
As money became a commodity, the money market became a component of the financial market for assets involved in short-term borrowing, lending, buying and selling with original maturities of one year or less. Trading in money markets is done over the counter and is wholesale.

Mastercard Incorporated is an American multinational financial services corporation headquartered in the Mastercard International Global Headquarters in Purchase, New York, United States. The Global Operations Headquarters is located in O'Fallon, Missouri, United States, a municipality of St. Charles County, Missouri. Throughout the world, its principal business is to process payments between the banks of merchants and the card issuing banks or credit unions of the purchasers who use the "Mastercard" brand debit, credit and prepaid to make purchases. Mastercard Worldwide has been a publicly traded company since 2006. Prior to its initial public offering, Mastercard Worldwide was a cooperative owned by the more than 25,000 financial institutions that issue its branded cards.
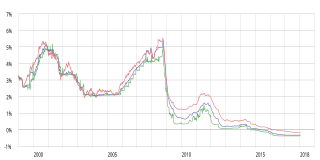
The Euro Interbank Offered Rate (Euribor) is a daily reference rate, published by the European Money Markets Institute, based on the averaged interest rates at which Eurozone banks offer to lend unsecured funds to other banks in the euro wholesale money market. Prior to 2015, the rate was published by the European Banking Federation.
Eonia is computed as a weighted average of all overnight unsecured lending transactions in the interbank market, undertaken in the European Union and European Free Trade Association (EFTA) countries by the Panel Banks. It is reported on an ACT/360 day count convention and is displayed to three decimal places. "Overnight" means from one TARGET day to the next. The panel of reporting banks is the same as for Euribor, and a list is provided by the overseers of the publication of the index. There is no clear definition of 'interbank market' leading to the potential of subjective assessment of what is an 'interbank loan', albeit all panel banks are subject to the Eonia Code of Conduct.

Cirrus is a worldwide ATM network. It is a subsidiary of Mastercard and based in Purchase, New York. Founded in 1982, it links Mastercard and Maestro credit, debit and prepaid cards and Cirrus ATM cards to a global network of millions of ATMs.

Plus System, Inc. is a Denver-based ATM network that provides cash to Visa cardholders. As a subsidiary of Visa Inc., Plus System connects all Visa credit, debit and prepaid cards, as well as ATM cards issued by various banks worldwide bearing the Visa logo.
A payment system is any system used to settle financial transactions through the transfer of monetary value, and includes the institutions, instruments, people, rules, procedures, standards, and technologies that make such an exchange possible. A common type of payment system is the operational network that links bank accounts and provides for monetary exchange using bank deposits.
An interbank network, also known as an ATM consortium or ATM network, is a computer network that enables ATM cards issued by a financial institution that is a member of the network to be used to perform ATM transactions through ATMs that belong to another member of the network.

The Malaysian Electronic Payment System (MEPS) is an interbank network service provider in Malaysia. In August 2017, MEPS has merged with Malaysian Electronic Clearing Corporation Sdn Bhd (MyClear) to form Payments Network Malaysia Sdn Bhd (PayNet).
Cashnet is an interbank network in India managed by Euronet Services India Pvt. Ltd. which is a subsidiary of Euronet Worldwide.
Financial services in South Korea refers to the services provided in ROK by the finance industry: banks, investment banks, insurance companies, credit card companies, consumer finance companies, government sponsored enterprises, and stock brokerages.
Financial services in China refers to the services provided in China by the finance industry: banks, investment banks, insurance companies, credit card companies, consumer finance companies, government sponsored enterprises, and stock brokerages.
Financial services in Japan refers to the services provided in Japan by the finance industry: banks, investment banks, insurance companies, credit card companies, consumer finance companies, government sponsored enterprises, and stock brokerages.

Eurocard was a credit card, introduced in 1964 by a Swedish banker in the Wallenberg family as an alternative to American Express. In 1968, it signed a deal with the Interbank Card Association so that their cards were accepted by each other's networks; this eventually led to a joint venture known as Maestro International in 1992, and merger in 2002.
Global Net is an interbank network in Peru operated by Peruvian bank "Interbank".
The interbank market is the top-level foreign exchange market where banks exchange different currencies. The banks can either deal with one another directly, or through electronic brokering platforms. The Electronic Broking Services (EBS) and Thomson Reuters Dealing are the two competitors in the electronic brokering platform business and together connect over 1000 banks. The currencies of most developed countries have floating exchange rates. These currencies do not have fixed values but, rather, values that fluctuate relative to other currencies.

The Central Bank of Kosovo is the central bank of Kosovo. It was founded in June 2008, the same year Kosovo declared its independence from Serbia, with the approval of Law No. 03/L-074 on the Central Bank of the Republic of Kosovo by the Kosovo Assembly. Before being established as the Central Bank of Kosovo, it operated as the Central Banking Authority of Kosovo. The official currency in Kosovo is the euro, which has been adopted unilaterally in 2002; however, Kosovo is not a member of the Eurozone. The headquarters of the CBK are located in the capital of Kosovo, Pristina.
The First National City Charge Service, marketed as The Everything Card, was an early credit card introduced by First National City Bank in the eastern United States in 1967. It was intended as a response to the BankAmericard, issued by BankAmerica. Issued under the initiative of National City Bank President Walter B. Wriston, the card followed the bank's purchase of an interest in the Carte Blanche charge card.
The interbank lending market is a market in which banks extend loans to one another for a specified term. Most interbank loans are for maturities of one week or less, the majority being overnight. Such loans are made at the interbank rate. A sharp decline in transaction volume in this market was a major contributing factor to the collapse of several financial institutions during the financial crisis of 2007.
LankaClear is the largest payments infrastructure provider in Sri Lanka. Established in February 2002, the organization is owned by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) and all CBSL-licensed commercial banks in the country. LankaClear is the operator of LankaPay, the country's largest interbank payment network.








