Isaac Grier Strain was born March 4, 1821, in Roxbury, Franklin County, Pennsylvania, of Scots-Irish origin, and died May 14, 1857, in Aspinwall, (alternative name of Colón, Panama) Colombia. At age 17 he joined the U.S. Navy to apprentice at sea; he became a midshipman.

Roxbury is an unincorporated community located off the Blue Mountain exit of the Pennsylvania Turnpike in Lurgan Township, Franklin County, Pennsylvania. Route 641 and Route 997 meet there.

Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state located in the northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The Appalachian Mountains run through its middle. The Commonwealth is bordered by Delaware to the southeast, Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, Lake Erie and the Canadian province of Ontario to the northwest, New York to the north, and New Jersey to the east.

Colón is a city and sea port in Panama, beside the Caribbean Sea, lying near the Atlantic entrance to the Panama Canal. It is the capital of Panama's Colón Province and has traditionally been known as Panama's second city. Originally it was located entirely on Manzanillo Island, surrounded by Limon Bay, Manzanillo Bay and the Folks River; however, since the disestablishment of the Panama Canal Zone, the city's limits have been redefined to include Fort Gulick, a former U.S. Army base, as well the former Canal Zone towns of Cristobal, Margarita and Coco Solo.
Naturally inclined toward exploration, he commanded an 1843 (1845 by some sources) exploratory expedition to the interior of Brazil, Province of São Paulo. In 1848 he began an exploration of the peninsula of Lower California; he worked with the U.S. Mexican Boundary Commission. He was promoted to lieutenant in 1850. Lieutenant Strain was a Corresponding Member of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia; the Historical and Geographical Institute of Brazil; and the American Ethnological Society of New York. In 1849 he explored parts of South America and wrote Cordillera and Pampa, Mountain and Plain: Sketches of a Journey in Chili and The Argentine Provinces in 1849, published in New York in 1853.

Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At 8.5 million square kilometers and with over 208 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the fifth most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populated city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 states, the Federal District, and the 5,570 municipalities. It is the largest country to have Portuguese as an official language and the only one in the Americas; it is also one of the most multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass immigration from around the world.

California is a state in the Pacific Region of the United States. With 39.6 million residents, California is the most populous U.S. state and the third-largest by area. The state capital is Sacramento. The Greater Los Angeles Area and the San Francisco Bay Area are the nation's second and fifth most populous urban regions, with 18.7 million and 9.7 million residents respectively. Los Angeles is California's most populous city, and the country's second most populous, after New York City. California also has the nation's most populous county, Los Angeles County, and its largest county by area, San Bernardino County. The City and County of San Francisco is both the country's second-most densely populated major city after New York City and the fifth-most densely populated county, behind only four of the five New York City boroughs.
The American Ethnological Society (AES) is the oldest professional anthropological association in the United States.
Leading a United States at peace, and in exercise of Manifest Destiny to expand from the Atlantic seaboard to the Pacific Ocean, U. S. President Franklin Pierce envisioned an Atlantic to Pacific canal route through the Isthmus of Darién, a region also known as the Darién Gap, located in Colombia, presently Panama. Henceforth, Secretary of the Navy James C. Dobbin in late 1853 ordered Lieutenant Strain to form and lead the United States Navy 1854 Darién Exploring Expedition s:Darien Exploring Expedition (1854). Setting forth from the Atlantic side of the Isthmus of Darién, his expedition into the Isthmus of Darién began January 20, 1854.

Franklin Pierce was the 14th president of the United States (1853–1857), a northern Democrat who saw the abolitionist movement as a fundamental threat to the unity of the nation. He alienated anti-slavery groups by championing and signing the Kansas–Nebraska Act and enforcing the Fugitive Slave Act, yet he failed to stem conflict between North and South, setting the stage for Southern secession and the American Civil War.

The Darién Gap is a break in the Pan-American Highway consisting of a large swath of undeveloped swampland and forest within Panama's Darién Province in Central America and the northern portion of Colombia's Chocó Department in South America. The gap begins in Yaviza, Panama and ends in Turbo, Colombia, and is 106 km long. Roadbuilding through this area is expensive and the environmental cost is high. Political consensus in favor of road construction has not emerged.

Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a sovereign state largely situated in the northwest of South America, with territories in Central America. Colombia shares a border to the northwest with Panama, to the east with Venezuela and Brazil and to the south with Ecuador and Peru. It shares its maritime limits with Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Jamaica, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic. Colombia is a unitary, constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments, with the capital in Bogota.
It was in the densely jungled Darién that France and England had sent explorers of their own. The Englishman Gisborne had put pen to perhaps fallacious or inaccurate, but certainly misleading, journals that would lend ambiguity and deaths to Strain's route for traversing the Gap.

France, officially the French Republic, is a country whose territory consists of metropolitan France in Western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The metropolitan area of France extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. It is bordered by Belgium, Luxembourg and Germany to the northeast, Switzerland and Italy to the east, and Andorra and Spain to the south. The overseas territories include French Guiana in South America and several islands in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans. The country's 18 integral regions span a combined area of 643,801 square kilometres (248,573 sq mi) and a total population of 67.3 million. France, a sovereign state, is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. Other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice.

England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to the west and Scotland to the north-northwest. The Irish Sea lies west of England and the Celtic Sea lies to the southwest. England is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight.
The Strain party, in part proceeding upon Gisborne's records, wandered circuitously, split, and became plagued by deteriorating equipment, unreliable and often dangerous native guides, malnourishment, foot-soreness, flesh-embedding parasites, and infectious tropical diseases. Six of Strain's party of 27 died by starvation. The courageous but ill-fated expedition nevertheless contributed to future establishments of land routes, a railroad, and the eventual linking of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans by a Panama Canal. The canal was completed in 1914, 60 years after Strain's expedition.

The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south and is bounded by Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east.
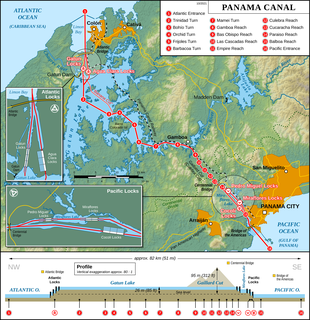
The Panama Canal is an artificial 82 km (51 mi) waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit for maritime trade. Canal locks are at each end to lift ships up to Gatun Lake, an artificial lake created to reduce the amount of excavation work required for the canal, 26 m above sea level, and then lower the ships at the other end. The original locks are 34 m wide. A third, wider lane of locks was constructed between September 2007 and May 2016. The expanded canal began commercial operation on June 26, 2016. The new locks allow transit of larger, post-Panamax ships, capable of handling more cargo.












