A total lunar eclipse took place on 3 March 2007, the first of two eclipses in 2007. The moon entered the penumbral shadow at 20:18 UTC, and the umbral shadow at 21:30 UTC. The total phase lasted between 22:44 UTC and 23:58 UTC with a distinctive brick-red shade. The moon left the umbra shadow at 01:11 UTC and left the penumbra shadow at 02:24 UTC 2007-03-04. The second lunar eclipse of 2007 occurred on 28 August.

A total lunar eclipse occurred on 28 August 2007, lasting just over 90 minutes. The Moon entered the Earth's penumbra at 7:53:40 UTC. The first partial phase began in earnest at 8:51:16 UTC when the Moon entered the Earth's umbra. It exited the penumbra at 13:20:57 UTC.

A total lunar eclipse occurred on February 20 and February 21, 2008. It was visible in the eastern evening sky on February 20 for all of North and South America, and on February 21 in the predawn western sky from most of Africa and Europe. Greatest Eclipse occurring on Thursday, February 21, 2008, at 03:26:03 UTC, totality lasting 49 minutes and 45.6 seconds.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on 16 August 2008, the second of two lunar eclipses in 2008, with the first being a total eclipse on 20 February 2008. The next lunar eclipse was a penumbral eclipse occurring on 9 February 2009, while the next total lunar eclipse occurred on 21 December 2010.

A total lunar eclipse occurred from 5:27 to 11:06 UTC on 21 December 2010, coinciding with the date of the Winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere and Summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere. It was visible in its entirety as a total lunar eclipse in North and South America, Iceland, Ireland, Britain and northern Scandinavia.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, May 16, 2003, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2003, the other being on November 9, 2003. A shallow total eclipse saw the Moon in relative darkness for 52 minutes and 3.1 seconds. The Moon was 12.938% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, and should have been significantly darkened. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 15 minutes and 3.1 seconds in total. Occurring only 0.5 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was 6.2% larger than average. At greatest eclipse the Moon was only 357,693 km from the Earth, making it a Super Full Moon.

A total lunar eclipse took place on 15 April 2014. It was the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2014, and the first in a tetrad. Subsequent eclipses in the tetrad are those of 8 October 2014, 4 April 2015, and 28 September 2015. Occurring 6.7 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday 8 October 2014. It is the second of two total lunar eclipses in 2014, and the second in a tetrad. Other eclipses in the tetrad are those of 15 April 2014, 4 April 2015, and 28 September 2015. Occurring only 2.1 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger, 1960.6 arcseconds.

A total lunar eclipse took place on 4 April 2015. It is the former of two total lunar eclipses in 2015, and the third in a tetrad. Other eclipses in the tetrad are those of 15 April 2014, 8 October 2014, and 28 September 2015.

A total lunar eclipse took place between 27 and 28 September 2015. It was seen on Sunday evening, 27 September, in the Americas; while in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, it was seen in the early hours of Monday morning, 28 September. It was the latter of two total lunar eclipses in 2015, and the final in a tetrad. Other eclipses in the tetrad are those of 15 April 2014, 8 October 2014, and 4 April 2015.

A total lunar eclipse occurred on Tuesday, 8 November 2022. The southern limb of the Moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow. It surpassed the previous eclipse as the longest total lunar eclipse visible from nearly all of North America since 17 August 1989, and until 26 June 2029. Occurring only 5.8 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. The next total lunar eclipse will take place on 14 March 2025. A lunar occultation of Uranus happened during the eclipse. It was the first total lunar eclipse on Election Day in US history. This event was referred in media coverage as a "beaver blood moon".

A total lunar eclipse occurred on 15–16 May 2022, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2022. The event occurred near lunar perigee; as a result, this event was referred to some in media coverage as a "super flower blood moon" and elsewhere as a "super blood moon", a supermoon that coincides with a total lunar eclipse. This was the longest total lunar eclipse visible from nearly all of North America since August 17, 1989 until the next eclipse on November 8.

