This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States is the title of all members of the Supreme Court of the United States other than the Chief Justice of the United States. The number of associate justices is eight, as set by the Judiciary Act of 1869.

The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. Established pursuant to Article III of the U.S. Constitution in 1789, it has original jurisdiction over a narrow range of cases, including suits between two or more states and those involving ambassadors. It also has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all federal court and state court cases that involve a point of federal constitutional or statutory law. The Court has the power of judicial review, the ability to invalidate a statute for violating a provision of the Constitution or an executive act for being unlawful. However, it may act only within the context of a case in an area of law over which it has jurisdiction. The court may decide cases having political overtones, but it has ruled that it does not have power to decide nonjusticiable political questions. Each year it agrees to hear about one hundred to one hundred fifty of the more than seven thousand cases that it is asked to review.

The Chief Justice of the United States is the chief judge of the Supreme Court of the United States, and as such the highest-ranking judge of the federal judiciary. Article II, Section 2, Clause 2 of the Constitution grants plenary power to the President of the United States to nominate, and with the advice and consent of the United States Senate, appoint a chief justice, who serves until they resign, are impeached and convicted, retire, or die.

David Hackett Souter is a retired Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. He served from October 1990 until his retirement in June 2009. Appointed by President George H. W. Bush to fill the seat vacated by William J. Brennan Jr., Souter sat on both the Rehnquist and Roberts Courts.

The New Hampshire Supreme Court is the supreme court of the U. S. state of New Hampshire and sole appellate court of the state. The Supreme Court is seated in the state capital, Concord. The Court is composed of a Chief Justice and four Associate Justices appointed by the Governor and Executive Council to serve during "good behavior" until retirement or the age of seventy. The senior member of the Court is able to specially assign lower-court judges, as well as retired justices, to fill vacancies on the Court.

Stephen Johnson Field was an American jurist. He was an Associate Justice of the United States Supreme Court from May 20, 1863, to December 1, 1897, the second longest tenure of any justice. Prior to this appointment, he was the fifth Chief Justice of California.

George Shiras Jr. was an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States who was nominated to the Court by Republican President Benjamin Harrison. At that time, he had 37 years of private legal practice, but had never judged a case. Shiras's only public service before he became a justice was as a federal elector in 1888, almost four years before his nomination in 1892.
Senior status is a form of semi-retirement for United States federal judges and judges in some state court systems. A judge must be at least 65 years of age and have served in federal courts for at least 15 years to qualify, with one less year of service required for each additional year of age. When that happens, they receive the full salary of a judge but have the option to take a reduced caseload, although many senior judges choose to continue to work full-time. Additionally, senior judges do not occupy seats; instead, their seats become vacant, and the president may appoint new full-time judges to fill their spots.
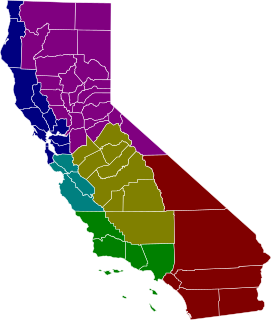
The California courts of appeal are the state intermediate appellate courts in the U.S. state of California. The state is geographically divided into six appellate districts. The courts of appeal form the largest state-level intermediate appellate court system in the United States, with 105 justices.

The demographics of the Supreme Court of the United States encompass the gender, ethnicity, and religious, geographic, and economic backgrounds of the 114 people who have been appointed and confirmed as justices to the Supreme Court. Some of these characteristics have been raised as an issue since the Court was established in 1789. For its first 180 years, justices were almost always white male Protestants.

The Supreme Court of Mississippi is the highest court in the state of Mississippi. It was created in the first constitution of the state following its admission as a State of the Union in 1817. Initially it was known as the "High Court of Errors and Appeals." The court is an appellate court, as opposed to a trial court. The Court Building is located in downtown Jackson, Mississippi, the state capital.
David Brewer is the name of:

The Fuller Court refers to the Supreme Court of the United States from 1888 to 1910, when Melville Fuller served as the eighth Chief Justice of the United States. Fuller succeeded Morrison R. Waite as Chief Justice after the latter's death, and Fuller served as Chief Justice until his death, at which point Associate Justice Edward Douglass White was nominated and confirmed as Fuller's replacement.
Justice Baker may refer to:
Rebecca Duncan is an American lawyer and judge, who has been an Associate Justice of the Oregon Supreme Court since 2017. She previously served on the Oregon Court of Appeals from 2010 to 2017.










