Related Research Articles

Burrhus Frederic Skinner was an American psychologist, behaviourist, author, inventor, and social philosopher. He was a professor of psychology at Harvard University from 1958 until his retirement in 1974.
Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction, or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes craniofacial surgery, hand surgery, microsurgery, and the treatment of burns. While reconstructive surgery aims to reconstruct a part of the body or improve its functioning, cosmetic surgery aims at improving the appearance of it.

Bartholomew was one of the twelve apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. He has also been identified as Nathanael or Nathaniel, who appears in the Gospel of John when introduced to Jesus by Philip, although many modern commentators reject the identification of Nathanael with Bartholomew.

Vitiligo is a long-term skin condition characterized by patches of the skin losing their pigment. The patches of skin affected become white and usually have sharp margins. The hair from the skin may also become white. The inside of the mouth and nose may also be involved. Typically both sides of the body are affected. Often the patches begin on areas of skin that are exposed to the sun. It is more noticeable in people with dark skin. Vitiligo may result in psychological stress and those affected may be stigmatized.
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin. It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin, hair, nails, and some cosmetic problems.
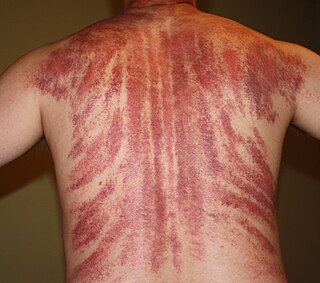
Gua sha or kerokan, is part of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which a tool is used to scrape people's skin in order to produce light petechiae. Practitioners believe that gua sha releases unhealthy bodily matter from blood stasis within sore, tired, stiff or injured muscle areas to stimulate new oxygenated blood flow to the areas, thus promoting metabolic cell repair, regeneration, healing and recovery.

Chlorhexidine, is a disinfectant and antiseptic that is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to sterilize surgical instruments. It may be used both to disinfect the skin of the patient and the hands of the healthcare providers. It is also used for cleaning wounds, preventing dental plaque, treating yeast infections of the mouth, and to keep urinary catheters from blocking. It is used as a liquid or powder.

A boil, also called a furuncle, is a deep folliculitis, infection of the hair follicle. It is most commonly caused by infection by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, resulting in a painful swollen area on the skin caused by an accumulation of pus and dead tissue. Boils which are expanded are basically pus-filled nodules. Individual boils clustered together are called carbuncles. Most human infections are caused by coagulase-positive S. aureus strains, notable for the bacteria's ability to produce coagulase, an enzyme that can clot blood. Almost any organ system can be infected by S. aureus.
An unguent is a soothing preparation spread on wounds, burns, rashes, abrasions or other topical injuries. It is similar to an ointment, though typically an unguent is less viscous and more oily. It is usually delivered as a semi-solid paste spread on the skin and is often oily to suspend the medication or other active ingredients.

The Sindh Institute of Skin Diseases known as Skin Hospital or Chamra Hospital is a 50-bed dermatological hospital. It is the only public sector skin hospital in Karachi and is located in the Regal Chowk area.

Sulfadimethoxine is a long-lasting sulfonamide antimicrobial medication used in veterinary medicine. It is used to treat many infections, including respiratory, urinary tract, enteric, and soft tissue infections and can be given as a standalone or combined with ormetoprim to broaden the target range. Like all sulfamides, sulfadimethoxine inhibits bacterial synthesis of folic acid by acting as a competitive inhibitor against PABA. It is the most common drug prescribed to dogs who have coccidiosis.

A staphylococcal infection or staph infection is an infection caused by members of the Staphylococcus genus of bacteria.

Brilliant green is one of the triarylmethane dyes. It is closely related to malachite green.
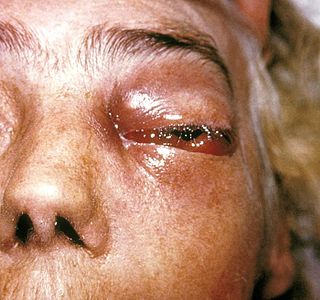
Mucormycosis, previously known as zygomycosis is a serious fungal infection, generally in people with less ability to fight infection. Symptoms depend on the part of the body infected. It most commonly infects the sinuses and brain resulting in a runny nose, one sided facial swelling and pain, headache, fever, and tissue death. Other forms of disease may infect the lungs, stomach and intestines, and skin.

Michael Jackson was an American entertainer who spent over four decades in the public eye, first as a child star with the Jackson 5 and later as a solo artist. From the mid-1980s, Jackson's appearance began to change. The changes to his face, particularly his nose, triggered widespread speculation of extensive cosmetic surgery, and his skin tone became much lighter. He was diagnosed with the skin disorder vitiligo, which results in white patches on the skin and sensitivity to sunlight. To treat the condition, he used fair-colored makeup and likely skin whitening prescription creams to cover up the uneven blotches of color caused by the illness. The creams would have further lightened his skin. The lighter skin resulted in criticism that he was trying to appear white. Jackson said he had not purposely bleached his skin and that he was not trying to be anything he was not.
Green nails may be (1) due to a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection causing a green nail syndrome or (2) the result of copper in tap water.

Nevus sebaceus or sebaceous nevus is a congenital, hairless plaque that typically occurs on the face or scalp. Such nevi are classified as epidermal nevi and can be present at birth, or early childhood, and affect males and females of all races equally. The condition is named for an overgrowth of sebaceous glands in the area of the nevus.
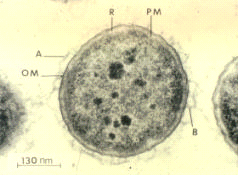
Aeromonas salmonicida is a pathogenic bacterium that severely impacts salmonid populations and other species. It was first discovered in a Bavarian brown trout hatchery by Emmerich and Weibel in 1894. Aeromonas salmonicida's ability to infect a variety of hosts, multiply, and adapt, make it a prime virulent bacterium. A. salmonicida is an etiological agent for furunculosis, a disease that causes sepsis, haemorrhages, muscle lesions, inflammation of the lower intestine, spleen enlargement, and death in freshwater fish populations. It is found worldwide with the exception of South America. The major route of contamination is poor water quality; however, it can also be associated stress factors such as overcrowding, high temperatures, and trauma. Spawning and smolting fish are prime victims of furunculosis due to their immunocompromised state of being.

Like humans and other animals, fish suffer from diseases and parasites. Fish defences against disease are specific and non-specific. Non-specific defences include skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the epidermis that traps microorganisms and inhibits their growth. If pathogens breach these defences, fish can develop inflammatory responses that increase the flow of blood to infected areas and deliver white blood cells that attempt to destroy the pathogens.
Nasal vestibulitis is the diffuse dermatitis of nasal vestibule. It is often caused by Staphylococcus aureus. It may be secondary to chronic rhinorrhea, nose picking or viral infections. In acute vestibulitis, the skin is red, swollen and tender. In chronic vestibulitis, induration of vestibular skin and crusting is seen. Antibiotic steroid ointment is sometimes helpful. Chronic fissures can be cauterized with Silver Nitrate.
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.