
The geography of Iraq is diverse and falls into five main regions: the desert, Upper Mesopotamia, the northern highlands of Iraq, Lower Mesopotamia, and the alluvial plain extending from around Tikrit to the Persian Gulf.
Kuwait is a country in the Arabian Peninsula, surrounding the Gulf of Kuwait at the head of the Persian Gulf. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, Kuwait was a prosperous trade port.

The Arabian peninsula, simplified Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian plate. From a geographical perspective, it is considered a subcontinent of Asia.
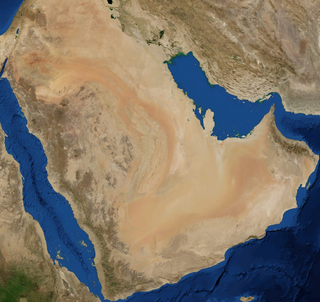
The Arabian Desert is a vast desert wilderness in Western Asia. It stretches from Yemen to the Persian Gulf and Oman to Jordan and Iraq. It occupies most of the Arabian Peninsula, with an area of 2,330,000 square kilometers (900,000 sq mi). It is the fifth largest desert in the world, and the largest in Asia. At its center is Ar-Rub'al-Khali , one of the largest continuous bodies of sand in the world.

The Iraq national football team represents Iraq in international football. The team is known by its fans as Asood Al-Rafidain, which means Lions of Mesopotamia, and is controlled by the Iraq Football Association (IFA), which is currently a member of the Asian Football Confederation (AFC) as well as the West Asian Football Federation (WAFF), the Union of Arab Football Associations (UAFA) and the Arab Gulf Cup Football Federation (AGCFF).

The Kuwait national football team is the national team of Kuwait and is controlled by the Kuwait Football Association. Kuwait made one World Cup finals appearance, in 1982, managing one point in the group stages. In the Asian Cup, Kuwait reached the final in 1976 and won the tournament in 1980.

The Syrian Desert, also known as the Syrian steppe, the Jordanian steppe, or the Badia, is a region of desert, semi-desert and steppe covering 500,000 square kilometers of the Middle East, including parts of south-eastern Syria, northeastern Jordan, northern Saudi Arabia, and western Iraq. It accounts for 85% of the land area of Jordan and 55% of Syria. To the south it borders and merges into the Arabian Desert. The land is open, rocky or gravelly desert pavement, cut with occasional wadis.

The International School of Choueifat (ISC) is a collection of private international schools run by SABIS school system in various countries of the Middle East. The first International School of Choueifat was founded in Choueifat, Lebanon in 1886 and later expanded to various parts of the Persian Gulf region. The first Choueifat school in the Persian Gulf opened in Sharjah, United Arab Emirates in 1975 and subsequently others opened in other cities across the Middle East. Since 1983 the School has also had a branch at Ashwicke Hall on the old Roman Fosse Way near Bath in England, which is also used as a summer school where students can study and learn sports during the harsh summers in the Middle East. In 1985 a branch was opened at Minneapolis in the US.
The Arabian Gulf Cup, also known as the Gulf Cup of Nations and often referred to simply as the Gulf Cup, is a biennial football competition for the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, in addition to neighbouring state Yemen, and is governed by the Arab Gulf Cup Football Federation. The history of the competition has also seen it held every three to four years due to political or organisational problems.

Hussein Saeed Mohammed Al-Ubaidi is a retired Iraqi footballer who played as a forward for the Iraqi Premier League club Al-Talaba and the Iraqi national team and is a former president of the Iraq Football Association. Saeed is in fifth place in the list of top international association goal scorers, with 78 goals. Along with Ahmed Radhi, he is considered to be the best Iraqi player of the 20th century and features in 25th place in Asia's Best Players of the Century list. On 24 April 1987, Saeed broke Falah Hassan's record to become the most capped Iraqi player with 110 caps. Hussein is currently the Iraqi national team's highest scoring player with 78 goals.

Arar is the capital of Northern Borders Province in Saudi Arabia. It has a population of 145,237.

Nasiriyah is a city in Iraq. It is situated along the banks of the Euphrates River, about 225 miles (370 km) southeast of Baghdad, near the ruins of the ancient city of Ur. It is the capital of the Dhi Qar Governorate. Its population 2003 was about 560,000, making it the fourth largest city in Iraq. It had a religiously diverse population of Muslims, Mandaeans and Jews in the early 20th century, but today its inhabitants are predominantly Shia Muslims.

The 22nd Arabian Gulf Cup was the 22nd edition of the biennial football competition, and took place between 13 and 26 November in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.

The 23rd Arabian Gulf Cup was the 23rd edition of the biennial football competition for the eight members of the Arab Gulf Cup Football Federation. It took place in Kuwait from 22 December 2017 until 5 January 2018. Oman won their second title, defeating the United Arab Emirates in the final on penalties following a goalless draw.
Al Kharjah, Saudi Arabia, is an oasis located at longitude 40.7189 east, latitude 21.0828 north.
Al Kharjah is a town in Iraq, that is south of Samara.
Lower Mesopotamia is a historical region of Iraq. Also known as the Sawad and al-'Irāq al-'Arabi in the Middle Ages, as opposed to "Persian Irāq", the Jibal. Lower Mesopotamia was home to ancient Sumerian and Babylonian civilisations.
Qahtan and Qahtani (Kahtani) or with the definit article al- as Al-Qahtani (Al-Kahtani) meaning coming from Qahtan may refer to:














