SDI may refer to:

Geographic Resources Analysis Support System is a geographic information system (GIS) software suite used for geospatial data management and analysis, image processing, producing graphics and maps, spatial and temporal modeling, and visualizing. It can handle raster, topological vector, image processing, and graphic data.
Enterprise information integration (EII) is the ability to support a unified view of data and information for an entire organization. In a data virtualization application of EII, a process of information integration, using data abstraction to provide a unified interface for viewing all the data within an organization, and a single set of structures and naming conventions to represent this data; the goal of EII is to get a large set of heterogeneous data sources to appear to a user or system as a single, homogeneous data source.
The High-level architecture (HLA) is a standard for distributed simulation, used when building a simulation for a larger purpose by combining (federating) several simulations. The standard was developed in the 90’s under the leadership of the US Department of Defense and was later transitioned to become an open international IEEE standard. It is a recommended standard within NATO through STANAG 4603. Today the HLA is used in a number of domains including defense and security and civilian applications. The architecture specifies the following components.
Enterprise application integration (EAI) is the use of software and computer systems' architectural principles to integrate a set of enterprise computer applications.
Open Platform Communications (OPC) is a series of standards and specifications for industrial telecommunication. An industrial automation task force developed the original standard in 1996 under the name OLE for Process Control. OPC specifies the communication of real-time plant data between control devices from different manufacturers.
Java EE Connector Architecture (JCA) is a Java-based technology solution for connecting application servers and enterprise information systems (EIS) as part of enterprise application integration (EAI) solutions. While JDBC is specifically used to connect Java EE applications to databases, JCA is a more generic architecture for connection to legacy systems. JCA was developed under the Java Community Process as JSR 16, JSR 112 and JSR 322.

The Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF) is an architecture framework for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) that provides visualization infrastructure for specific stakeholders concerns through viewpoints organized by various views. These views are artifacts for visualizing, understanding, and assimilating the broad scope and complexities of an architecture description through tabular, structural, behavioral, ontological, pictorial, temporal, graphical, probabilistic, or alternative conceptual means.
TNTlite is a free geospatial analysis system providing a complete fully featured Geographic information system, RDBMS, and automated image processing system with CAD, TIN, surface modeling, map layout and innovative data publishing tools. All this capability is available in a single integrated system with an identical interface, functionality, and geodata structure for use on Mac OS X and Windows platforms. The interface, database text content, messages, map production, and all other internal aspects of TNTmips have been localized for use in 27 languages including Japanese, Chinese, Arabic, Turkish, Thai, German, Spanish, French and others. The professional version of TNTmips is in use in over 120 nations while it is in use as TNTmips Free in almost every nation for educational, self learning, and small projects. The product includes 74 free tutorial and application booklets with step-by-step lessons.
A mashup, in web development, is a web page or web application that uses content from more than one source to create a single new service displayed in a single graphical interface. For example, a user could combine the addresses and photographs of their library branches with a Google map to create a map mashup. The term implies easy, fast integration, frequently using open application programming interfaces and data sources to produce enriched results that were not necessarily the original reason for producing the raw source data. The term mashup originally comes from British - West Indies slang meaning to be intoxicated, or as a description for something or someone not functioning as intended. In recent English parlance it can refer to music, where people seamlessly combine audio from one song with the vocal track from another—thereby mashing them together to create something new.
Geospatial metadata is a type of metadata that is applicable to objects that have an explicit or implicit geographic extent, i.e. are associated with some position on the surface of the globe. Such objects may be stored in a geographic information system (GIS) or may simply be documents, data-sets, images or other objects, services, or related items that exist in some other native environment but whose features may be appropriate to describe in a (geographic) metadata catalog.

Web mapping is the process of using the maps delivered by geographic information systems (GIS) in World Wide Web. A web map on the World Wide Web is both served and consumed, thus web mapping is more than just web cartography, it is a service by which consumers may choose what the map will show. Web GIS emphasizes geodata processing aspects more involved with design aspects such as data acquisition and server software architecture such as data storage and algorithms, than it does the end-user reports themselves.
CEN ISO/IEEE 11073 Health informatics - Medical / health device communication standards enable communication between medical, health care and wellness devices and with external computer systems. They provide automatic and detailed electronic data capture of client-related and vital signs information, and of device operational data.
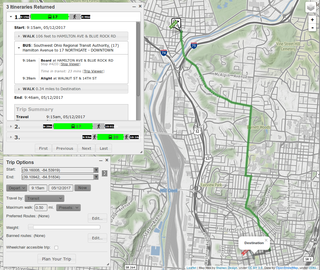
A journey planner, trip planner, or route planner is a specialised search engine used to find an optimal means of travelling between two or more given locations, sometimes using more than one transport mode. Searches may be optimised on different criteria, for example fastest, shortest, fewest changes, cheapest. They may be constrained for example to leave or arrive at a certain time, to avoid certain waypoints, etc. A single journey may use a sequence of several modes of transport, meaning that the system may know about public transport services as well as transport networks for private transportation. Trip planning or Journey planning is sometimes distinguished from route planning, where route planning is typically thought of as using private modes of transportation such as driving, walking, or cycling, normally using a single mode at a time. Trip or Journey planning by contrast would make use of at least one public transport mode which operates according to published schedules; given that public transport services only depart at specific times, an algorithm must therefore not only find a path to a destination, but seek to optimise it so as to minimise the waiting time incurred for each leg.
In business, master data management (MDM) is a method used to define and manage the critical data of an organization to provide, with data integration, a single point of reference. The data that is mastered may include reference data- the set of permissible values, and the analytical data that supports decision making.
The IEC 61970 series of standards deals with the application program interfaces for energy management systems (EMS). The series provides a set of guidelines and standards to facilitate:

The OMG standard seeks to promote the free flow of information between government agencies and citizens by establishing a common set of technical standards for organizing and sharing public data.
Manufacturing execution systems (MES) are computerized systems used in manufacturing, to track and document the transformation of raw materials to finished goods. MES provides information that helps manufacturing decision makers understand how current conditions on the plant floor can be optimized to improve production output. MES works in real time to enable the control of multiple elements of the production process.
An integration platform is software which integrates different applications and services. It differentiates itself from the enterprise application integration which has a focus on supply chain management. It uses the idea of system integration to create an environment for engineers.
Geographic data and information are defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as data and information having an implicit or explicit association with a location relative to the Earth.