Related Research Articles
Calculus is the mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
C is a general-purpose, imperative computer programming language, supporting structured programming, lexical variable scope and recursion, while a static type system prevents many unintended operations. By design, C provides constructs that map efficiently to typical machine instructions, and therefore it has found lasting use in applications that had formerly been coded in assembly language, including operating systems, as well as various application software for computers ranging from supercomputers to embedded systems.
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function for which sufficiently small changes in the input result in arbitrarily small changes in the output. Otherwise, a function is said to be a discontinuous function. A continuous function with a continuous inverse function is called a homeomorphism.

The derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value with respect to a change in its argument. Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. For example, the derivative of the position of a moving object with respect to time is the object's velocity: this measures how quickly the position of the object changes when time advances.
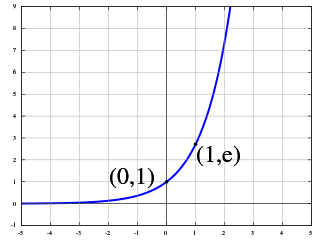
In mathematics, an exponential function is a function of the form

JavaScript, often abbreviated as JS, is a high-level, interpreted programming language that conforms to the ECMAScript specification. It is a language that is also characterized as dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based and multi-paradigm.
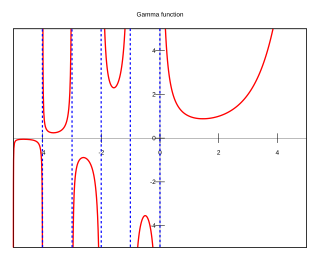
In mathematics, the gamma function is one of a number of extensions of the factorial function with its argument shifted down by 1, to real and complex numbers. Derived by Daniel Bernoulli, if n is a positive integer,
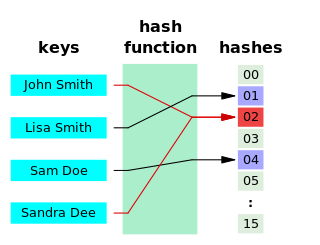
A hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size onto data of a fixed size. The values returned by a hash function are called hash values, hash codes, digests, or simply hashes. Hash functions are often used in combination with a hash table, a common data structure used in computer software for rapid data lookup. Hash functions accelerate table or database lookup by detecting duplicated records in a large file. One such application is finding similar stretches in DNA sequences. They are also useful in cryptography. A cryptographic hash function allows one to easily verify whether some input data map onto a given hash value, but if the input data is unknown it is deliberately difficult to reconstruct it by knowing the stored hash value. This is used for assuring integrity of transmitted data, and is the building block for HMACs, which provide message authentication.
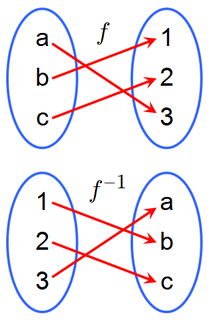
In mathematics, an inverse function is a function that "reverses" another function: if the function f applied to an input x gives a result of y, then applying its inverse function g to y gives the result x, and vice versa, i.e., f(x) = y if and only if g(y) = x.

In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that can describe displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. Integration is one of the two main operations of calculus, with its inverse operation, differentiation, being the other. Given a function f of a real variable x and an interval [a, b] of the real line, the definite integral
PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor is a general-purpose programming language originally designed for web development. It was originally created by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994; the PHP reference implementation is now produced by The PHP Group. PHP originally stood for Personal Home Page, but it now stands for the recursive initialism PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor.

In mathematics, the trigonometric functions are functions of an angle. They relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of its sides. Trigonometric functions are important in the study of triangles and modeling periodic phenomena, among many other applications.

In mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point.
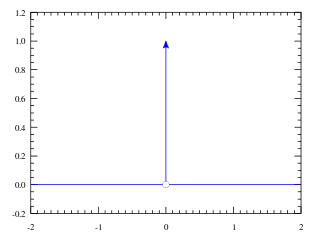
In mathematics, the Dirac delta function is a generalized function or distribution introduced by the physicist Paul Dirac. It is used to model the density of an idealized point mass or point charge as a function equal to zero everywhere except for zero and whose integral over the entire real line is equal to one. As there is no function that has these properties, the computations made by the theoretical physicists appeared to mathematicians as nonsense until the introduction of distributions by Laurent Schwartz to formalize and validate the computations. As a distribution, the Dirac delta function is a linear functional that maps every function to its value at zero. The Kronecker delta function, which is usually defined on a discrete domain and takes values 0 and 1, is a discrete analog of the Dirac delta function.
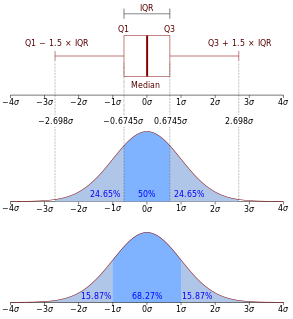
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample in the sample space can be interpreted as providing a relative likelihood that the value of the random variable would equal that sample. In other words, while the absolute likelihood for a continuous random variable to take on any particular value is 0, the value of the PDF at two different samples can be used to infer, in any particular draw of the random variable, how much more likely it is that the random variable would equal one sample compared to the other sample.

The Fourier transform (FT) decomposes a function of time into the frequencies that make it up, in a way similar to how a musical chord can be expressed as the frequencies of its constituent notes. The Fourier transform of a function of time is itself a complex-valued function of frequency, whose absolute value represents the amount of that frequency present in the original function, and whose complex argument is the phase offset of the basic sinusoid in that frequency. The Fourier transform is called the frequency domain representation of the original signal. The term Fourier transform refers to both the frequency domain representation and the mathematical operation that associates the frequency domain representation to a function of time. The Fourier transform is not limited to functions of time, but in order to have a unified language, the domain of the original function is commonly referred to as the time domain. For many functions of practical interest, one can define an operation that reverses this: the inverse Fourier transformation, also called Fourier synthesis, of a frequency domain representation combines the contributions of all the different frequencies to recover the original function of time. In image processing the notion of a time domain is replaced by that of a spatial domain where the intensity of a signal is identified by its spatial position rather than at any point in time.

C++ is a general-purpose programming language. It has imperative, object-oriented and generic programming features, while also providing facilities for low-level memory manipulation.

The Myers–Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is an introspective self-report questionnaire with the purpose of indicating differing psychological preferences in how people perceive the world around them and make decisions.

In mathematics, a function was originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a function of time. Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable. The concept of function was formalized at the end of the 19th century in terms of set theory, and this greatly enlarged the domains of application of the concept.

A cryptographic hash function is a special class of hash function that has certain properties which make it suitable for use in cryptography. It is a mathematical algorithm that maps data of arbitrary size to a bit string of a fixed size and is designed to be a one-way function, that is, a function which is infeasible to invert. The only way to recreate the input data from an ideal cryptographic hash function's output is to attempt a brute-force search of possible inputs to see if they produce a match, or use a rainbow table of matched hashes. Bruce Schneier has called one-way hash functions "the workhorses of modern cryptography". The input data is often called the message, and the output is often called the message digest or simply the digest.
References
This article needs additional or more specific categories .(December 2018) |
| This cognitive psychology-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |