
The United Nations Economic and Social Council is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, responsible for coordinating the economic and social fields of the organization, specifically in regards to the fifteen specialised agencies, the eight functional commissions, and the five regional commissions under its jurisdiction.

The Group of Western European and Other States, also known as the Western European and Other States Group or WEOG, is one of the five United Nations regional groups and is composed of 28 Member States mainly from Western Europe, but also from Oceania, Northern America, and Western Asia.

The United Nations Regional Groups are the geopolitical regional groups of member states of the United Nations. Originally, the UN member states were unofficially organized into five groups as an informal means of sharing the distribution of posts for General Assembly committees. Now this grouping has taken on a much more expansive and official role. Many UN bodies are allocated on the basis of geographical representation. Top leadership positions, including Secretary-General and President of the General Assembly, are rotated among the regional groups. The groups also coordinate substantive policy and form common fronts for negotiations and bloc voting.

The Group of African States, or African Group, is one of the five United Nations regional groups and is composed of 54 Member States from the African continent. The African Group is the largest regional group, and compose 28% of all United Nations members.

The Group of Eastern European States (EEG) is one of the five United Nations regional groups and is composed of 23 Member States from Eastern, Central and Southern Europe.

The 2011 United Nations Security Council election was held on 21 and 24 October 2011 during the Sixty-sixth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Azerbaijan, Guatemala, Morocco, Pakistan, and Togo, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2012. Azerbaijan was elected after 17 rounds on 24 October, while the other four new members were chosen on 21 October.

The 2013 United Nations Security Council election was held on 17 October 2013 during the 68th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The Assembly elected Chad, Chile, Lithuania, Nigeria, and Saudi Arabia for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2014. The following day, Saudi Arabia announced that it was declining the seat, accusing UNSC of using "double standards" and being unable to resolve important issues in the Middle East. A second round of voting therefore took place on 6 December, in which Jordan was elected to the council in lieu of Saudi Arabia.

The 1991 United Nations Security Council election was held on 16 October 1991 during the Forty-sixth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Cape Verde, Hungary, Japan, Morocco, and Venezuela, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1992.
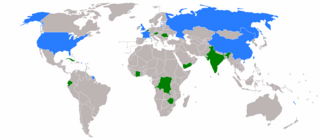
The 1990 United Nations Security Council election was held on 1 November 1990 during the Forty-fifth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Austria, Belgium, Ecuador, India, and Zimbabwe, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1991.
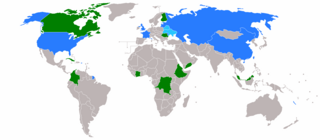
The 1989 United Nations Security Council election was held on 18 October 1989 during the Forty-fourth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Côte d'Ivoire, Cuba, Romania, South Yemen, and Zaire, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1990. This was the first time Yemen was elected to the Council, as Yemeni unification occurred during South Yemen membership.
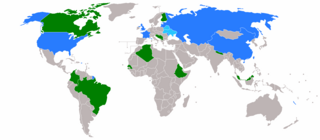
The 1988 United Nations Security Council election was held on 26 October 1988 during the Forty-third session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Canada, Colombia, Ethiopia, Finland, and Malaysia, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1989.

The 1987 United Nations Security Council election was held on 15 October 1987 during the Forty-second session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Algeria, Brazil, Nepal, Senegal, and Yugoslavia, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1988.

The 1985 United Nations Security Council election was held on 17 October 1985 during the Fortieth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Bulgaria, Congo, Ghana, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1986. 1985 marks the first election of Congo and the United Arab Emirates to the Council.

The 1976 United Nations Security Council election was held on 21 October 1976 during the Thirty-first session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Canada, the Federal Republic of Germany, India, Mauritius, and Venezuela, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1977. Both Mauritius and West Germany were elected members of the Council for the first time.

The 1981 United Nations Security Council election was held on 15 October 1981 during the Thirty-sixth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Guyana, Jordan, Poland, Togo, and Zaire, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1982. Togo and Zaire were elected for the first time.

The 1970 United Nations Security Council election was held on 26 October 1970 during the Twenty-fifth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Argentina, Belgium, Italy, Japan, and Somalia, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1971.
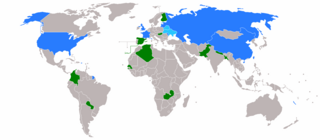
The 1968 United Nations Security Council election was held on 1 November 1968 during the Twenty-third session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Colombia, Finland, Nepal, Spain, and Zambia, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1969.

The 1966 United Nations Security Council election was held on 11 November 1966 during the Twenty-first session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Brazil, Canada, Denmark, Ethiopia, and India, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1967.

The Group of Latin America and Caribbean Countries, or GRULAC, is one of the five United Nations Regional Groups composed of 33 Member States from Central and South America, as well as some islands in the West Indies. Its members compose 17% of all United Nations members.
















