
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty, during the king Wu Ding's reign, who was mentioned as the twenty-first Shang king by the same. Ancient historical texts such as the Records of the Grand Historian and the Bamboo Annals describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze River. These Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is one of the world's oldest civilizations, and is regarded as one of the cradles of civilization.

Economic history is the study of economies or economic phenomena of the past. Analysis in economic history is undertaken using a combination of historical methods, statistical methods and the application of economic theory to historical situations and institutions. The topic includes financial and business history and overlaps with areas of social history such as demographic and labor history. The quantitative—in this case, econometric—study of economic history is also known as cliometrics.
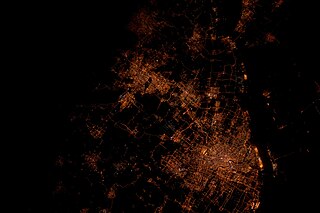
The Yangtze Delta or Yangtze River Delta is a triangle-shaped megalopolis generally comprising the Wu Chinese-speaking areas of Shanghai, southern Jiangsu province and northern Zhejiang province. The area lies in the heart of the Jiangnan region, where Yangtze River drains into the East China Sea. Having a fertile soil, the Yangtze Delta abundantly produces grain, cotton, hemp and tea. In 2018, the Yangtze Delta had a GDP of approximately US$2.2 trillion, about the same size as Italy.
The economic history of India begins with the Indus Valley Civilization, whose economy appears to have depended significantly on trade and examples of overseas trade, notable being Indus-Mesopotamia relations. The Vedic period saw countable units of precious metal being used for exchange. The term Nishka appears in this sense in the Rigveda. Later Vedic period began codifying the ancient Indian population based on caste, a social stratification which created a hierarchy of priests (Brahmins), warriors (Kshatriyas), merchants (Vaishyas) and laborers (Shudras).
Pamela Kyle Crossley is an historian of modern China, northern Asia, and global history and holds the Charles and Elfriede Collis Professor of History, Dartmouth College. She is a founding appointment of the Dartmouth Society of Fellows.
The Chinese Library Classification, also known as Classification for Chinese Libraries (CCL), is effectively the national library classification scheme in China. It is used in almost all primary and secondary schools, universities, academic institutions, as well as public libraries. It is also used by publishers to classify all books published in China.

The Great Divergence is a term made popular by Kenneth Pomeranz's 2000 book by that title, referring to the process by which the Western world overcame pre-modern growth constraints and emerged during the 19th century as the most powerful and wealthy world civilization, eclipsing Mughal India, Qing China, the Islamic World, Joseon Korea, and Tokugawa Japan.

Joel Mokyr is a Netherlands-born American-Israeli economic historian. He is a professor of economics and history at Northwestern University, where he has taught since 1974; in 1994 he was named the Robert H. Strotz Professor of Arts and Sciences. He is also a Sackler Professorial Fellow at the University of Tel Aviv's Eitan Berglas School of Economics.

Oded Galor is an Israeli economist who is currently Herbert H. Goldberger Professor of Economics at Brown University. He is the founder of unified growth theory. Galor has contributed to the understanding of process of development over the entire course of human history and the role of deep-rooted factors in the transition from stagnation to growth and in the emergence of the vast inequality across the globe. Moreover, he has pioneered the exploration of the impact of human evolution, population diversity, and inequality on the process of development over most of human existence.
The Cambridge History of China is an ongoing series of books published by the Cambridge University Press (CUP) covering the history of China from the founding of the Qin dynasty in 221 BC to 1982 AD. Chinese history before the Qin dynasty is covered in an independent volume, The Cambridge History of Ancient China (1999) which follows the Pinyin romanization system; all other volumes use Wade–Giles romanization.

The economy of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) of China was the largest in the world during that period. It is regarded as one of China's three golden ages. The period was marked by the increasing political influence of the merchants, the gradual weakening of imperial rule, and technological advances.

The economic history of China covers thousands of years and the region has undergone alternating cycles of prosperity and decline. China, for last two millennia, was one of the world's largest and most advanced economies. Economic historians usually divide China's history into three periods: the pre-imperial era before the rise of Qin; the early imperial era from Qin to the rise of the Song ; and the late imperial era, from Song to the fall of the Qing.

Anthony Philip "Tony" Thirlwall is Professor of Applied Economics at the University of Kent. He has made major contributions to regional economics; the analysis of unemployment and inflation; balance of payments theory, and to growth and development economics with particular reference to developing countries. He is the author of the bestselling textbook Economics of Development: Theory and Evidence now in its ninth edition. He is also the biographer and literary executor of the famous Cambridge economist Nicholas Kaldor. Perhaps his most notable contribution has been to show that if long-run balance of payments equilibrium is a requirement for a country, its growth of national income can be approximated by the ratio of the growth of exports to the income elasticity of demand for imports.
The Qing conquest theory is a theory proposed by Chinese academics that attempts to explain the Great Divergence, the overtaking of China by the Western world as the major economic and industrial world power. Specifically, the theory seeks to explain how Europe could experience an industrial revolution, but China did not. Theory supporters claim that although the prosperous Song and Ming dynasties moved China toward a modern age, the restrictions placed on commerce and industry and the persecution of non-orthodox thought after the Manchu conquest of China caused the country to stagnate and fall behind the West.
Denis Patrick O'Brien is an English economist who has worked in industrial economics and the history of economic thought.
Deng Xiaoping and the Making of Modern China is a book by Sir Richard Evans chronicling the rise of Deng Xiaoping as the leader of the People's Republic of China. The first British edition was published in 1993 by the Hamilton company. The first American edition was published by Viking Books in 1993. This was Evans's first book. Evans had served as the Ambassador of the United Kingdom to China, from 1984 to 1988. To conduct his research, with approval of PRC officials, Evans had interviewed several PRC governmental officials.
Kevin Hjortshøj O'Rourke, is an Irish economist and historian, who specialises in economic history and international economics. Since 2011, he has been Chichele Professor of Economic History at the University of Oxford and a Fellow of All Souls College, Oxford. He was Professor of Economics at Trinity College, Dublin from 2000 to 2011, and had previously taught at Columbia University and University College, Dublin.
This article delineates the history of modernisation theory. Modernisation refers to a model of a progressive transition from a 'pre-modern' or 'traditional' to a 'modern' society. The theory looks at the internal factors of a country while assuming that, with assistance, "traditional" countries can be brought to development in the same manner more developed countries have. Modernisation theory attempts to identify the social variables that contribute to social progress and development of societies, and seeks to explain the process of social evolution. Modernisation theory is subject to criticism originating among socialist and free-market ideologies, world-systems theorists, globalisation theorists and dependency theorists among others. Modernisation theory not only stresses the process of change, but also the responses to that change. It also looks at internal dynamics while referring to social and cultural structures and the adaptation of new technologies.

The Journal of Global History is an academic history journal dedicated to the study of comparative, world, and global history. Established in 2006, the JGH is printed and published online by Cambridge University Press. The goal of the journal is to discuss interdisciplinary topics and new methodological modes of analysis concerning the study of the past over time and space.













