
Spray drying is a method of producing a dry powder from a liquid or slurry by rapidly drying with a hot gas. This is the preferred method of drying of many thermally-sensitive materials such as foods and pharmaceuticals. A consistent particle size distribution is a reason for spray drying some industrial products such as catalysts. Air is the heated drying medium; however, if the liquid is a flammable solvent such as ethanol or the product is oxygen-sensitive then nitrogen is used.
Flow measurement is the quantification of bulk fluid movement. Flow can be measured in a variety of ways. The common types of flowmeters that find industrial application can be listed as below:

Settling is the process by which particulates settle to the bottom of a liquid and form a sediment. Particles that experience a force, either due to gravity or due to centrifugal motion will tend to move in a uniform manner in the direction exerted by that force. For gravity settling, this means that the particles will tend to fall to the bottom of the vessel, forming a slurry at the vessel base.
In chemistry, a suspension is a heterogeneous mixture that contains solid particles sufficiently large for sedimentation. The particles may be visible to the naked eye, usually must be larger than one micrometer, and will eventually settle, although the mixture is only classified as a suspension when and while the particles have not settled out. A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which the solute particles do not dissolve, but get suspended throughout the bulk of the solvent, left floating around freely in the medium. The internal phase (solid) is dispersed throughout the external phase (fluid) through mechanical agitation, with the use of certain excipients or suspending agents. An example of a suspension would be sand in water. The suspended particles are visible under a microscope and will settle over time if left undisturbed. This distinguishes a suspension from a colloid, in which the suspended particles are smaller and do not settle. Colloids and suspensions are different from solution, in which the dissolved substance (solute) does not exist as a solid, and solvent and solute are homogeneously mixed.

A hydrocyclone is a device to classify, separate or sort particles in a liquid suspension based on the ratio of their centripetal force to fluid resistance. This ratio is high for dense and coarse particles, and low for light and fine particles. Hydrocyclones also find application in the separation of liquids of different densities.
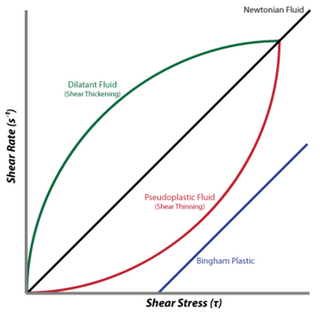
A dilatant (/daɪleɪtənt/) material is one in which viscosity increases with the rate of shear strain. Such a shear thickening fluid, also known by the initialism STF, is an example of a non-Newtonian fluid. This behaviour is usually not observed in pure materials, but can occur in suspensions.

A volumetric flask is a piece of laboratory apparatus, a type of laboratory flask, calibrated to contain a precise volume at a certain temperature. Volumetric flasks are used for precise dilutions and preparation of standard solutions. These flasks are usually pear-shaped, with a flat bottom, and made of glass or plastic. The flask's mouth is either furnished with a plastic snap/screw cap or fitted with a joint to accommodate a PTFE or glass stopper. The neck of volumetric flasks is elongated and narrow with an etched ring graduation marking. The marking indicates the volume of liquid contained when filled up to that point. The marking is typically calibrated "to contain" at 20 °C and indicated correspondingly on a label. The flask's label also indicates the nominal volume, tolerance, precision class, relevant manufacturing standard and the manufacturer’s logo. Volumetric flasks are of various sizes, containing from 1 milliliter to 20 liters of liquid.
Brake fluid is a type of hydraulic fluid used in hydraulic brake and hydraulic clutch applications in automobiles, motorcycles, light trucks, and some bicycles. It is used to transfer force into pressure, and to amplify braking force. It works because liquids are not appreciably compressible.
Electrorheological (ER) fluids are suspensions of extremely fine non-conducting but electrically active particles in an electrically insulating fluid. The apparent viscosity of these fluids changes reversibly by an order of up to 100,000 in response to an electric field. For example, a typical ER fluid can go from the consistency of a liquid to that of a gel, and back, with response times on the order of milliseconds. The effect is sometimes called the Winslow effect after its discoverer, the American inventor Willis Winslow, who obtained a US patent on the effect in 1947 and wrote an article published in 1949.

A Coulter counter
is an apparatus for counting and sizing particles suspended in electrolytes. It is used for cells, bacteria, prokaryotic cells and virus particles.
A colloid mill is a machine that is used to reduce the particle size of a solid in suspension in a liquid, or to reduce the droplet size in emulsions. Colloid mills work on the rotor-stator principle: a rotor turns at high speeds. The resulting high levels of hydraulic shear applied to the process liquid disrupt structures in the fluid. Colloid mills are frequently used to increase the stability of suspensions and emulsions, but can also be used to reduce the particle size of solids in suspensions. Higher shear rates lead to smaller droplets, down to approximately 1 µm which are more resistant to emulsion separation.
A dispersion is a system in which distributed particles of one material are dispersed in a continuous phase of another material. The two phases may be in the same or different states of matter.
A high-shear mixer disperses, or transports, one phase or ingredient into a main continuous phase (liquid), with which it would normally be immiscible. A rotor or impeller, together with a stationary component known as a stator, or an array of rotors and stators, is used either in a tank containing the solution to be mixed, or in a pipe through which the solution passes, to create shear. A high-shear mixer can be used to create emulsions, suspensions, lyosols, and granular products. It is used in the adhesives, chemical, cosmetic, food, pharmaceutical, and plastics industries for emulsification, homogenization, particle size reduction, and dispersion.
The term separator in oilfield terminology designates a pressure vessel used for separating well fluids produced from oil and gas wells into gaseous and liquid components. A separator for petroleum production is a large vessel designed to separate production fluids into their constituent components of oil, gas and water. A separating vessel may be referred to in the following ways: Oil and gas separator, Separator, Stage separator, Trap, Knockout vessel, Flash chamber, Expansion separator or expansion vessel, Scrubber, Filter. These separating vessels are normally used on a producing lease or platform near the wellhead, manifold, or tank battery to separate fluids produced from oil and gas wells into oil and gas or liquid and gas. An oil and gas separator generally includes the following essential components and features:

Field-flow fractionation, abbreviated FFF, is a separation technique where a field is applied to a fluid suspension or solution pumped through a long and narrow channel, perpendicular to the direction of flow, to cause separation of the particles present in the fluid, depending on their differing "mobilities" under the force exerted by the field. It was invented and first reported by J. Calvin Giddings. The method of FFF is unique to other separation techniques due to the fact that it can separate materials over a wide colloidal size range while maintaining high resolution. Although FFF is an extremely versatile technique, there is no "one size fits all" method for all applications.
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface. There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics and engineering.

Formazine (formazin) is a heterocyclic polymer produced by reaction of hexamethylenetetramine with hydrazine sulfate.
In rheology, the Farris Effect describes the decrease of the viscosity of a suspension upon increasing the dispersity of the solid additive, at constant volume fraction of the solid additive. That is, that a broader particle size distribution yields a lower viscosity than a narrow particle size distribution, for the same concentration of particles. The phenomenon is names after Richard J. Farris, who modeled the effect. The effect is relevant whenever suspensions are flowing, particularly for suspensions with high loading fractions. Examples include hydraulic fracturing fluids, metal injection molding feedstocks, cosmetics, and various geological processes including sedimentation and lava flows.









