
Schizophrenia is a mental illness characterized by abnormal behavior, strange speech, and a decreased ability to understand reality. Other symptoms may include false beliefs, unclear or confused thinking, hearing voices that do not exist, reduced social engagement and emotional expression, and lack of motivation. People with schizophrenia often have additional mental health problems such as anxiety, depression, or substance-use disorders. Symptoms typically come on gradually, begin in young adulthood, and, in many cases, never resolve.

Asenapine, sold under the trade names Saphris and Sycrest among others, is an atypical antipsychotic medication used to treat schizophrenia and acute mania associated with bipolar disorder.
CapOpus is the name of a randomized controlled trial (RCT) running in Denmark at Psychiatric Center Bispebjerg and physically located at Bispebjerg Hospital in Copenhagen. It is an intervention aimed at reducing cannabis consumption in young persons with comorbid severe mental illness such as schizophrenia or schizotypal personality disorder, and cannabis dependency. It is run by psychiatrist Merete Nordentoft.

Perospirone (Lullan) is an atypical antipsychotic of the azapirone family. It was introduced in Japan by Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma in 2001 for the treatment of schizophrenia and acute cases of bipolar mania.

Bradanicline is a drug which was being developed by Targacept that acts as a partial agonist at the α7 subtype of the neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It showed cognitive enhancing effects in animal studies, and was being developed through a collaboration between Targacept and AstraZeneca as a potential treatment for schizophrenia and attention deficit disorder. Phase I clinical trials were completed successfully, and it was in phase II trials.

Pipotiazine (Piportil), also known as pipothiazine, is a typical antipsychotic of the phenothiazine class used in the United Kingdom and other countries for the treatment of schizophrenia. Its properties are similar to those of chlorpromazine. A 2004 systematic review investigated its efficacy for people with schizophrenia:

LY-404,039, also known as pomaglumetad, is an amino acid analog drug that acts as a highly selective agonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor group II subtypes mGluR2 and mGluR3. Pharmacological research has focused on its potential antipsychotic and anxiolytic effects. LY-404,039 is intended as a treatment for schizophrenia and other psychotic and anxiety disorders by modulating glutamatergic activity and reducing presynaptic release of glutamate at synapses in limbic and forebrain areas relevant to these disorders. Human studies investigating therapeutic use of LY-404,039 have focused on the prodrug LY-2140023, a methionine amide of LY-404,039 (also called pomaglumetad methionil or LY-2140023 monohydrate) since LY-404,039 exhibits low oral absorption and bioavailability in humans.
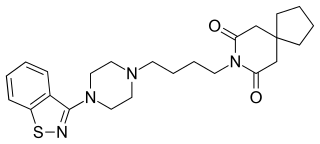
Tiospirone (BMY-13,859), also sometimes called tiaspirone or tiosperone, is an atypical antipsychotic of the azapirone class. It was investigated as a treatment for schizophrenia in the late 1980s and was found to have an effectiveness equivalent to those of typical antipsychotics in clinical trials but without causing extrapyramidal side effects. However, development was halted and it was not marketed. Perospirone, another azapirone derivative with antipsychotic properties, was synthesized and assayed several years after tiospirone. It was found to be both more potent and more selective in comparison and was commercialized instead.
Idalopirdine (INN) (code names Lu AE58054,) is a potent and selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist under development by Lundbeck as an augmentation therapy for the treatment of cognitive deficits associated with Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia. As of October 2013 it is in phase III clinical trials.
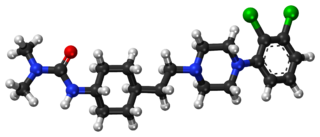
Cariprazine, sold under the brand names Vraylar in the United States and Reagila in Europe, is an atypical antipsychotic which is used in the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar mania, and bipolar depression. It acts primarily as a D3 receptor and D2 receptor partial agonist, with high selectivity for the D3 receptor. Positive Phase III study results were published for schizophrenia and mania in early 2012, and for bipolar disorder I depression from a Phase II trial in 2015. It is also potentially useful as an add-on therapy in major depressive disorder.

