
Caracas, officially Santiago de León de Caracas, is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and centre of the Greater Caracas Area. Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the northern part of the country, following the contours of the narrow Caracas Valley on the Venezuelan coastal mountain range. Terrain suitable for building lies between 760 and 1,140 m above sea level, although there is some settlement above this range. The valley is close to the Caribbean Sea, separated from the coast by a steep 2,200-metre-high (7,200 ft) mountain range, Cerro El Ávila; to the south there are more hills and mountains. The Metropolitan Region of Caracas has an estimated population of 4,923,201.

The Orinoco River is one of the longest rivers in South America at 2,140 kilometres (1,330 mi). Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers 880,000 square kilometres (340,000 sq mi), with 76.3 percent of it in Venezuela and the remainder in Colombia. It is the third largest river in the world by discharge volume of water. The Orinoco River and its tributaries are the major transportation system for eastern and interior Venezuela and the llanos of Colombia. The environment in the Orinoco's basin is extremely diverse; it hosts a wide variety of flora and fauna.
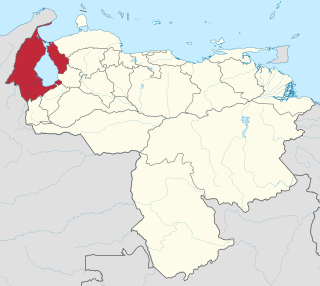
Zulia State is one of the 23 states of Venezuela. The state capital is Maracaibo. As of the 2011 census, it has a population of 3,704,404, the largest population among Venezuela's states. It is also one of the few states in Venezuela in which voseo is widely used.

Valencia is the capital city of Carabobo State, and the third largest city in Venezuela.

Vichada Department is a department of the Republic of Colombia in South America. Vichada is located in the eastern plains of Colombia, in the Orinoquía Region within the Orinoco river basin bordering the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela to the north and east. To the north the department also borders with Arauca Department, to the northwest with Casanare Department, to the west with Meta Department, to the southwest narrowly bordering with Guaviare Department and to the south with Guainía Department. The department is the second largest in Colombia and scarcely populated in comparison to other departments.

Amazonas State is one of the 23 states (estados) into which Venezuela is divided. It covers nearly a fifth of the area of Venezuela, but has less than 1% of Venezuela's population.

Apure State is one of the 23 states (estados) into which Venezuela is divided. Its territory formed part of the provinces of Mérida, Maracaibo, and Barinas, in accordance with successive territorial ordinations pronounced by the colonial authorities. In 1824 the Department of Apure was created, under jurisdiction of Barinas, which laid the foundations for the current entity. In 1856 it separated from Barinas and for the first time Apure appeared as an independent province, which in 1864 acquired the status of state. In 1881, however, a new territorial division combined Apure and Guayana to form a single state named Bolívar. In 1899 it reestablished its autonomy and finally, by means of the Constitution of 1909, gained its current borders.

Barquisimeto is a city in Venezuela. It is the capital of the state of Lara and head of Iribarren Municipality. It is an important urban, industrial, commercial and transportation center of the country, recognized as the fourth-largest city by population and area in Venezuela after Caracas, Maracaibo and Valencia.

Ciudad Guayana is a city in Bolívar State, Venezuela. It stretches 40 kilometers along the south bank of the Orinoco river, at the point where it is joined by its main tributary, the Caroní river. The Caroni crosses the city south-north and divides it on its two main halves: the old town of San Félix in the east, and the new town of Puerto Ordaz in the west. The city was officially founded in 1961 by the unification of this two former settlements, but the history of San Félix goes back to its foundation in 1724. Within the city limits are located the site of Cachamay Falls and Llovizna Falls. There are three bridges across the Caroni and the second crossing over the Orinoco, the Orinoquia Bridge, was inaugurated in the city in 2006. With approximately one million people, it is Venezuela's fastest-growing city due to its important iron, steel, aluminium and hydroelectric industries. Ciudad Guayana is one of Venezuela's five most important ports, since most goods produced in the industry-rich Bolívar state are shipped through it, as ocean-going vessels can sail to it from the Atlantic Ocean up the Orinoco river.

Los Llanos is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, in northwestern South America. It is an ecoregion of the flooded grasslands and savannas biome.
Venezuela is a federation made up of twenty-three states, a Capital District and the Federal Dependencies, which consist of a large number of islands and islets on the Caribbean Sea. Venezuela also claims the Guayana Esequiba territory which comprises six districts in the independent nation of Guyana.

The Orinoco Delta is a vast river delta of the Orinoco River, located in eastern Venezuela.

Guayana Esequiba is a territory administered and controlled by Guyana, however it is claimed by Venezuela.

Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. It is often considered part of the Caribbean region because of its strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). Guyana is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Venezuela to the west, and Suriname to the east. With an area of 215,000 square kilometres (83,000 sq mi), Guyana is the third-smallest sovereign state on mainland South America after Uruguay and Suriname.
The 1986 Copa Libertadores was the 27th edition of the Copa Libertadores, CONMEBOL's annual international club tournament. River Plate won the competition for the first time ever.

Joan Orpí i del Pou, also Juan Orpín or Juan Urpín was a Spanish conquistador, known for founding New Barcelona in Venezuela, and for founding the short-lived Province of New Catalonia (1633–1654).

Indigenous peoples in Suriname, Native Surinamese, or Amerindian Surinamese, are Surinamese people who are of indigenous ancestry. They comprise approximately 3.8% of Suriname's population of 566,846.

A crisis concerning who is the legitimate President of Venezuela has been underway since 10 January 2019, when the opposition-majority National Assembly declared that incumbent Nicolás Maduro's 2018 reelection was invalid and the body declared its president, Juan Guaidó, to be acting president of the nation.

















