Telecommunications in Greenland include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.

CANTAT-3 was the third Canadian transatlantic telecommunications cable, in regular operation from 1994 to 2010, carrying 3 x 2.5 Gbit/s between Canada and Europe. It branches to both Iceland and the Faroe Islands. It is out of normal service for international bandwidth and is currently operated by Føroya Tele to service oil platforms in the North Sea.
Telecommunications in Iceland is a diversified market.

Air Greenland A/S, also known as Greenlandair, is the flag carrier of Greenland, owned by the Greenlandic Government. It operates a fleet of 28 aircraft, including 2 airliners used for transatlantic and charter flights, 8 fixed-wing aircraft primarily serving the domestic network, and 18 helicopters feeding passengers from the smaller communities into the domestic airport network. Flights to heliports in the remote settlements are operated on contract with the government of Greenland.

Nuuk Airport is an airport serving Nuuk, the capital of Greenland. The airport is a technical base and focus city for Air Greenland, the flag carrier airline of Greenland, linking the capital with several towns in western and south-western part of the country, including the airline hub at Kangerlussuaq Airport. With connections to Iceland, Nuuk Airport is also one of six international airports in Greenland but serves only destinations within Greenland and Iceland. International connections are made with flights to either Keflavík International Airport in Iceland or Kangerlussuaq Airport.
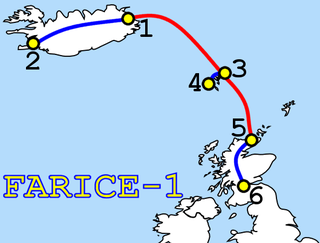
FARICE-1 is a submarine communications cable connecting Iceland, the Faroe Islands and Scotland. The cable has been in use since January 2004 and is 100% owned by the Icelandic state. The cable had an initial design capacity of 720 Gbit/s and is a two fibre pair design. The length of the cable is 1205 km for the direct route between Iceland and Scotland. The cable structure and repeaters were made by Pirelli and the terminal equipment was supplied by TYCO. In the year 2013 the terminal equipment was upgraded by Ciena bringing the total capacity of the submarine cable to 11 Tbit/s. The cable has service access points in Reykjavik and Keflavik Airport as well as in London Telehouse East. The company Farice ehf sells services over the FARICE-1 cable. FARICE-2 was never built. DANICE is the complementary submarine cable.

South East Asia–Middle East–Western Europe 4 is an optical fibre submarine communications cable system that carries telecommunications between Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Italy, Tunisia, Algeria and France. It is intended to be a complement to, rather than a replacement for, the SEA-ME-WE 3 cable.

Alcatel–Lucent S.A. was a multinational telecommunications equipment company, headquartered in Boulogne-Billancourt, France. It was formed in 2006 by the merger of France-based Alcatel and U.S.-based Lucent, the latter being a successor of AT&T's Western Electric and a holding company of Bell Labs.
40 Gigabit Ethernet (40GbE) and 100 Gigabit Ethernet (100GbE) are groups of computer networking technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at rates of 40 and 100 gigabits per second (Gbit/s), respectively. These technologies offer significantly higher speeds than 10 Gigabit Ethernet. The technology was first defined by the IEEE 802.3ba-2010 standard and later by the 802.3bg-2011, 802.3bj-2014, 802.3bm-2015, and 802.3cd-2018 standards. The first succeeding Terabit Ethernet specifications were approved in 2017.
JASURAUS was a 5.332 Gbit/s, 2,800 km optical submarine telecommunications cable that connected Port Hedland, Australia, to Jakarta, Indonesia, with a further interconnection to the APCN and which was decommissioned in 2012.
The Telstra Endeavour is a submarine cable connecting Sydney and Hawaii. The cable went live in October 2008, with a capacity of 1.28 terabits per second in the future It was proposed on 28 March 2007 by Telstra, the largest telecommunications carrier in Australia.
TEAMS is an initiative spearheaded by the government of Kenya to link the country to the rest of the world through a submarine fibre optic cable. It was first proposed as an alternative to EASSy, the East African Submarine Cable System. The Kenyan government had grown frustrated with the ownership model favoured by South Africa, the time it was taking and what it perceived as an attempt by South Africa to control the cable. As a result, in November 2006, the Kenyan government decided to partner with the Emirates Telecommunication Establishment (Etisalat) to build its own fibre optic cable.

Iceland is among the top countries in the world in terms of Internet deployment and use. 99.68% of Icelanders used in the internet in 2021.

The DANICE submarine communications cable system transits 2250 km of the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea to connect Iceland and Denmark. It consists of four fibre pairs, capable of carrying in total up to 36.4 Tbit/s of data using 100Gbit/s coherent wavelength technology available in 2013. The cable went into operation in November 2009 and has had no submarine faults. The operator of the cable is Farice ehf. The complementary cable is FARICE-1. DANICE has cable landing points at:

Tusass is a Greenlandic postal and telecommunications company dating back to 1879. Tusass is the largest telecommunications company in Greenland. The company's headquarters are located in Nuuk.
Europe India Gateway (EIG) is a submarine communications cable system that connects the U.K., Portugal, Gibraltar, Monaco, France, Libya, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Djibouti, Oman, United Arab Emirates, and India.

The West Africa Cable System (WACS) is a submarine communications cable linking South Africa with the United Kingdom along the west coast of Africa that was constructed by Alcatel-Lucent. The cable consists of four fibre pairs and is 14,530 km in length, linking from Yzerfontein in the Western Cape of South Africa to London in the United Kingdom. It has 14 landing points, 12 along the western coast of Africa and 2 in Europe completed on land by a cable termination station in London. The total cost for the cable system is $650 million. WACS was originally known as the Africa West Coast Cable (AWCC) and was planned to branch to South America but this was dropped and the system eventually became the West African Cable System.
Honotua is a submarine communications cable system that connects several islands of French Polynesia via Tahiti to Hawaii. The cable was laid by the cableship Île de Ré (câblier) between December 2009 and June 2010.
A super-channel is an evolution in dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) in which multiple, coherent optical carriers are combined to create a unified channel of a higher data rate, and which is brought into service in a single operational cycle.

The South Atlantic Inter Link (SAIL) is a submarine communications cable in the South Atlantic Ocean linking Kribi, Cameroon with Fortaleza, Brazil.












