| Look up Leeward Islands in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Leeward Islands is the northern islands of the Lesser Antilles.
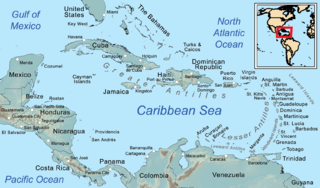
The Leeward Islands are a group of islands geographically situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. Starting with the Virgin Islands east of Puerto Rico, they extend southeast to Guadeloupe and its dependencies. In English, the term Leeward Islands refers to the northern islands of the Lesser Antilles chain. The more southerly part of this chain, geographically starts with Martinique and is called the Windward Islands. The island of Dominica is geographically and historically part of the Leeward Islands, however for political reasons in 1940 the management of the island was transferred from the British Leeward Islands to the British Windward Islands.
Leeward Islands may also refer to:
- Leeward Islands (Society Islands), the western islands of the Society Islands in French Polynesia
- Pulau Bawah, old colonial name for the group of six Indonesian islands was Leeward Islands
- Sotavento Islands ("Sotavento" means "Leeward"), the southern island group of Cape Verde archipelago
- Northwestern Hawaiian Islands, sometimes called the "Leeward Islands"
- British Leeward Islands, a former British colony in the Lesser Antilles
- 45614 Leeward Islands, a British LMS Jubilee Class locomotive

The Leeward Islands are the western part of the Society Islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the South Pacific. They lie south of the Line Islands, east of the Cooks and north of the Austral Islands. Their area is 395 km² with a population of over 33,000. The islands to the west comprise a three atoll group: Manuae, Motu One atoll, lying most northerly of the Leeward Islands, and to the southeast Maupihaa atoll. More to the east lies a mainly high island cluster consisting of Maupiti, Tupai atoll, Bora Bora, the most known of the Leeward Islands in the western world due to its World War II United States naval base and subsequent tourism industry, Taha'a, lying just north of the largest island of the group, Raiatea which possesses the largest city and local capital of the Leeward Islands, namely Uturoa, as well as the highest elevation, the just over 1,000 m mount Tefatua, and finally the easternmost island of the group, Huahine which at high tide is divided into two: Huahine Nui to the north and Huahine Iti to the south.
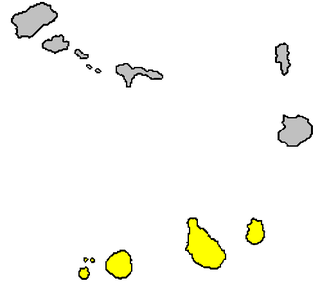
The Sotavento Islands is the southern island group of the Cape Verde archipelago. There are four main islands. The western three islands, Brava, Fogo and Santiago, are rocky and volcanic agricultural islands, with the longest histories of human habitation. The fourth and easternmost island Maio is a flat desert island whose economy was primarily based on salt, giving it more in common with the Barlavento islands Sal and Boa Vista. The Ilhéus do Rombo are barren islets north of Brava. The total area of the Sotavento Islands is 1,803 km2 (696 sq mi).

The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands or Leeward Islands are the small islands and atolls in the Hawaiian island chain located northwest of the islands of Kauai and Niihau. Politically, they are all part of Honolulu County in the U.S. state of Hawaii, except Midway Atoll, which is a territory distinct from Hawaii and grouped as one of the United States Minor Outlying Islands. The United States Census Bureau defines this area, except Midway, as Census Tract 114.98 of Honolulu County. Its total land area is 3.1075 square miles (8.048 km2). All the islands except Nihoa are north of the Tropic of Cancer, making them the only islands in Hawaii that lie outside the tropics.