Related Research Articles

The COVID-19 pandemic is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus reached the United Kingdom in late January 2020. As of 24 March 2021, there have been 4.3 million cases confirmed and 126,172 deaths overall among people who had recently tested positive – the world's eleventh-highest death rate by population and the highest death toll in Europe. There have been 150,837 deaths where the death certificate mentioned COVID, with around 90% giving it as the main cause. There has been some disparity between the outbreak's severity in each of the four countries. Health in the UK is devolved, with England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each having their own publicly-funded healthcare systems and governments.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Iraq is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. During the pandemic, Iraq reported its first confirmed cases of SARS-CoV-2 infections on 22 February in Najaf. By April, the number of confirmed cases had exceeded the hundred mark in Baghdad, Basra, Sulaymaniyah, Erbil and Najaf.
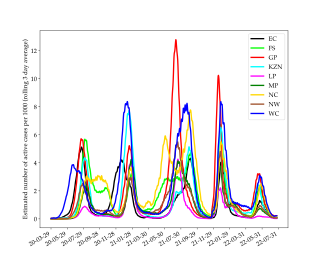
The COVID-19 pandemic in South Africa is part of the ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. On 5 March 2020, Minister of Health Zweli Mkhize confirmed the spread of the virus to South Africa, with the first known patient being a male citizen who tested positive upon his return from Italy. The first death to have occurred from the disease was reported on 27 March 2020.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Montenegro is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have spread to Montenegro when its first case was confirmed on 17 March 2020, making it the last European country to register a case of SARS-CoV-2.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Ghana is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The first two cases in Ghana were confirmed on 12 March 2020, when two infected people came to Ghana, one from Norway and the other from Turkey.

The COVID-19 pandemic has affected educational systems worldwide, leading to the near-total closures of schools, universities and colleges.
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed by diagnostic test to have reached the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda on Wednesday, the 18 of March 2020; and the individuals arrived from the UK and US. Those individuals had been traced to back to the fourth and sixth of March. This was the first it was confirmed and some believe that COVID-19 could have been on island undetected with asymptomatic individuals before that time.
The COVID-19 pandemic reached Northern Ireland on 27 February 2020. The Department of Health reports 2,129 deaths overall among people who had recently tested positive. The Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency reports 2,917 where the death certificate mentioned COVID as one possible cause. Northern Ireland has the lowest COVID death rate in the United Kingdom. The vast majority of deaths linked to COVID were among those over the age of 75 and almost half were in nursing care homes.
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached Somaliland in March 2020. As of 3 March 2021, there are 1581 cases and 56 deaths. 30060 tests have been conducted.
As of 2021, the COVID‑19 pandemic is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV‑2). Its impact has been broad, affecting general society, economy, culture, ecology, politics, and other areas. These aspects are discussed across many articles:

Coronavirus disease 2019 affects men and women differently both in terms of the outcome of infection and the effect of the disease upon society. The mortality due to COVID-19 is significantly higher in men. Slightly more men than women contract COVID with a ratio of 1:0.9.

The worldwide disruption caused by the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in numerous effects on the environment and climate. The global reduction in modern human activity such as the considerable decline in planned travel was coined anthropause and has caused a large drop in air pollution and water pollution in many regions. In China, lockdowns and other measures resulted in a 25 percent reduction in carbon emissions and 50 percent reduction in nitrogen oxides emissions, which one Earth systems scientist estimated may have saved at least 77,000 lives over two months. Other positive effects on the environment include governance-system-controlled investments towards a sustainable energy transition and other goals related to environmental protection such as the European Union's seven-year €1 trillion budget proposal and €750 billion recovery plan "Next Generation EU" which seeks to reserve 25% of EU spending for climate-friendly expenditure.

The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted crime and illicit economies such as organised crime, terrorism, street crime, online crime, illegal markets and smuggling, human and wildlife trafficking, slavery, robberies and burglaries.

The COVID-19 pandemic affects the global fashion industry as governments close down manufacturing plants, and through store closures, and event cancellations to slow the spread of the virus. The coronavirus pandemic has had a major impact on fashion brands worldwide. At the same time, the fashion industry faces challenges in consumer demand. New opportunities are also presenting themselves as fashion brands shift to making fashionable coronavirus face masks.

A systematic review notes that children with COVID-19 have milder effects and better prognoses than adults. However, children are susceptible to "multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children" (MIS-C), a rare but life-threatening systemic illness involving persistent fever and extreme inflammation following exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus.

The United Nations response to the COVID-19 pandemic has been led by its Secretary-General and can be divided into formal resolutions at the General Assembly and at the Security Council (UNSC), and operations via its specialized agencies and chiefly the World Health Organization in the initial stages, but involving more humanitarian-oriented agencies as the humanitarian impact became clearer, and then economic organizations, like the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, the International Labour Organization, and the World Bank, as the socioeconomic implications worsened. In June 2020, the Secretary-General launched the 'UN Comprehensive Response to COVID-19'; the UN has also launched a global vaccination initiative. Given the impact on the global economy, funding has been an especial problem, as it has for ongoing operations, and the 'UN Comprehensive Response to COVID-19' has a dedicated funding package attached. The UNSC has been criticized for a slow coordinated response, especially regarding the global ceasefire, which aims to open up humanitarian access to the world's most vulnerable in conflict zones.

This article documents the chronology of the response to the COVID-19 pandemic in September 2020, which originated in Wuhan, China in December 2019. Some developments may become known or fully understood only in retrospect. Reporting on this pandemic began in December 2019.

The COVID-19 pandemic has affected animals directly and indirectly. SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is zoonotic, which likely to have originated from animals such as bats and pangolins. Human impact on wildlife and animal habitats may be causing such spillover events to become much more likely.

The New Zealand Government responded to the COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand in various ways. In early February 2020, the Government barred entry to most travellers from China in response to the global COVID-19 pandemic originating in Wuhan. In addition, the Government sponsored several repatriation flights for returning citizens, residents, and their family members, beginning with Wuhan in February 2020. Following the country's first case originating from Iran, the Government imposed travel restrictions on travellers originating from Iran.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in Ghana during 2021.
References
- ↑ "Some L.A. County mortuaries and funeral homes simply have no more room for the dead". www.msn.com.
- ↑ "COVID-19 Changes Funerals and How Families Grieve". WebMD.
- ↑ "COVID-19 and Your Health". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. February 11, 2020.