In music theory, a scale is any set of musical notes ordered by fundamental frequency or pitch. A scale ordered by increasing pitch is an ascending scale, and a scale ordered by decreasing pitch is a descending scale. Some scales contain different pitches when ascending than when descending, for example, the melodic minor scale.
The chromatic scale is a musical scale with twelve pitches, each a semitone above or below its adjacent pitches. As a result, in 12-tone equal temperament, the chromatic scale covers all 12 of the available pitches. Thus, there is only one chromatic scale.
The term blues scale refers to several different scales with differing numbers of pitches and related characteristics.

In music, modulation is the change from one key to another. This may or may not be accompanied by a change in key signature. Modulations articulate or create the structure or form of many pieces, as well as add interest. Treatment of a chord as the tonic for less than a phrase is considered tonicization.
Modulation is the essential part of the art. Without it there is little music, for a piece derives its true beauty not from the large number of fixed modes which it embraces but rather from the subtle fabric of its modulation.
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Six is the ordinal form of the number six.
Chromaticism is a compositional technique interspersing the primary diatonic pitches and chords with other pitches of the chromatic scale. Chromaticism is in contrast or addition to tonality or diatonicism. Chromatic elements are considered "elaborations of or substitutions for diatonic scale members".
Chromaticism is almost by definition an alteration of, an interpolation in or deviation from this basic diatonic organization.
Shruti or śruti (//), is a Sanskrit word, found in the Vedic texts of Hinduism where it means lyrics and "what is heard" in general. It is also an important concept in Indian music, where it means the smallest interval of pitch that the human ear can detect and a singer or musical instrument can produce. The musical shruti concept is found in ancient and medieval Sanskrit texts such as the Natya Shastra, the Dattilam, the Brihaddeshi, and the Sangita Ratnakara. Chandogya Upanishad speaks of the division of the octave in 22 parts.

Colorfulness, chroma and saturation are attributes of perceived color relating to chromatic intensity. As defined formally by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) they respectively describe three different aspects of chromatic intensity, but the terms are often used loosely and interchangeably in contexts where these aspects are not clearly distinguished.
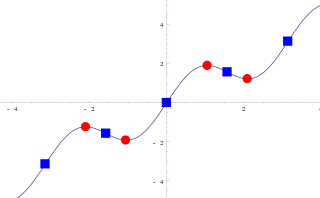
In mathematics, particularly in calculus, a stationary point of a differentiable function of one variable is a point on the graph of the function where the function's derivative is zero. Informally, it is a point where the function "stops" increasing or decreasing.

The chromatic circle is a geometrical space that shows relationships among the 12 equal-tempered pitch classes making up the familiar chromatic scale on a circle.
A heptatonic scale is a musical scale that has seven pitches per octave. Examples include the major scale or minor scale; e.g., in C major: C D E F G A B C—and in the relative minor, A minor, natural minor: A B C D E F G A; the melodic minor scale, A B C D E F♯G♯A ascending, A G F E D C B A descending; the harmonic minor scale, A B C D E F G♯A; and a scale variously known as the Byzantine, and Hungarian, scale, C D E♭ F♯ G A♭ B C. Indian classical theory postulates seventy-two seven-tone scale types, whereas others postulate twelve or ten seven-tone scale types collectively called thaat.
The chromatic harmonica is a type of harmonica that uses a button-activated sliding bar to redirect air from the hole in the mouthpiece to the selected reed-plate desired. When the button is not pressed, an altered diatonic major scale of the key of the harmonica is available, while depressing the button accesses the same scale a semitone higher in each hole. Thus, the instrument is capable of playing the 12 notes of the Western chromatic scale. The chromatic harmonica can thus be contrasted with a standard harmonica, which can play only the notes in a given musical key.
Dichromatic may refer to:
In music, fingering, or on stringed instruments stopping, is the choice of which fingers and hand positions to use when playing certain musical instruments. Fingering typically changes throughout a piece; the challenge of choosing good fingering for a piece is to make the hand movements as comfortable as possible without changing hand position too often. A fingering can be the result of the working process of the composer, who puts it into the manuscript, an editor, who adds it into the printed score, or the performer, who puts his or her own fingering in the score or in performance.
German declension is the paradigm that German uses to define all the ways articles, adjectives and sometimes nouns can change their form to reflect their role in the sentence: subject, object, etc. Declension allows speakers to mark a difference between subjects, direct objects, indirect objects and possessives by changing the form of the word—and/or its associated article—instead of indicating this meaning through word order or prepositions. As a result, German can take a much more fluid approach to word order without the meaning being obscured. In English, a simple sentence must be written in strict word order. This sentence cannot be expressed in any other word order than how it is written here without changing the meaning. A translation of the same sentence from German to English would appear rather different and can be expressed with a variety of word order with little or no change in meaning.
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case ending, which indicate the grammatical cased of nouns or adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs.

Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the common practice music of the period 1600–1900.
Lithuanian declension is similar to declensions in ancient Indo-European languages such as Sanskrit, Latin or Ancient Greek. It is one of the most complicated declension systems among modern Indo-European and modern European languages.






