Venus is a planet in the Solar System, named after Venus (mythology), the Ancient Roman goddess of love.

Venera 2MV-1 No.1, also known as Sputnik 19 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme, and was intended to become the first spacecraft to land on Venus. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the atmosphere a few days later. It was the first of two Venera 2MV-1 spacecraft, both of which failed to leave Earth orbit.

Venera 2MV-1 No.2, also known as Sputnik 20 in the Western world, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme, and was intended to become the first spacecraft to land on Venus. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the atmosphere a few days later. It was the second of two Venera 2MV-1 spacecraft, both of which failed to leave Earth orbit. The previous mission, Venera 2MV-1 No.1, was launched several days earlier.
Kosmos 27, also known as Zond 3MV-1 No.3 was a space mission intended as a Venus flyby. The spacecraft was launched by a Molniya-M carrier rocket from LC-1 at Baikonur on March 27, 1964. The Blok L stage and probe reached Earth orbit successfully, but the attitude control system failed to operate and so the stage could not be oriented properly for main engine start. It reentered the atmosphere one day after launch and burned up. Examination of telemetry data found that the failure was due to a design flaw in the circuitry of the BOZ unit, which resulted in power not being transferred to the attitude control jets on the Blok L stage.

Venera 3 was a Venera program space probe that was built and launched by the Soviet Union to explore the surface of Venus. It was launched on 16 November 1965 at 04:19 UTC from Baikonur, Kazakhstan, USSR. The probe comprised an entry probe, designed to enter the Venus atmosphere and parachute to the surface, and a carrier/flyby spacecraft, which carried the entry probe to Venus and also served as a communications relay for the entry probe.
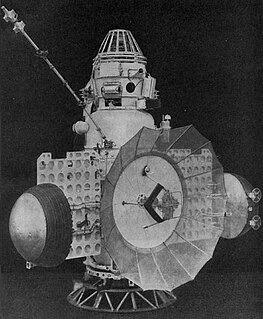
Venera 2, also known as 3MV-4 No.4 was a Soviet spacecraft intended to explore Venus. A 3MV-4 spacecraft launched as part of the Venera programme, it failed to return data after flying past Venus.

Fincantieri S.p.A. is an Italian shipbuilding company based in Trieste, Italy. Already the largest shipbuilder in Europe, after the acquisition of Vard in 2013 and 50% of STX France in 2018, Fincantieri group doubled in size to become the fourth largest in the world. The company builds both commercial and military vessels.
Venera 2MV-2 No.1, also known as Sputnik 21 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme, and was intended to make a flyby of Venus. Due to a problem with the rocket which launched it, it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the atmosphere a few days later. It was the second Venera 2MV-2 spacecraft, both of which failed to leave Earth orbit.
William Doxford & Sons Ltd, often referred to simply as Doxford, was a British shipbuilding and marine engineering company.

The State Dockyard was a ship building and maintenance facility operated by the Government of New South Wales in Carrington, Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia between 1942 and 1987.

The 3MV planetary probe is a designation for a common design used by early Soviet unmanned probes to Mars and Venus. It was an incremental improvement of earlier 2MV probes and was used for Zond 1, Zond 2 and Zond 3 missions to Mars as well as several Venera probes. It was standard practice of the Soviet space program to use standardized components as much as possible. All probes shared the same general characteristics and differed only in equipment necessary for specific missions. Each probe also incorporated improvements based on experience with earlier missions.
It was superseded by the 4MV family.
German submarine U-564 was a Type VIIC U-boat built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine for service during the Second World War. The RAF sank her in the Bay of Biscay on 14 June 1943.
Zond 3MV-1 No.2, also known as Venera 1964A in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1964 as part of the Zond program. Due to a problem with its carrier rocket third stage, it failed to reach low Earth orbit.

Kosmos 96, or 3MV-4 No.6, was a Soviet spacecraft intended to explore Venus. A 3MV-4 spacecraft launched as part of the Venera programme, Kosmos 96 was to have made a flyby of Venus; however, due to a launch failure, it did not depart low Earth orbit.
The Eisenhower Lock is one of the seven canal locks on the St Lawrence River leg of the St Lawrence Seaway.
It is one of two locks located near Massena, New York.
TSS Princess Maud was a ferry that operated from 1934 usually in the Irish Sea apart from a period as a troop ship in the Second World War and before being sold outside the United Kingdom in 1965. She was built by William Denny and Brothers of Dumbarton on the Firth of Clyde for the London Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS). When the LMS was nationalised in 1948 she passed to the British Transport Commission and onward to British Rail in 1962. She was sold to Lefkosia Compania Naviera, Panama in 1965. Renamed Venus she was for service in Greek waters. It is understood she saw use as an accommodation ship in Burmeister & Wain, Copenhagen.





