Hydroxynorephedrine may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Hydroxynorephedrine may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
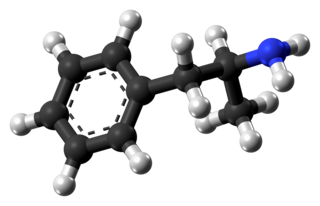
Amphetamine is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. Amphetamine was discovered in 1887 and exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers, levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine, in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with recreational use.

Dextroamphetamine is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and amphetamine enantiomer that is prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. Dextroamphetamine was also used by military air, tank and special forces as a 'go-pill' during fatigue-inducing missions such as night-time bombing missions or extended combat operations.

Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) is a sympathomimetic agent which is used as a decongestant and appetite suppressant. It is commonly used in prescription and over-the-counter cough and cold preparations. In veterinary medicine, it is used to control urinary incontinence in dogs.

Adderall, Adderall XR, and Mydayis, combination drugs containing four salts of the two enantiomers of amphetamine, are central nervous system (CNS) stimulants of the phenethylamine class. Adderall is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. By salt content, the active ingredients are 25% levoamphetamine salts and 75% dextroamphetamine salts.

Phenylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2COCH3. It is a colorless oil that is soluble in organic solvents. This substance is used in the manufacture of methamphetamine and amphetamine, where it is commonly known as P2P. Due to the illicit uses in clandestine chemistry, it was declared a schedule II controlled substance in the United States in 1980. In humans, phenylacetone occurs as a metabolite of amphetamine and methamphetamine via FMO3-mediated oxidative deamination.
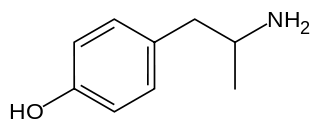
4-Hydroxyamphetamine (4HA), also known as hydroxyamfetamine, hydroxyamphetamine, oxamphetamine, norpholedrine, para-hydroxyamphetamine, and α-methyltyramine, is a drug that stimulates the sympathetic nervous system.

Metaraminol, also known as metaradrine, a stereoisomer of meta-hydroxynorephedrine (3,β-dihydroxyamphetamine), is a potent sympathomimetic amine used in the prevention and treatment of hypotension, particularly as a complication of anesthesia. It is an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist with some β effect.

Lisdexamfetamine, sold under the brand name Vyvanse among others, is a medication used for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults and children six and older, as well as for moderate to severe binge eating disorder in adults. The safety and the efficacy of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in children with ADHD three to five years old have not been established.

Methamphetamine is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is mainly used as a recreational drug and less commonly as a second-line treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and obesity. Methamphetamine was discovered in 1893 and exists as two enantiomers: levo-methamphetamine and dextro-methamphetamine. Methamphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is an equal mixture of levomethamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine in their pure amine forms. It is rarely prescribed over concerns involving human neurotoxicity and potential for recreational use as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant, among other concerns, as well as the availability of safer substitute drugs with comparable treatment efficacy. Dextromethamphetamine is a much stronger CNS stimulant than levomethamphetamine.

Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH), also known as dopamine beta-monooxygenase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DBH gene. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase catalyzes the chemical reaction:
The molecular formula C9H13NO2 (molar mass: 167.20 g/mol, exact mass: 167.094629) may refer to:

meta-Hydroxynorephedrine or 3-hydroxynorephedrine, also known as 3,β-dihydroxyamphetamine, is an adrenergic drug of the amphetamine class which was patented as a vasopressor and nasal decongestant but was never marketed. It is the racemic form of the sympathomimetic drug metaraminol.
Dihydroxyamphetamine may refer to:

p-Hydroxynorephedrine, or 4-hydroxynorephedrine, is the para-hydroxy analog of norephedrine and an active sympathomimetic metabolite of amphetamine in humans. When it occurs as a metabolite of amphetamine, it is produced from both p-hydroxyamphetamine and norephedrine.
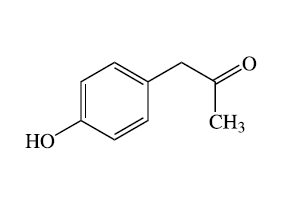
4-Hydroxyphenylacetone is the para-hydroxy analog of phenylacetone, an inactive metabolite of amphetamine in humans. When it occurs as a metabolite of amphetamine, it is produced directly from the inactive metabolite phenylacetone.