
The Duchy of Schleswig was a duchy in Southern Jutland (Sønderjylland) covering the area between about 60 km north and 70 km south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been divided between the two countries since 1920, with Northern Schleswig in Denmark and Southern Schleswig in Germany. The region is also called Sleswick in English.

Frisia is a coastal region along the southeastern corner of the North Sea in what today is mostly a large part of the Netherlands, including modern Friesland and smaller parts of northern Germany. Frisia is the traditional homeland of the Frisians, a Germanic people that speaks Frisian languages, which together with English and Scots form the Anglo-Frisian language group.

Skåne County, sometimes referred to as Scania County in English, is the southernmost county or län, of Sweden, basically corresponding to the traditional province Skåne. It borders the counties of Halland, Kronoberg and Blekinge and connected to Capital Region, Denmark by the Oresund Bridge. The seat of residence for the Skåne Governor is the city of Malmö. The headquarters of Skåne Regional Council is the town of Kristianstad.

Halland (help·info) is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden, on the western coast of Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Småland, Scania and the sea of Kattegat. Until 1645 and the Second Treaty of Brömsebro, it was part of the Kingdom of Denmark.

The provinces of Sweden are historical, geographical and cultural regions. Sweden has 25 provinces and they have no administrative function, but remain historical legacies and the means of cultural identification. Dialects and folklore rather follows the provincial borders than the borders of the counties.

South Jutland County is a former county on the south-central portion of the Jutland Peninsula in southern Denmark.

Tønder is a municipality in Region of Southern Denmark on the Jutland peninsula in south Denmark. The municipality covers an area of 1,278 km2, and has a total population of 37,777 (2018). Its mayor is Laurids Rudebeck, a member of the Venstre political party.

Christian III reigned as King of Denmark from 1534 until his death, and King of Norway from 1537 until his death. During his reign, Christian established Lutheranism as the state religion within his realms as part of the Protestant Reformation.
Amt is a type of administrative division governing a group of municipalities, today only in Germany, but formerly also common in other countries of Northern Europe. Its size and functions differ by country and the term is roughly equivalent to a US township or county or English shire district.

Skåneland or Skånelandene (Danish) is a region on the southern Scandinavian peninsula. It includes the Swedish provinces of Blekinge, Halland and Scania. The Danish island of Bornholm is sometimes also included. Skåneland has no official recognition or function and the term is not in common usage. Equivalent terms in English and Latin are "the Scanian provinces" and "Terrae Scaniae" respectively. The term is mostly used in historical contexts and not in daily speech. In Danish, Skånelandene is used more often. The terms have no political implications as the region is not a geopolitical entity but a cultural region, without officially established political borders.

Götaland is one of three lands of Sweden and comprises ten provinces. Geographically it is located in the south of Sweden, bounded to the north by Svealand, with the deep woods of Tiveden, Tylöskog and Kolmården marking the border.
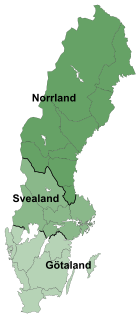
The lands of Sweden are three traditional parts, each consisting of several provinces, in Sweden. The division into lands goes back to the foundation of modern Sweden, when Götaland, the land of the Geats, merged with Svealand, the land of the Swedes, to form the country. While Norrland and Österland were added later. The lands have no administrative function but are still seen by many Swedes as an important part of their identity.
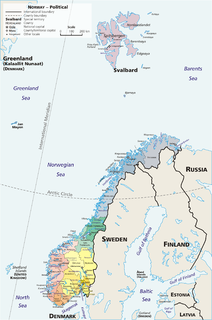
Norway is divided into 18 administrative regions, called counties ; until 1918, they were known as amter. The counties form the first-level subdivisions of Norway and are further divided into 422 municipalities. The island territories of Svalbard and Jan Mayen are outside the county division and ruled directly at the national level. The capital Oslo is considered both a county and a municipality.

The Region of Southern Denmark is an administrative region of Denmark established on Monday 1 January 2007 as part of the 2007 Danish Municipal Reform, which abolished the traditional counties ("amter") and set up five larger regions. At the same time, smaller municipalities were merged into larger units, cutting the number of municipalities from 271 before 1 January 2006 to 98. The Region of Southern Denmark has 22 municipalities. The reform was implemented in Denmark on 1 January 2007, although the merger of the Funish municipalities of Ærøskøbing and Marstal, being a part of the reform, was given the go-ahead to be implemented on Sunday 1 January 2006, one year before the main reform. It borders Schleswig-Holstein (Germany) to the south and Central Denmark Region to the north and is connected to Region Zealand via the Great Belt Fixed Link.
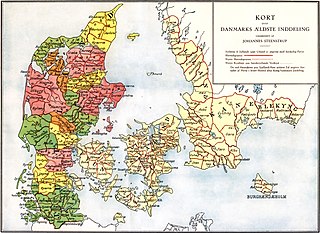
The traditional districts of Denmark differ from the country's administrative country subdivisions, as their existence and extent are usually not defined by law. Danes will often refer to their traditional districts if asked where they come from, rather than the administrative unit which have been changed several times.

Tønder County is a former province in Denmark, located the south-western part of Southern Jutland. Tønder County was established in 1920 following the reunification of Denmark with South Jutland following the Schleswig Plebiscites. It was dissolved in 1970 when the bulk of the county merged with three other counties to form South Jutland County. Tønder County corresponded geographically to the northern part of the former Prussian Kreis Tondern except for Hviding Herred, which had been part of Kreis Hadersleben. Kreis Tondern had in turn been established in 1867 in order to simplify the intricate administrative structures of the Duchy of Schleswig, and was formed from regions belonging to Ribe County and Løgumkloster County.
Syssel is a historical type of country subdivision in Scandinavia.

Blekinge is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden, situated in the south of the country. It borders Småland, Scania and the Baltic Sea. It is the country's second-smallest province by area, and the smallest province located on the mainland.

Uthlande, Utlande is a term for the islands, halligen and marshes off the mainland of North Frisia in the Southwest Jutland, modern Nordfriesland district, Germany.


















