This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Theodore II Doukas Laskaris or Ducas Lascaris was Emperor of Nicaea from 1254 to 1258.
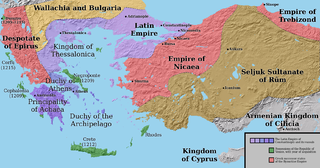
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire was the largest of the three Byzantine Greek rump states founded by the aristocracy of the Byzantine Empire that fled after Constantinople was occupied by Western European and Venetian forces during the Fourth Crusade. Founded by the Laskaris family, it lasted from 1204 to 1261, when the Nicaeans restored the Byzantine Empire in Constantinople.
Michael II Asen was emperor of Bulgaria from 1246 to 1256 or 1257. He was the son of Ivan Asen II of Bulgaria and Irene Komnene Doukaina. He succeeded his half-brother, Kaliman I Asen. His mother or other relative must have ruled Bulgaria during his minority.

Michael II Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Comnenus Ducas, often called Michael Angelos in narrative sources, was from 1230 until his death in 1266/68 the ruler of the Despotate of Epirus, which included Epirus in northwestern Greece, the western part of Greek Macedonia and Thessaly, and western Greece as far south as Nafpaktos.
John Doukas, Latinized as Ducas is the name of several Byzantine aristocrats and their descendants. It may refer to any of the following:
The Laskaris or Lascaris family was a Byzantine Greek noble family whose members formed the ruling dynasty of the Empire of Nicaea from 1204 to 1261 and remained among the senior nobility up to the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire, whereupon many emigrated to Italy and then to Smyrna. According to George Pachymeres, they were also called Tzamantouros (Tζαμάντουρος). The feminine form of the name is Laskarina (Λασκαρίνα).
Alexios Komnenos Strategopoulos was a Byzantine general during the reign of Michael VIII Palaiologos, rising to the rank of megas domestikos and Caesar. Of noble descent, he appears in the sources already at an advanced age in the early 1250s, leading armies for the Empire of Nicaea against Epirus. After falling out of favour and being imprisoned by Theodore II Laskaris, Strategopoulos sided with the aristocrats around Michael Palaiologos, and supported him in his rise to the throne after Theodore II's death in 1258. He participated in the Pelagonia campaign in 1259, going on to capture Epirus, but his successes were undone in the next year and he was captured by the Epirotes. Released after a few months, he led the unexpected reconquest of Constantinople from the Latin Empire in July 1261, restoring the Byzantine Empire. He was captured again by the Epirotes in the next year and spent several years in captivity in Italy, before being released. He retired from public affairs and died in the early 1270s.

Theodora Doukaina Komnene Palaiologina, usually known simply as Theodora Palaiologina, was the Empress consort of the Byzantine emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos.

The Siege of Constantinople (1235) was a joint Bulgarian-Nicaean siege on the capital of the Latin Empire. Latin emperor John of Brienne was besieged by the Nicaean emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes and Tsar Ivan Asen II of Bulgaria. The siege remained unsuccessful.

The Siege of Constantinople in 1260 was the failed attempt by the Nicaean Empire, the major remnant of the fractured Byzantine Empire, to retake Constantinople from the Latin Empire and re-establish the City as the political, cultural and spiritual capital of a revived Byzantine Empire.
Alexios Raoul was a Byzantine aristocrat and general of the Empire of Nicaea. He attained the rank of protovestiarios during the reign of Emperor John III Vatatzes.
Nikephoros Tarchaneiotes was a 13th-century Byzantine aristocrat and general.
Ioannes III may refer to:
Leo Gabalas was a Byzantine Greek magnate and independent ruler of a domain, centered on the island of Rhodes and including nearby Aegean islands, which was established in the aftermath of the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire by the Fourth Crusade in 1204. He acknowledged some form of suzerainty by the Empire of Nicaea, but remained virtually independent until his death, sometime in the early 1240s.
The Genoese occupation of Rhodes refers to the period between 1248 and late 1249/early 1250 during which the city of Rhodes and parts of the island were under Genoese control. The Genoese took possession of the city and island, a dependency of the Empire of Nicaea, in a surprise attack in 1248, and held it, with aid from the Principality of Achaea, against Nicaean attacks until 1250.

The Vatatzes or Batatzes family was a noble Byzantine family of the 11th–14th centuries with several branches, which produced several senior generals of the Byzantine army and, after John III Doukas Vatatzes intermarried with the Laskaris, the ruling line of the Empire of Nicaea until the usurpation of Michael VIII Palaiologos in 1261. The feminine form of the name is Vatatzina or Batatzina (Βατατζίνα).
Andronikos Lapardas or Andronicus Lapardas was a Byzantine general during the late Komnenian period.
Andronikos Komnenos Palaiologos, was a megas domestikos (commander-in-chief) of the Empire of Nicaea and the father of the Byzantine emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos, the founder of the Palaiologan dynasty.





