
A computer program is a collection of instructions that performs a specific task when executed by a computer. A computer requires programs to function.

A programmer, developer ("dev"), coder, or software engineer is a person who creates computer software. The term computer programmer can refer to a specialist in one area of computers, or to a generalist who writes code for many kinds of software. One who practices, or professes, a formal approach to programming may also be known as a programmer analyst. On the other hand, "code monkey" is a derogatory term for a programmer who simply writes code without any involvement in the design or specifications.
Hierarchical File System (HFS) is a proprietary file system developed by Apple Inc. for use in computer systems running Mac OS. Originally designed for use on floppy and hard disks, it can also be found on read-only media such as CD-ROMs. HFS is also referred to as Mac OS Standard, while its successor, HFS Plus, is also called Mac OS Extended.

Edward Livingston was an American jurist and statesman. He was an influential figure in the drafting of the Louisiana Civil Code of 1825, a civil code based largely on the Napoleonic Code. Livingston represented both New York and then Louisiana in Congress and served as the U.S. Secretary of State from 1831 to 1833.
Source lines of code (SLOC), also known as lines of code (LOC), is a software metric used to measure the size of a computer program by counting the number of lines in the text of the program's source code. SLOC is typically used to predict the amount of effort that will be required to develop a program, as well as to estimate programming productivity or maintainability once the software is produced.

Valentin Vitalyevich Lebedev is a Soviet cosmonaut who made two flights into space. His stay aboard the Space Station Salyut 7 with Anatoly Berezovoy in 1982, which lasted 211 days, was recorded in the Guinness Book of Records.
In Linux, Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is a device mapper target that provides logical volume management for the Linux kernel. Most modern Linux distributions are LVM-aware to the point of being able to have their root file systems on a logical volume.
The device mapper is a framework provided by the Linux kernel for mapping physical block devices onto higher-level virtual block devices. It forms the foundation of the logical volume manager (LVM), software RAIDs and dm-crypt disk encryption, and offers additional features such as file system snapshots.
In computer science, storage virtualization is "the process of presenting a logical view of the physical storage resources to" a host computer system, "treating all storage media in the enterprise as a single pool of storage."
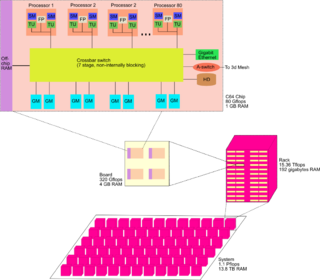
A cellular architecture is a type of computer architecture prominent in parallel computing. Cellular architectures are relatively new, with IBM's Cell microprocessor being the first one to reach the market. Cellular architecture takes multi-core architecture design to its logical conclusion, by giving the programmer the ability to run large numbers of concurrent threads within a single processor. Each 'cell' is a compute node containing thread units, memory, and communication. Speed-up is achieved by exploiting thread-level parallelism inherent in many applications.
Vinum, is a logical volume manager, also called software RAID, allowing implementations of the RAID-0, RAID-1 and RAID-5 models, both individually and in combination. Vinum is part of the base distribution of the FreeBSD operating system. Versions exist for NetBSD, OpenBSD and DragonFly BSD. Vinum source code is currently maintained in the FreeBSD source tree. Vinum supports RAID levels 0, 1, 5, and JBOD.

CheatCodes.com is a gaming website that has published video game cheat codes, FAQs, and walkthroughs since 1996. The website currently publishes content for PlayStation 4, PlayStation 3, PlayStation 2, PlayStation, Xbox One, Xbox 360, Xbox, Wii U, Wii, GameCube, Nintendo 64, PlayStation Vita, PlayStation Portable, Nintendo DS, Game Boy Advance, Game Boy, N-Gage, Dreamcast, Facebook, Android, iOS, and PC games.
In memory addressing for Intel x86 computer architectures, segment descriptors are a part of the segmentation unit, used for translating a logical address to a linear address. Segment descriptors describe the memory segment referred to in the logical address.
The segment descriptor contains the following fields:
- A segment base address
- The segment limit which specifies the segment size
- Access rights byte containing the protection mechanism information
- Control bits

The LVG C.II was a 1910s German two-seat reconnaissance biplane designed at the Luft-Verkehrs-Gesellschaft for the Luftstreitkräfte.

In computing, an emulator is hardware or software that enables one computer system to behave like another computer system. An emulator typically enables the host system to run software or use peripheral devices designed for the guest system.
Emulation refers to the ability of a computer program in an electronic device to emulate another program or device. Many printers, for example, are designed to emulate Hewlett-Packard LaserJet printers because so much software is written for HP printers. If a non-HP printer emulates an HP printer, any software written for a real HP printer will also run in the non-HP printer emulation and produce equivalent printing. Since at least the 1990s, many video game enthusiasts have used emulators to play classic arcade games from the 1980s using the games' original 1980s machine code and data, which is interpreted by a current-era system.

The Bavarian State Office for Digitizing, Broadband and Survey or LDBV, until 31 December 2013 Bavarian State Office for Survey and Geoinformation or LVG, is the name of the new division of the Bavarian Department of Survey, Information and Communication Technology within the Bavarian State Ministry of Finance formed on 1 August 2005 as part of the administrative reform in Bavaria. It was formed by a merge of the Bavarian State Survey Office and the survey departments of the district finance divisions responsible for cadastral survey.
Core Storage is a logical volume management system on macOS that was introduced by Apple to Mac OS X Lion. Core Storage is a layer between the disk partition and the file system.
Low-level design (LLD) is a component-level design process that follows a step-by-step refinement process. This process can be used for designing data structures, required software architecture, source code and ultimately, performance algorithms. Overall, the data organization may be defined during requirement analysis and then refined during data design work. Post-build, each component is specified in detail.










