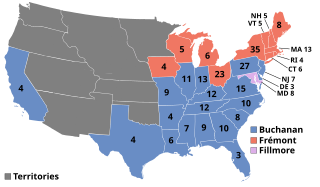
The United States presidential election of 1856 was the 18th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 1856. In a three-way election, Democrat James Buchanan defeated Republican nominee John C. Frémont and American Party nominee Millard Fillmore.

The 1860 United States presidential election was the nineteenth quadrennial presidential election to select the President and Vice President of the United States. The election was held on Tuesday, November 6, 1860. In a four-way contest, the Republican Party ticket of Abraham Lincoln and Hannibal Hamlin emerged triumphant. The election of Lincoln served as the primary catalyst of the American Civil War.

The United States presidential election of 1908 was the 31st quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1908. Secretary of War and Republican Party nominee William Howard Taft defeated three-time Democratic nominee William Jennings Bryan.

The United States presidential election of 1936 was the thirty-eighth quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1936. In the midst of the Great Depression, incumbent Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt defeated Republican Governor Alf Landon of Kansas. Roosevelt won the highest share of the popular and electoral vote since the largely uncontested 1820 election. The sweeping victory consolidated the New Deal Coalition in control of the Fifth Party System.

The Constitutional Union Party was a political party in the United States created in 1860 which ran against the Republicans and Democrats as a fourth party in 1860. It was made up of conservative former Whigs who wanted to avoid secession over the slavery issue. These former Whigs teamed up with former Know Nothings and a few Southern Democrats who were against secession to form the Constitutional Union Party. The party's name comes from its simple platform, which consists of the resolution "to recognize no political principle other than the Constitution of the country, the Union of the states, and the Enforcement of the Laws". The party hoped that by not taking a firm stand either for or against slavery or its expansion, the issue could be pushed aside.

In United States presidential elections, a faithless elector is a member of the United States Electoral College who does not vote for the presidential or vice presidential candidate for whom they had pledged to vote. That is, they break faith with the candidate they were pledged to and vote for another candidate, or fail to vote. A pledged elector is only considered a faithless elector by breaking their pledge; unpledged electors have no pledge to break.

A walkover, also W.O. or w/o is the awarding of a victory to a contestant because there are no other contestants or the other contestants have been disqualified or have forfeited. The term can apply in sport but also to elections, when it is also referred to as winning "by default". The word is used more generally by extension, particularly in politics, for a contest in which the winner is not the only participant but has little or no competition. The narrow and extended meanings of "walkover" as a single word are both found from 1829.
The United States Senate elections of 1856 and 1857 were elections which had the young Republican Party assume its position as one of the United States's two main political parties. The Whigs and Free Soilers were gone by the time the next Congress began.
The United States Senate elections of 1796 and 1797 were elections for the United States Senate which, coinciding with John Adams's election as President, had the ruling Federalist Party gain one seat.
The United States Senate elections of 1860 and 1861 were elections corresponding with Abraham Lincoln's election to the presidency. The nascent Republican Party increased their Senate seats in the general elections, and after southern Democrats withdrew to join the Confederacy, Republicans gained control of the United States Senate. To establish a quorum with fewer members, a lower total seat number was taken into account.
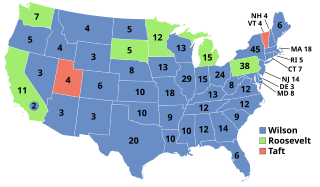
The 1912 United States elections elected the members of the 63rd United States Congress, occurring during the Fourth Party System. Amidst a division between incumbent Republican President William Howard Taft and former Republican President Theodore Roosevelt, the Democratic Party won the Presidency and both chambers of Congress, the first time they accomplished that feat since the 1892 election.

The 1852 United States elections elected the members of the 33rd United States Congress. The election marked the end of the Second Party System, as the Whig Party ceased to function as a national party following this election. Democrats won the presidency and retained control of both houses of Congress.
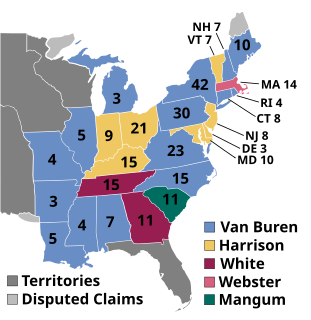
The 1836 United States elections elected the members of the 25th United States Congress. The election saw the emergence of the Whig Party, which succeeded the National Republican Party in the Second Party System as the primary opposition to the Democratic Party. The Whigs chose their name in symbolic defiance to the leader of the Democratic Party, "King" Andrew Jackson, and supported a national bank and the American System. Despite the emergence of the Whigs as a durable political party, Democrats retained the Presidency and a majority in both houses of Congress.
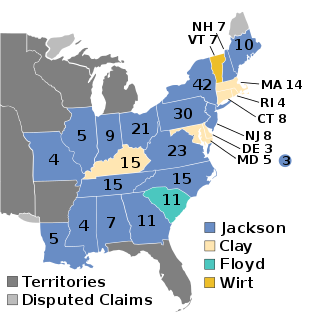
The 1832 United States elections elected the members of the 23rd United States Congress. Taking place during the Second Party System and a political conflict over the re-authorization of the Second Bank of the United States, the elections were contested between Andrew Jackson's Democratic Party and opponents of Jackson, including the National Republicans. Though the Democrats retained the presidency and the House, they lost their Senate majority. The Anti-Masonic Party also fielded the first notable presidential candidacy from a third party.

Following is a table of United States presidential elections in New Hampshire, ordered by year. Since its admission to statehood in 1788, New Hampshire has participated in every U.S. presidential election.















