Buffalo is the second largest city in the U.S. state of New York and the largest city in Western New York. As of 2017, the population was 258,612. The city is the county seat of Erie County and a major gateway for commerce and travel across the Canada–United States border, forming part of the bi-national Buffalo Niagara Region.

The Erie Canal is a canal in New York, United States that is part of the east–west, cross-state route of the New York State Canal System. Originally, it ran 363 miles (584 km) from where Albany meets the Hudson River to where Buffalo meets Lake Erie. It was built to create a navigable water route from New York City and the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes. When completed in 1825, it was the second longest canal in the world and greatly affected the development and economy of New York, New York City, and the United States.

The Hudson River is a 315-mile (507 km) river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York in the United States. The river originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York, flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the Upper New York Bay between New York City and Jersey City. It eventually drains into the Atlantic Ocean at New York Harbor. The river serves as a political boundary between the states of New Jersey and New York at its southern end. Further north, it marks local boundaries between several New York counties. The lower half of the river is a tidal estuary, deeper than the body of water into which it flows, occupying the Hudson Fjord, an inlet which formed during the most recent period of North American glaciation, estimated at 26,000 to 13,300 years ago. Tidal waters influence the Hudson's flow from as far north as the city of Troy.

The Niagara River is a river that flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. There are differing theories as to the origin of the river's name. According to Iroquoian scholar Bruce Trigger, Niagara is derived from the name given to a branch of the locally residing native Neutral Confederacy, who are described as being called the Niagagarega people on several late-17th-century French maps of the area. According to George R. Stewart, it comes from the name of an Iroquois town called Ongniaahra, meaning "point of land cut in two".

Erie County is a highly populated county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2010 census, the population was 919,040. The county seat is Buffalo. The county's name comes from Lake Erie. It was named by European colonists for the regional Iroquoian language-speaking Erie tribe of Native Americans, who lived south and east of the lake before 1654.

Erie is a city on the south shore of Lake Erie and the county seat of Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. Named for the lake and the Native American Erie people who lived in the area until the mid-17th century, Erie is the fourth-largest city in Pennsylvania, as well as the largest city in Northwestern Pennsylvania, with a population of 101,786 at the 2010 census. The estimated population in 2017 had decreased to 97,369. The Erie metropolitan area, equivalent to all of Erie County, consists of 276,207 residents. The Erie-Meadville, PA Combined Statistical Area has a population of 369,331, as of the 2010 Census.

Fort Erie is a town on the Niagara River in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. It is directly across the river from Buffalo, New York and is the site of Old Fort Erie which played a prominent role in the War of 1812.
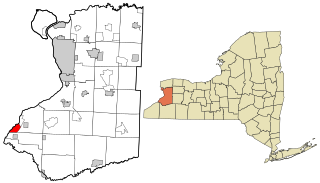
Hamburg is a town in Erie County, New York, United States. As of the 2010 census, the town had a population of 56,936. It is named after the city of Hamburg, in Germany. The town is on the western border of the county and is south of Buffalo. Hamburg is one of the Southtowns in Erie County. The villages of Hamburg and Blasdell are in the town.

The Regional Municipality of Niagara, also colloquially known as the Niagara Region, is a regional municipality comprising twelve municipalities of Southern Ontario, Canada. The regional seat is in Thorold. It is the southern end of the Golden Horseshoe, the largest megalopolis in Canada.

The Maumee River is a river running from northeastern Indiana into northwestern Ohio and Lake Erie in the United States. It is formed at the confluence of the St. Joseph and St. Marys rivers, where Fort Wayne, Indiana, has developed, and meanders northeastwardly for 137 miles (220 km) through an agricultural region of glacial moraines before flowing into the Maumee Bay of Lake Erie. The city of Toledo is located at the mouth of the Maumee. The Maumee was designated an Ohio State Scenic River on July 18, 1974. The Maumee watershed is Ohio’s breadbasket; it is two-thirds farmland, mostly corn and soybeans. It is the largest watershed of any of the rivers feeding the Great Lakes, and supplies five percent of Lake Erie’s water.

Upstate New York is the portion of the American state of New York lying north of the New York metropolitan area. The Upstate region includes most of the state of New York, excluding New York City, the Lower Hudson Valley, and Long Island, although the precise boundary is debated. Major cities in Upstate New York include Buffalo, Rochester, Albany, and Syracuse.

Northeast Ohio refers to the northeastern region of the U.S. state of Ohio. In its greatest definition, the region contains six metropolitan areas, including Cleveland–Elyria, Akron, Canton–Massillon, Youngstown–Warren, Mansfield, and Weirton–Steubenville, along with eight micropolitan statistical areas. Most of the region is considered either part of the Cleveland–Akron–Canton, OH Combined Statistical Area and media market or the Youngstown–Warren, OH-PA Combined Statistical Area and media market. In total the region is home to 4,529,596 residents. Northeast Ohio also includes most of the area known historically as the Connecticut Western Reserve. In 2011, the Intelligent Community Forum ranked Northeast Ohio as a global Smart 21 Communities list. It has the highest concentration of Hungarian Americans in the United States.

Western New York is the westernmost region of the state of New York. It includes the cities of Buffalo, Rochester, Niagara Falls, the surrounding suburbs, as well as the outlying rural areas of the Great Lakes lowlands, the Genesee Valley, and the Southern Tier. The historic beginnings of the region can be defined by its original eastern boundary of Preemption Line, created by the December 16, 1786 political settlement between the states of New York and Massachusetts, both of which claimed political dominion over the land. This eastern boundary shifted because of changing county borders in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.

Western Pennsylvania refers to the western third of the state of Pennsylvania in the United States. Pittsburgh is the region's principal city, with a metropolitan area population of about 2.4 million people, and serves as its economic and cultural center. Erie, Altoona, and Johnstown are its other metropolitan centers. As of the 2010 census, Western Pennsylvania's total population is nearly 4 million.

The Greater Pittsburgh Region is a populous region in the United States which is named for its largest city and economic center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. There are several official and unofficial boundary definitions which may be used to describe this region. In the most restrictive definition, the region encompasses Pittsburgh's urban core county, Allegheny, and six nearby Pennsylvania counties.
Tom Langmyer is an author, broadcast executive and media consultant.

Erie Commodores FC is an American soccer team based in Erie, Pennsylvania which competes in the National Premier Soccer League (NPSL), a nationwide amateur league at the fourth tier of the American Soccer Pyramid. The team plays their home matches at McConnell Family Stadium.