This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2023) |

The following is a list of the nine sovereign states and one territory where Portuguese is an official language.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2023) |

The following is a list of the nine sovereign states and one territory where Portuguese is an official language.
Portuguese is a Western Romance language of the Indo-European language family, originating in the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is the official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau and São Tomé and Príncipe, while having co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, and Macau. Portuguese-speaking people or nations are "Lusophones". As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Celtic phonology.

Spanish or Castilian (castellano) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a global language with about 500 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 600 million when including speakers as a second language. Spanish is the official language of 20 countries, as well as one of the six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's fourth-most spoken language overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language. The country with the largest population of native speakers is Mexico.
The Iberian Romance, Ibero-Romance or sometimes Iberian languages are a group of Romance languages that developed on the Iberian Peninsula, an area consisting primarily of Spain, Portugal, Gibraltar, Andorra and southern France. They are today more commonly separated into West Iberian and Occitano-Romance language groups.

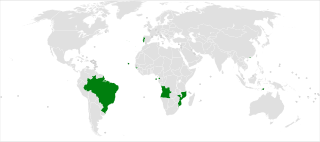
The Community of Portuguese Language Countries, also known as the Lusophone Community, is an international organization and political association of Lusophone nations across four continents, where Portuguese is an official language. The CPLP operates as a privileged, multilateral forum for the mutual cooperation of the governments, economies, non-governmental organizations, and peoples of the Lusofonia. The CPLP consists of 9 member states and 33 associate observers, located in Europe, South America, Asia, Africa and Oceania, totaling 38 countries and 4 organizations.
Papiamento or Papiamentu is a Portuguese-based creole language spoken in the Dutch Caribbean. It is the most widely spoken language on the Caribbean ABC islands, with official status in Aruba and Curaçao.

Ibero-America or Iberian America is generally considered to be the region in the Americas comprising countries or territories where Spanish or Portuguese are predominant languages. Portugal and Spain are themselves included in some definitions, such as that of the Ibero-American Summit and the Organization of Ibero-American States. The Organization of Ibero-American States also includes Spanish-speaking Equatorial Guinea, in Central Africa, but not the Portuguese-speaking African countries. The Latin Recording Academy, the organization responsible for the Latin Grammy Awards, also includes Spain and Portugal as well as the Latino population of Canada and the United States in their definition of Ibero-America.

The region known as Hispanic America and historically as Spanish America is all the Spanish-speaking countries of the Americas. In all of these countries, Spanish is the main language - sometimes sharing official status with one or more indigenous languages or English, and Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion.

Portuguese creoles are creole languages which have Portuguese as their substantial lexifier. The most widely-spoken creoles influenced by Portuguese are Cape Verdean Creole, Guinea-Bissau Creole and Papiamento.

The languages of East Timor include both Austronesian and Papuan languages. The lingua franca and national language of East Timor is Tetum, an Austronesian language influenced by Portuguese, with which it has equal status as an official language. The language of the Oecusse exclave is Uab Meto (Dawan). Fataluku is a Papuan language widely used in the eastern part of the country. Both Portuguese and Tetum have official recognition under the Constitution of East Timor, as do other indigenous languages, including: Bekais, Bunak, Galoli, Habun, Idalaka, Kawaimina, Kemak, Lovaia, Makalero, Makasae, Mambai, Tokodede and Wetarese.
Latin Americans are the citizens of Latin American countries.
The Portuguese language developed in the Western Iberian Peninsula from Latin spoken by Roman soldiers and colonists starting in the 3rd century BC. Old Portuguese, also known as Medieval Galician, began to diverge from other Romance languages after the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the Germanic invasions, also known as barbarian invasions, in the 5th century, and started appearing in written documents around the 9th century. By the 13th century, Galician-Portuguese had its own literature and began to split into two languages. However, the debate of whether Galician and Portuguese are nowadays varieties of the same language, much like American English or British English, is still present. In all aspects—phonology, morphology, lexicon and syntax—Portuguese is essentially the result of an organic evolution of Vulgar Latin with some influences from other languages, namely the native Gallaecian and Lusitanian languages spoken prior to the Roman domination.

Portuguese is spoken in a number of African countries and is the official language in six African countries: Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau, Cape Verde, São Tomé and Príncipe and Equatorial Guinea. There are Portuguese-speaking communities in most countries of Southern Africa, a mixture of Portuguese settlers and Angolans and Mozambicans who left their countries during the civil wars. A rough estimate has it that there are about 14 million people who use Portuguese as their sole mother tongue across Africa, but depending on the criteria applied, the number might be considerably higher, since many Africans speak Portuguese as a second language, in countries like Angola and Mozambique, where Portuguese is an official language, but also in countries like South Africa and Senegal, thanks to migrants coming from Portuguese-speaking countries. Some statistics claim that there are over 60 million Portuguese speakers in the continent.
In linguistics, a sprachraum is a geographical region where a common first language, with dialect varieties, or group of languages is spoken.

The Portuguese-speaking African countries, also known as Lusophone Africa, consist of six African countries in which the Portuguese language is an official language: Angola, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, São Tomé and Príncipe and, since 2011, Equatorial Guinea. The six countries are former colonies of the Portuguese Empire. From 1778 until independence, Equatorial Guinea was also a colony of the Spanish Empire.
The Portuguese language began to be used regularly in documents and poetry around the 12th century. Unlike neighboring Romance languages that adopted formal orthographies by the 18th century, the Portuguese language did not have a uniform spelling standard until the 20th century. The formation of the Portuguese Republic in 1911 was motivation for the establishment of orthographic reform in Portugal and its overseas territories and colonies. Brazil would adopt an orthographic standard based on, but not identical to, the Portuguese standard a few decades later.

Guinean Portuguese is the variety of Portuguese spoken in Guinea-Bissau, where it is the official language.

The languages of Venezuela refers to the official languages and various dialects spoken in established communities within the country. In Venezuela, Castellan is the official language and is the mother tongue of the majority of Venezuelans. Although there is an established official language, there are countless languages of indigenous villages spoken throughout Venezuela, and various regions also have languages of their own.
The Portuguese Language Orthographic Agreement of 1990 is an international treaty whose purpose is to create a unified orthography for the Portuguese language, to be used by all the countries that have Portuguese as their official language. It was signed in Lisbon, on 16 December 1990, at the end of a negotiation, begun in 1980, between the Sciences Academy of Lisbon and the Brazilian Academy of Letters. The signatories included official representatives from all of the Portuguese-language countries except East Timor, which was under Indonesian occupation at the time, but later adhered to the Agreement, in 2004.
The Portuguese language is spoken in Asia by small communities either in regions which formerly served as colonies to Portugal, notably Macau and East Timor where the language is official albeit not widely spoken, Lusophone immigrants, notably the Brazilians in Japan or by some Afro-Asians and Luso-Asians. In Larantuka, Indonesia and Daman and Diu, India, Portuguese has a religious connotation, according to Damanese Portuguese-Indian Association, there are 10 – 12,000 Portuguese speakers in the territory.

This article provides details regarding the geographical distribution of all Portuguese-speakers, a.k.a.Lusophones, regardless of legislative status. The Portuguese language is one of the most widely spoken languages in the world and is an official language of countries on four continents.