This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
HTML has been in use since 1991, but HTML 4.0 was the first standardized version where international characters were given reasonably complete treatment. When an HTML document includes special characters outside the range of seven-bit ASCII, two goals are worth considering: the information's integrity, and universal browser display.
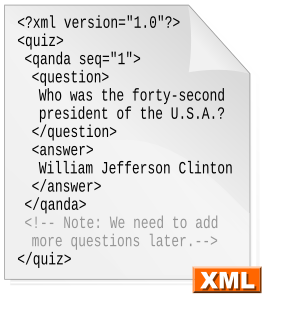
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The W3C's XML 1.0 Specification and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the presentation layer is layer 6 and serves as the data translator for the network. It is sometimes called the syntax layer.

The Meta-Object Facility (MOF) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for model-driven engineering. Its purpose is to provide a type system for entities in the CORBA architecture and a set of interfaces through which those types can be created and manipulated. The official reference page may be found at OMG's website.
The Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards (OASIS) is a global nonprofit consortium that works on the development, convergence, and adoption of open standards for security, Internet of Things, energy, content technologies, emergency management, and other areas.
Enterprise application integration (EAI) is the use of software and computer systems' architectural principles to integrate a set of enterprise computer applications.
The Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI-PMH) is a protocol developed for harvesting metadata descriptions of records in an archive so that services can be built using metadata from many archives. An implementation of OAI-PMH must support representing metadata in Dublin Core, but may also support additional representations.
An enterprise messaging system (EMS) or messaging system in brief is a set of published enterprise-wide standards that allows organizations to send semantically precise messages between computer systems. EMS systems promote loosely coupled architectures that allow changes in the formats of messages to have minimum impact on message subscribers. EMS systems are facilitated by the use of structured messages, and appropriate protocols, such as DDS, MSMQ, AMQP or SOAP with web services.
In computer science, overhead is any combination of excess or indirect computation time, memory, bandwidth, or other resources that are required to perform a specific task. It is a special case of engineering overhead. Overhead can be a deciding factor in software design, with regard to structure, error correction, and feature inclusion. Examples of computing overhead may be found in functional programming, data transfer, and data structures.
The Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) is an open, multidisciplinary, neutral, 501(c)(3) non-profit standards developing organization (SDO) that has been working through productive, consensus-based collaborative teams, since its formation in 1997, to develop global standards and innovations to streamline medical research data and ensure a link with healthcare. The CDISC mission is "to develop and support global, platform-independent data standards that enable information system interoperability to improve medical research and related areas of healthcare". The CDISC vision is "informing patient care and safety through higher quality medical research". The CDISC suite of standards supports medical research of any type from protocol through analysis and reporting of results. They have been shown to decrease resources needed by 60% overall and 70–90% in the start-up stages when they are implemented at the beginning of the research process.
The XML Protocol ("XMLP") is a standard being developed by the W3C XML Protocol Working Group to the following guidelines, outlined in the group's charter:
- An envelope for encapsulating XML data to be transferred in an interoperable manner that allows for distributed extensibility.
- A convention for the content of the envelope when used for RPC applications. The protocol aspects of this should be coordinated closely with the IETF and make an effort to leverage any work they are doing, see below for details.
- A mechanism for serializing data representing non-syntactic data models such as object graphs and directed labeled graphs, based on the data types of XML Schema.
- A mechanism for using HTTP transport in the context of an XML Protocol. This does not mean that HTTP is the only transport mechanism that can be used for the technologies developed, nor that support for HTTP transport is mandatory. This component merely addresses the fact that HTTP transport is expected to be widely used, and so should be addressed by this Working Group. There will be coordination with the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
Information exchange or information sharing are informal terms that can either refer to bidirectional information transfer in telecommunications and computer science or communication seen from a system-theoretic or information-theoretic point of view. As "information" in this context invariably refers to (electronic) data that encodes and represents the information at hand, a broader treatment can be found under data exchange.
A MetaServer is considered a central broker providing a collated view for dispersed web resources. It is used to collect data from various web services, web pages, databases, or other online resources/repositories and then present the combined results to the client using a standard web protocol.
Apache ObJectRelationalBridge (OJB) is an Object/Relational mapping tool that allows transparent persistence for Java Objects against relational databases. It was released on April 6, 2005.
SOAPjr is a protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. It is a hybrid of SOAP and JSON-RPC.
XHTML+RDFa is an extended version of the XHTML markup language for supporting RDF through a collection of attributes and processing rules in the form of well-formed XML documents. XHTML+RDFa is one of the techniques used to develop Semantic Web content by embedding rich semantic markup.
Version 1.1 of the language is a superset of XHTML 1.1, integrating the attributes according to RDFa Core 1.1. In other words, it is an RDFa support through XHTML Modularization.
Electronic Business using eXtensible Markup Language, commonly known as e-business XML, or ebXML as it is typically referred to, is a family of XML based standards sponsored by OASIS and UN/CEFACT whose mission is to provide an open, XML-based infrastructure that enables the global use of electronic business information in an interoperable, secure, and consistent manner by all trading partners.


