Kosmos 60 was an E-6 series probe, launched by the Soviet Union on March 12, 1965. It was the sixth attempt at a lunar soft-landing mission, with a design similar to that of Luna 4. The spacecraft achieved Earth orbit but failed to leave orbit for its journey to the Moon due to a failure of the power supply in the control system, and was designated Kosmos 60. It had an on-orbit mass of 6530 kg (14,400 lb). The satellite reentered the Earth's atmosphere on 17 March 1965.
Kosmos 212 was one of a series of Soviet Soyuz programme test spacecraft whose purpose was to further test and develop the passenger version. Scientific data and measurements were relayed to earth by multichannel telemetry systems equipped with space-borne memory units. Kosmos 212 and Kosmos 213 automatically docked in orbit on April 15, 1968. Both spacecraft landed on Soviet territory.
Kosmos 213 was one of a series of Soviet Soyuz programme test spacecraft whose purpose was to further test and develop the passenger version. Scientific data and measurements were relayed to earth by multichannel telemetry systems equipped with space-borne memory units. Kosmos 212 and Kosmos 213 automatically docked in orbit on April 15, 1968. Both spacecraft landed on Soviet territory.
Kosmos 419, also known as 3MS No.170 was a failed Soviet spacecraft intended to visit Mars. The spacecraft was launched on May 10, 1971, however due to an upper stage malfunction it failed to depart low Earth orbit.

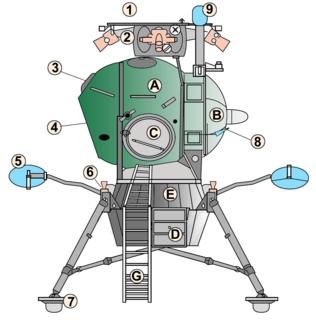
Kosmos 434 was the final unmanned test flight of the Soviet LK Lander. It performed the longest burn of the four unmanned LK Lander tests. It finished in a 186 km by 11,804 km orbit. This test qualified the lander as flightworthy.

Kosmos 110 was a Soviet spacecraft launched on 22 February 1966 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome aboard a Voskhod rocket. It carried two dogs, Veterok and Ugolyok.

Kosmos 557 was the designation given to DOS-3, the third space station in the Salyut program. It was originally intended to be launched as Salyut-3, but due to its failure to achieve orbit on May 11, 1973, three days before the launch of Skylab, it was renamed Kosmos-557.

Soyuz 7K-OK was the first generation of Soyuz spacecraft in use from 1967 to 1971. This first generation was used for the first ferry flights to the Salyut space station program; Soyuz spacecraft in their current generation are still in use to ferry crew to and from the ISS.
Kosmos 1818 was a nuclear powered Soviet surveillance satellite in the RORSAT program, which monitored NATO vessels using radar. Kosmos 1818 was the first satellite to use the TOPAZ-1 fission reactor. In July 2008, the satellite was damaged, and leaked a trail of sodium coolant.
Kosmos 1867 is a nuclear powered radar ocean reconnaissance satellite (RORSAT) that was launched by the Soviet Union on July 10, 1987. It was put into an orbit of about 800 km (500 mi). Its mission was to monitor the oceans for naval and merchant vessels, and had a mission life of about eleven months.
Kosmos 2, also known as 1MS #1 and occasionally in the West as Sputnik 12 was a scientific research and technology demonstration satellite launched by the Soviet Union in 1962. It was the second satellite to be designated under the Kosmos system, and the first spacecraft to be launched as part of the MS programme. Its primary missions were to develop systems for future satellites, and to record data about cosmic rays and radiation.
Kosmos 5, also known as 2MS #2 and occasionally in the West as Sputnik 15 was a scientific research and technology demonstration satellite launched by the Soviet Union in 1962. It was the fifth satellite to be designated under the Kosmos system, and the third spacecraft to be launched as part of the MS programme, after Kosmos 2 and Kosmos 3. Its primary missions were to develop systems for future satellites, and to record data about artificial radiation around the Earth.
Kosmos 10, also known as Zenit-2 #5, was a Soviet reconnaissance satellite launched in 1962. It was the tenth satellite to be designated under the Kosmos system, and the fourth successful launch of a Soviet reconnaissance satellite, following Kosmos 4, Kosmos 7 and Kosmos 9.
Kosmos 459, also known as DS-P1-M No.5 was a satellite which was used as a target for tests of anti-satellite weapons. It was launched by the Soviet Union in 1971 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme, and used as a target for Kosmos 462, as part of the Istrebitel Sputnik programme.
Kosmos 393, known before launch as DS-P1-Yu No.34, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1971 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 325-kilogram (717 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used as a radar calibration target for anti-ballistic missile tests.
Kosmos 408, known before launch as DS-P1-Yu No.37, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1971 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 250-kilogram (550 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used as a radar calibration target for anti-ballistic missile tests.
Kosmos 421, known before launch as DS-P1-Yu No.48, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1971 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 325-kilogram (717 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used as a radar calibration target for anti-ballistic missile tests.
Kosmos 423, known before launch as DS-P1-Yu No.47, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1971 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 325-kilogram (717 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used as a radar calibration target for anti-ballistic missile tests.
Kosmos 426, also known as DS-U2-K No.1, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1971 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 680-kilogram (1,500 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used to study charged particles and radiation in the Earth's magnetosphere.
Kosmos 2421 was a Russian spy satellite launched in 2006, but began fragmenting in early 2008. It also had the Konus-A gamma-ray burst experiment by the Yoffe FizTekh Institute. Three separate fragmentation events produced about 500 pieces of trackable debris, but about half of those had already re-entered by the fall of 2008.