Brexpiprazole, sold under the brand name Rexulti, is an atypical antipsychotic. It is a dopamine D2 receptor partial agonist and has been described as a "serotonin–dopamine activity modulator" (SDAM). The drug received FDA approval on July 13, 2015 for the treatment of schizophrenia, and as an adjunctive treatment for depression. It has been designed to provide improved efficacy and tolerability (e.g., less akathisia, restlessness and/or insomnia) over established adjunctive treatments for major depressive disorder (MDD).

Bitopertin is a glycine reuptake inhibitor which was under development by Roche as an adjunct to antipsychotics for the treatment of persistent negative symptoms or suboptimally-controlled positive symptoms associated with schizophrenia. Research into this indication has been largely halted as a result of disappointing trial results, but Roche continues to develop bitopertin for the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).

BL-1020 (perphenazine 4-aminobutanoate) is an investigational orally-active antipsychotic for the possible treatment of schizophrenia, it's an ester of GABA and perphenazine, and pharmacologically it acts as a D2 antagonist and GABA agonist. It has shown pro-cognitive effects in the trials. In March 2013, it went into the II/III trial phase. It has been introduced by BioLineRx, a biopharmaceutical development company.

AVN-211 (CD-008-0173) is a drug which acts as a highly selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist and is under development by Avineuro Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of schizophrenia. In early 2011, it successfully completed phase IIa clinical trials, with benefits on positive symptoms and some procognitive effects observed, and in mid 2013, phase IIb clinical trials for schizophrenia began. Avineuro Pharmaceuticals has also expressed intention to start clinical trials of AVN-211 for Alzheimer's disease in 2015.

Encenicline is a selective partial agonist of the α7 nicotinic receptor, and is in phase III clinical trials for the treatment of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia.
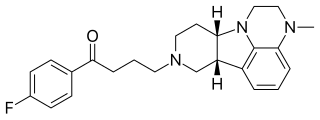
Lumateperone is an investigational butyrophenone antipsychotic which is currently under development by Intra-Cellular Therapies, licensed from Bristol-Myers Squibb, for the treatment of schizophrenia, as well as for bipolar depression and other neurological indications.

Brilaroxazine, also known by the developmental code names RP-5063 and RP-5000, is an investigational atypical antipsychotic which is under development by Reviva Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Reviva Pharmaceuticals also intends to investigate brilaroxazine for the treatment of bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, psychosis/agitation associated with Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease psychosis, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADD/ADHD), and autism. As of May 2015, it is in phase III clinical trials for schizophrenia.
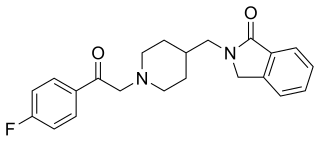
Roluperidone (former developmental code names MIN-101, CYR-101, MT-210) is a 5-HT2A and σ2 receptor antagonist that is under development by Minerva Neurosciences for the treatment of schizophrenia. One of its metabolites also has some affinity for the H1 receptor. As of May 2018, the drug is in phase III clinical trials.
Panamesine (INN; developmental code name EMD-57455) is a sigma receptor antagonist that was under development by Merck as a potential antipsychotic for the treatment of schizophrenia in the 1990s but was never marketed. It is a selective antagonist of both sigma receptor subtypes, the σ1 and σ2 receptors (IC50 = 6 nM). In addition, the major metabolite of the drug, EMD-59983, has high affinity for the sigma receptors (IC50 = 24 nM) and the dopamine D2 (IC50 = 23 nM) and D3 receptors, with potent antidopaminergic activity. Panamesine reached phase II clinical trials for schizophrenia prior to the discontinuation of its development.
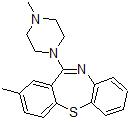
Metiapine is a typical antipsychotic medication of the dibenzothiazepine group. There is scarce research on the safety and efficacy of metiapine in humans, though limited human trials exist.
















