
A periplus or periplous is a manuscript document that lists the ports and coastal landmarks, in order and with approximate intervening distances, that the captain of a vessel could expect to find along a shore. In that sense the periplus was a type of log. It served the same purpose as the later Roman itinerarium of road stops; however, the Greek navigators added various notes, which if they were professional geographers became part of their own additions to Greek geography.
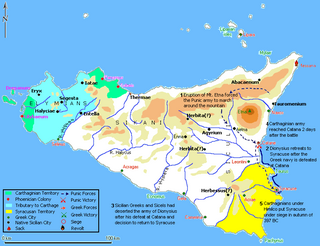
The Siege of Syracuse in 397 BC was the first of four unsuccessful sieges Carthaginian forces would undertake against Syracuse from 397 to 278 BC. In retaliation to the Siege of Motya by Dionysius of Syracuse, Himilco of the Magonid family of Carthage led a substantial force to Sicily. After retaking Motya and founding Lilybaeum, Himilco sacked Messana, then laid siege of Syracuse in the autumn of 397 BC after the Greek navy was crushed at Catana.

The Battle of Ebro River was a naval battle fought near the mouth of Ebro River in the spring of 217 BC between a Carthaginian fleet of approximately 27 quinqueremes, under the command of Himilco, and a Roman fleet of 55 ships, under Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus. Hasdrubal Barca, the Carthaginian commander in Iberia, had launched a joint expedition to destroy the Roman base north of the Ebro River. The Carthaginian naval contingent was totally defeated after a surprise attack by the Roman ships, losing 29 ships and the control of seas around Iberia. The reputation of the Romans was further enhanced in Iberia after this victory, causing rebellion among some of the Iberian tribes under Carthaginian control.

The Punics, also known as Carthaginians, were a people from Ancient Carthage who traced their origins to the Phoenicians. Punic is the English adjective, derived from the Latin adjective punicus to describe anything Carthaginian. Their language, Punic, was a dialect of Phoenician.
Leptines was a military leader from Syracuse, Sicily, active during his brother, Dionysius the Elder's wars. He showed bravery in the fights against Carthage and mercy with the Thurians.
Mago was commander of the Carthaginian fleet under Himilco in the war against Dionysius I of Syracuse, 396 BCE.

The Siege of Akragas took place in 406 BC in Sicily; the Carthaginian enterprise ultimately lasted a total of eight months. The Carthaginian army under Hannibal Mago besieged the Dorian Greek city of Akragas in retaliation for the Greek raids on Punic colonies in Sicily. The city managed to repel Carthaginian attacks until a relief army from Syracuse defeated part of the besieging Carthaginian army and lifted the siege of the city.
The Battle of Gela took place in the summer of 405 BC in Sicily. The Carthaginian army under Himilco, which had spent the winter and spring in the captured city of Akragas, marched to confront the Greeks at Gela. The Syracuse government had deposed Daphnaeus, the unsuccessful general of the Greek army at Akragas, with Dionysius, another officer who had been a follower of Hermocrates. Dionysius schemed and gained full dictatorial powers. When the Carthaginians advanced on Gela and put the town under siege, Dionysius marched from Syracuse to confront the threat. He planned to use a complex three-pronged attack plan against the Carthaginians, which failed due to lack of proper coordination. Dionysius chose to evacuate Gela, as the defeat caused discontent in Syracuse and he did not wish to lose his power. Himilco sacked the abandoned city after the Greeks had fled to Camarina.
The Siege of Motya took place either in 398 or 397 BC in western Sicily. Dionysius, after securing peace with Carthage in 405 BC, had steadily increased his military power and had tightened his grip on Syracuse. He had fortified Syracuse against sieges and had created a large army of mercenaries and a large fleet, in addition to employing the catapult and quinqueremes for the first time in history. In 398 BC, he attacked and sacked the Phoenician city of Motya despite the Carthaginian relief effort led by Himilco. Carthage also lost most of her territorial gains secured in 405 BC after Dionysius declared war on Carthage in 398 BC.
The Battle of Messene took place in 397 BC in Sicily. Carthage, in retaliation for the attack on Motya by Dionysius, had sent an army under Himilco, to Sicily to regain lost territory. Himilco sailed to Panormus, and from there again sailed and marched along the northern coast of Sicily to Cape Pelorum, 12 miles (19 km) north of Messene. While the Messenian army marched out to offer battle, Himilco sent 200 ships filled with soldiers to the city itself, which was stormed and the citizens were forced to disperse to forts in the countryside. Himilco later sacked and leveled the city, which was again rebuilt after the war.

The Battle of Catana took place in the summer of 397 BC. The Greek fleet under Leptines, the brother of Dionysius I of Syracuse, engaged the Carthaginian fleet under Mago near the city of Catana in Sicily. While the Greek army under Dionysius was present near the city of Catana during the battle, the Carthaginian army under Himilco was away in the interior of Sicily, making a detour around the erupting Mount Etna. The Carthaginian fleet crushed the Greek fleet in the battle, leading to the Carthaginian siege of Syracuse later in 397 BC.
The Magonids were a political dynasty of Ancient Carthage from 550 BCE to 340 BCE. The dynasty was first established under Mago I, under whom Carthage became pre-eminent among the Phoenician colonies in the western Mediterranean. Under the Magonids, the Carthaginian Empire expanded to include Sardinia, Libya, and for almost a decade much of Sicily.
The Battle of Abacaenum took place between the Carthaginian forces under Mago and the Greek army under Dionysius in 393 BC near the Sicilian town on Abacaenum in north-eastern Sicily. Dionysius, tyrant of Syracuse, had been expanding his influence over Sicels' territories in Sicily. After Dionysius' unsuccessful siege in 394 BC of Tauromenium, a Carthaginian ally, Mago decided to attack Messana. However, the Carthaginian army was defeated by the Greeks near the town of Abacaenum and had to retire to the Carthaginian territories in Western Sicily. Dionysius did not attack the Carthaginians but continued to expand his influence in eastern Sicily.
The Battle of Chrysas was a battle fought in 392 BC in the course of the Sicilian Wars, between the Carthaginian army under Mago and a Greek army under Dionysius I, tyrant of Syracuse, who was aided by Agyris, tyrant of the Sicel city of Agyrium. Mago had been defeated by Dionysius at Abacaenum in 393, which had not damaged the Carthaginian position in Sicily. Reinforced by Carthage in 392, Mago moved to attack the Sicles allied with Syracuse in central Sicily. After the Carthaginians reached and encamped near the river Chrysas, the Sicels harassed the Carthaginian supply lines causing a supply shortage, while the Greek soldiers rebelled and deserted Dionysius when he refused to fight a pitched battle. Both Mago and Dionysius agreed to a peace treaty, which allowed the Carthaginians to formally occupy the area west of the River Halycus, while Dionysius was given lordship over the Sicel lands. The peace would last until 383, when Dionysius attacked the Carthaginians again.
Mago II, also known as Magon, was Shofet of Carthage from 396 to 375 BCE, and was a member of the Magonid dynasty. He became Shofet after the suicide of Himilco II in 396 BCE and was succeeded by Mago III in 375.
The Sack of Camarina in Sicily took place in 405 BC as part of the Sicilian Wars.
The Battle of Cronium was part of the Sicilian Wars and took place in Sicily. A Syracusan army, led by Dionysius I, was defeated by a Carthaginian army, led by Himilco Mago, Mago II's son. The Carthaginians won the day having routed the enemy army. Leptines, Dionysius' brother, was killed during the battle. The location of Cronium is considered to be close to modern Palermo.