A total lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node on 27 July 2018. The Moon passed through the center of Earth's shadow in what was the first central lunar eclipse since 15 June 2011. It was also the second total lunar eclipse in 2018, after the one on 31 January. It was the longest total lunar eclipse of the 21st century, but not the longest in the 3rd millennium. The longest total lunar eclipse of the 3rd millennium will occur on May 12, 2264, lasting 106 minutes and 13.2 seconds, which will be the longest total lunar eclipse since 2000, and the longest one until 3107.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, December 30, 1982. A shallow total eclipse saw the Moon in relative darkness for 1 hour 3 seconds. The Moon was 18% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, and should have been significantly darkened. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours and 16 minutes in total. This was a supermoon since perigee was on the same day. It was also a blue moon, the second full moon of December for the eastern hemisphere where the previous full moon was on December 1. Since total lunar eclipses are also known as blood moons, this combination is known as a super blue blood moon.

A total lunar eclipse occurred on 21 January 2019 UTC. For observers in the Americas, the eclipse took place between the evening of Sunday, 20 January and the early morning hours of Monday, 21 January. For observers in Europe and Africa, the eclipse occurred during the morning of 21 January. The Moon was near its perigee on 21 January and as such can be described as a "supermoon".

A total lunar eclipse occurred on 26 May 2021. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are exactly or very closely aligned with Earth between the other two, which can only happen at a full moon. The eclipsed moon appeared as a faint red disk in the sky due to a small amount of light being refracted through the earth's atmosphere; this appearance gives a lunar eclipse its nickname of a Blood Moon.

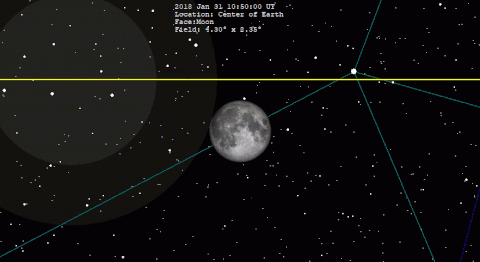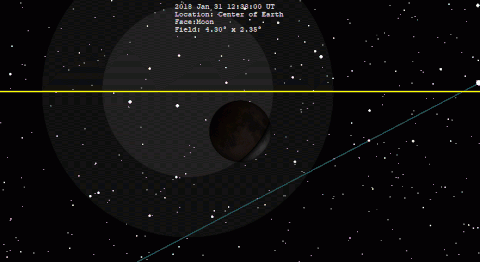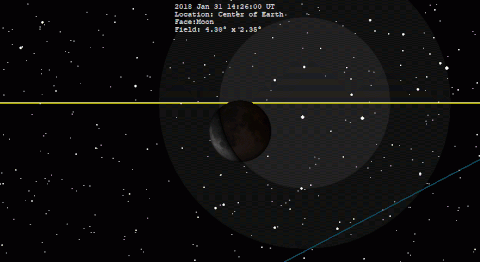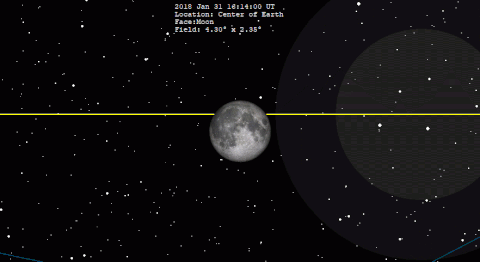
A total lunar eclipse will take place on Saturday, January 31, 2037. The Moon will be plunged into darkness for 1 hour and 3 minutes 41 seconds, in a moderately deep total eclipse which will see the Moon 20.74% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may be stained a deep red colour for observers in north and west North America, most of Asia, Australia and New Zealand. The partial eclipse will last for 3 hours and 17 minutes 28 seconds in total. It occurs during a supermoon (perigee), and blue moon, just like the eclipse of January 31, 2018, one metonic cycle previous.

A total solar eclipse occurred on March 20, 2015. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with a partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. This total solar eclipse is notable in that the path of totality passed over the North Pole. Totality was visible in the Faroe Islands and Svalbard.

A partial solar eclipse occurred on Thursday, October 23, 2014, with a magnitude of 0.81141. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. Occurring only 5.7 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.

A partial solar eclipse took place on February 15, 2018. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.