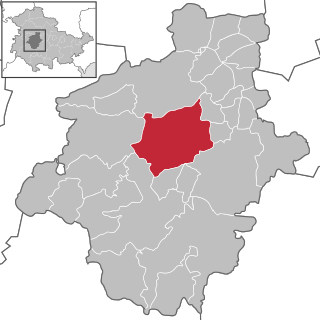
Gotha is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, located 20 kilometres west of Erfurt and 25 km east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the end of monarchy in Germany in 1918. The House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha originating here spawned many European rulers, including the royal houses of the United Kingdom, Belgium, Portugal and Bulgaria.

The Almanach de Gotha is a directory of Europe's royalty and higher nobility, also including the major governmental, military and diplomatic corps, as well as statistical data by country. First published in 1763 by C.W. Ettinger in Gotha in Thuringia, Germany, at the ducal court of Frederick III, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg, it came to be regarded as an authority in the classification of monarchies and their courts, reigning and former dynasties, princely and ducal families, and the genealogical, biographical and titulary details of Europe's highest level of aristocracy. It was published from 1785 annually by Justus Perthes Publishing House in Gotha, until 1944. The Soviets destroyed the Almanach de Gotha's archives in 1945.

Saxe-Gotha was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in the former Landgraviate of Thuringia. The ducal residence was erected at Gotha.

Alfred, Hereditary Prince of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, was the only son and heir apparent of Alfred, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. He died aged 24 under circumstances still not entirely clear. He was a first cousin of King George V of the United Kingdom, Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany and Tsar Nicholas II of Russia.

Somalis are an ethnic group belonging to the Cushitic peoples inhabiting the Horn of Africa. The overwhelming majority of Somalis speak the Somali language, which is part of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family. They are predominantly Sunni Muslim. Ethnic Somalis number around 28-30 million and are principally concentrated in Somalia, Ethiopia, Kenya, and Djibouti (534,000). A Somali diaspora is also found in parts of the Middle East, African Great Lakes region, Southern Africa, North America, Oceania, and Western Europe.

The House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha is a German dynasty that ruled the duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, which was one of the Ernestine duchies. It is a cadet branch of the Saxon House of Wettin.

Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld was one of the Saxon Duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin Dynasty. Established in 1699, the Saxe-Coburg-Saalfield line lasted until the reshuffle of the Ernestine territories that occurred following the extinction of the Saxe-Gotha line in 1825, in which the Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld line received Gotha, but lost Saalfeld to Saxe-Meiningen.

The Somali Civil War is an ongoing civil war taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the military junta led by Siad Barre during the 1980s. By 1988–90, the Somali Armed Forces began engaging various armed rebel groups, including the Somali Salvation Democratic Front in the northeast, the Somali National Movement in the northwest, and the United Somali Congress in the south. The clan-based armed opposition groups eventually managed to overthrow the Barre government in 1991.

Frederick II, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg, was a duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg.

Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg was a duchy ruled by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in today's Thuringia, Germany. The extinction of the line in 1825 led to a major re-organisation of the Thuringian states.

The Gotha Go 145 was a German World War II-era biplane of wood and fabric construction used by Luftwaffe training units. Although obsolete by the start of World War II, the Go 145 remained in operational service until the end of the War in Europe as a night harassment bomber.
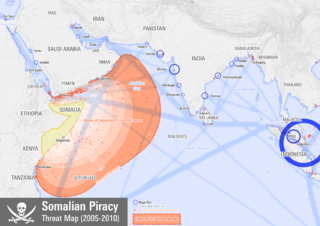
Piracy off the coast of Somalia refers to criminal violence and threats to shipping in the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel and Somali Sea, in what some say are disputed territorial waters. It had primarily been a threat to international fishing vessels, expanding to international shipping since the second phase of the Somali Civil War, around 2000.