Lehigh Valley Railroad Station | |
 | |
| Location | W. Buffalo St. and Taughannock Blvd., Ithaca, New York |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 42°26′29.1″N76°30′46.9″W / 42.441417°N 76.513028°W Coordinates: 42°26′29.1″N76°30′46.9″W / 42.441417°N 76.513028°W |
| Area | 2 acres (0.81 ha) |
| Built | 1898 |
| Architect | A. B. Wood |
| Architectural style | Classical Revival, Romanesque |
| NRHP reference # | 74001311 [1] |
| Added to NRHP | December 31, 1974 |
Lehigh Valley Railroad Station is a historic railway station located at 806 West Buffalo Street, Ithaca in Tompkins County, New York.

Ithaca is a city in the Finger Lakes region of New York. It is the seat of Tompkins County, as well as the largest community in the Ithaca–Tompkins County metropolitan area. This area contains the municipalities of the Town of Ithaca, the village of Cayuga Heights, and other towns and villages in Tompkins County. The city of Ithaca is located on the southern shore of Cayuga Lake, in Central New York, about 45 miles (72 km) south-west of Syracuse. It is named after the Greek island of Ithaca. Additionally, Ithaca is located 247 miles (398 km) southeast of Toronto, and 223 miles (359 km) northwest of New York City.

Tompkins County is a county located in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2010 census, the population was 101,564. The county seat is Ithaca. The name is in honor of Daniel D. Tompkins, who served as Governor of New York and Vice President of the United States.
The Passenger Station and Freight Station were designed by local architect A. B. Wood [2] and built in 1898 by the Lehigh Valley Railroad. The Passenger Station is a Classical Revival structure with a Romanesque feeling. It is a massive square building with extensions and sheltering roofs for baggage operations. At one corner is the entrance marquee and a four sided street clock mounted in a Corinthian column. The main waiting room section has a hipped roof and features a pedimented porte cochere. The Freight Station is a long, gray painted frame building with a two-story clapboarded section and a long freight storage part. Lehigh Valley passenger trains making stops there included the Black Diamond, Maple Leaf and Star. [3]
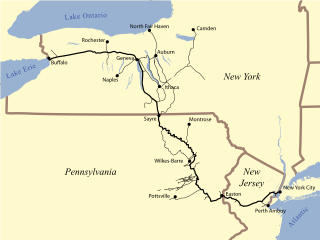
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was one of a number of railroads built in the northeastern United States primarily to haul anthracite coal. The railroad was authorized on April 21, 1846, for freight and transportation of passengers, goods, wares, merchandise and minerals in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the railroad was incorporated/established on September 20, 1847, as the Delaware, Lehigh, Schuylkill and Susquehanna Railroad Company. On January 7, 1853, the railroad's name was changed to Lehigh Valley Railroad. It was sometimes known as the Route of the Black Diamond, named after the anthracite it transported. At the time, anthracite was transported by boat down the Lehigh River; the railroad was meant to be faster transportation. The railroad ended operations in 1976 and merged into Conrail along with several northeastern railroads that same year.

Romanesque Revival is a style of building employed beginning in the mid-19th century inspired by the 11th- and 12th-century Romanesque architecture. Unlike the historic Romanesque style, however, Romanesque Revival buildings tended to feature more simplified arches and windows than their historic counterparts.

The Corinthian order is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of ancient Greek and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon, the Tuscan order and the Composite order. The Corinthian, with its offshoot the Composite, is the most ornate of the orders. This architectural style is characterized by slender fluted columns and elaborate capitals decorated with acanthus leaves and scrolls. There are many variations.
It was used as a passenger station until 1961. In 1966, local resident Joseph O. Ciaschi, an early local leader in the historic preservation movement, [4] converted the abandoned building into a restaurant. [5] Known as The Station, the restaurant operated until September 2005, when it was closed and the building converted for use as a branch office of the Chemung Canal Trust Company, an Elmira-based bank.
Chemung Canal Trust Company is a New York State chartered trust company based in Elmira, New York, USA. It was founded as a publicly traded bank in 1833. In 1857, the Arnot family gained control of the bank and operated a private family bank until 1903, when the bank again became publicly owned. Originally housed in the Chemung Canal Bank Building, the bank moved to 129 East Water Street in 1920, and then to its current home at One Chemung Canal Plaza in 1971.

Elmira is a city in Chemung County, New York, United States. It is the principal city of the Elmira, New York, metropolitan statistical area, which encompasses Chemung County, New York. The population was 29,200 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Chemung County.
The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974. [1]

The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance. A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property.






















