D20, D-20 or d20 may refer to:

The kowari, also known as the brush-tailed marsupial rat, Kayer rat, Byrne's crest-tailed marsupial rat, bushy-tailed marsupial rat and kawiri, is a small carnivorous marsupial native to the dry grasslands and deserts of central Australia. It is monotypical in its genus.

The subfamily Dasyurinae includes several genera of small carnivorous marsupials native to Australia: quolls, kowari, mulgara, kaluta, dibblers, phascogales, pseudantechinuses, and the Tasmanian devil. The subfamily is defined largely on biochemical criteria.
The Open-pool Australian lightwater reactor (OPAL) is a 20 megawatt (MW) pool-type nuclear research reactor. Officially opened in April 2007, it replaced the High Flux Australian Reactor as Australia's only nuclear reactor, and is located at the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) Research Establishment in Lucas Heights, New South Wales, a suburb of Sydney. Both OPAL and its predecessor have been commonly known as simply the Lucas Heights reactor, after their location.

The International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD) maintains a database of powder diffraction patterns, the Powder Diffraction File (PDF), including the d-spacings and relative intensities of observable diffraction peaks. Patterns may be experimentally determined, or computed based on crystal structure and Bragg's law. It is most often used to identify substances based on x-ray diffraction data, and is designed for use with a diffractometer. Release 2016 of the PDF contains 848,000+ unique material data sets. Each data set contains diffraction, crystallographic and bibliographic data, as well as experimental, instrument and sampling conditions, and select physical properties in a common standardized format.
A diffractometer is a measuring instrument for analyzing the structure of a material from the scattering pattern produced when a beam of radiation or particles interacts with it.
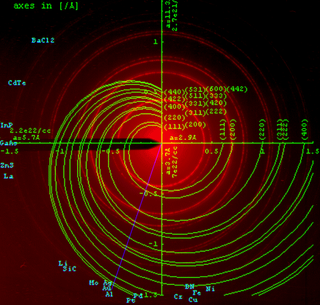
Powder diffraction is a scientific technique using X-ray, neutron, or electron diffraction on powder or microcrystalline samples for structural characterization of materials. An instrument dedicated to performing such powder measurements is called a powder diffractometer.

The Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) is a statutory body of the Australian government, formed in 1987 to replace the Australian Atomic Energy Commission. Its head office and main facilities are in southern outskirts of Sydney at Lucas Heights, in the Sutherland Shire.

ISIS Neutron and Muon Source is a pulsed neutron and muon source. It is situated at the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory of the Science and Technology Facilities Council, on the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire, United Kingdom. It uses the techniques of muon spectroscopy and neutron scattering to probe the structure and dynamics of condensed matter on a microscopic scale ranging from the subatomic to the macromolecular.
Wombats are a family of Australian marsupials. Wombat or Wombats may also refer to:
X-ray crystal truncation rod scattering is a powerful method in surface science, based on analysis of surface X-ray diffraction (SXRD) patterns from a crystalline surface.

The tribe Dasyurini includes several genera of small carnivorous marsupials native to Australia: quolls, kowari, mulgara, kaluta, dibblers, neophascogales, pseudantechinuses, and the Tasmanian devil.
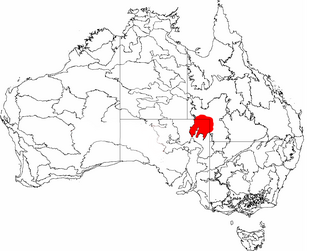
Sturt Stony Desert is an area in the north-east of South Australia, far south western border area of Queensland and the far west of New South Wales.
Mulgara is a triplestore and fork of the original Kowari project. It is open-source, scalable, and transaction-safe. Mulgara instances can be queried via the iTQL query language and the SPARQL query language.

Rigaku Corporation is an international manufacturer and distributor of scientific, analytical and industrial instrumentation specializing in X-ray related technologies, including X-ray crystallography, X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray reflectivity, X-ray fluorescence (XRF), automation, cryogenics and X-ray optics.

Miniflex is an X-ray diffraction (XRD) analytical measuring instrument produced by Rigaku. The current instrument is the fourth in a series introduced in 1973.
The index of physics articles is split into multiple pages due to its size.

Alan Kenneth Soper FRS is an STFC Senior Fellow at the ISIS neutron source based at the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory in Oxfordshire.
Hilger & Watts was a well-known British manufacturing company that made theodolites and scientific instruments.
Abdullah Al Kuwari is a Qatari footballer. He currently plays.









