
Maribor is the second-largest city in Slovenia and the largest city of the traditional region of Lower Styria. It is also the seat of the City Municipality of Maribor, the seat of the Drava statistical region and the Eastern Slovenia region. Maribor is also the economic, administrative, educational, and cultural centre of eastern Slovenia.

Marburg is a university town in the German federal state (Bundesland) of Hesse, capital of the Marburg-Biedenkopf district (Landkreis). The town area spreads along the valley of the river Lahn and has a population of approximately 76,000.

Graz is the capital city of the Austrian state of Styria and second-largest city in Austria after Vienna. As of 1 January 2021, it had a population of 331,562. In 2018, the population of the Graz larger urban zone (LUZ) stood at 652,654, based on principal-residence status. Graz is known as a college and university city, with four colleges and four universities. Combined, the city is home to more than 60,000 students. Its historic centre (Altstadt) is one of the best-preserved city centres in Central Europe.
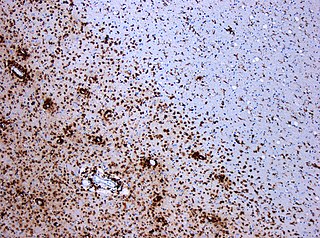
Multiple sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks or building up over time. In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances.

Marburg virus disease is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and primates caused by either of the two Marburgviruses: Marburg virus (MARV) and Ravn virus (RAVV). Its clinical symptoms are very similar to those of Ebola virus disease (EVD).

Rudolf Maister was a Slovene military officer, poet and political activist. The soldiers who fought under Maister's command in northern Slovenia became known as "Maister's fighters". Maister was also an accomplished poet and self-taught painter.

Ptuj is a town in northeastern Slovenia that is the seat of the Municipality of Ptuj. Ptuj, the oldest recorded city in Slovenia, has been inhabited since the late Stone Age and developed from a Roman military fort. Ptuj was located at a strategically important crossing of the Drava River, along a prehistoric trade route between the Baltic Sea and the Adriatic. The area is part of the traditional region of Styria and it was part of the Austria-Hungarian Empire. In the early 20th century the majority of the residents spoke German, but today the population is largely Slovene. Residents of Ptuj are known as Ptujčani in Slovene.

The genus Marburgvirus is the taxonomic home of Marburg marburgvirus, whose members are the two known marburgviruses, Marburg virus (MARV) and Ravn virus (RAVV). Both viruses cause Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. Both are Select agents, World Health Organization Risk Group 4 Pathogens, National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Category A Priority Pathogens, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Category A Bioterrorism Agents, and are listed as Biological Agents for Export Control by the Australia Group.

Styria, also Slovenian Styria or Lower Styria, is a traditional region in northeastern Slovenia, comprising the southern third of the former Duchy of Styria. The population of Styria in its historical boundaries amounts to around 705,000 inhabitants, or 34.5% of the population of Slovenia. The largest city is Maribor.
Betaherpesvirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the order Herpesvirales and in the family Herpesviridae. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 26 species in this subfamily, divided among 5 genera. Diseases associated with this subfamily include: human cytomegalovirus (HHV-5): congenital CMV infection; HHV-6: 'sixth disease' ; HHV-7: symptoms analogous to the 'sixth disease'.
Morpurgo is an Italian surname of Jewish origin. Originally Marpurg, from the Austrian city Marburg an der Drau. Key ancestor was Moises Jacob, father of Petachia, in Bad Radkersburg, Austria. Petachia (1355–1460) had three sons who died in Maribor. Their subsequent multinational progeny took the surnames Maribor, Marburg, Marpurg, Morpurgo, Marlborough, Murphy.

Otto Marburg was an Austrian neurologist known for his contributions to the understanding of multiple sclerosis and for advances in neurooncology.

Baló's concentric sclerosis is a disease in which the white matter of the brain appears damaged in concentric layers, leaving the axis cylinder intact. It was described by József Mátyás Baló who initially named it "leuko-encephalitis periaxialis concentrica" from the previous definition, and it is currently considered one of the borderline forms of multiple sclerosis.

The Pyramid is a low hill in the city of Maribor, Slovenia. It is a popular excursion spot, affording a good view of the city. An ascent takes 15 to 30 minutes.

Marburg's Bloody Sunday was a massacre that took place on Monday, 27 January 1919 in the city of Maribor in Slovenia. Soldiers from the army of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, under the command of Slovene officer Rudolf Maister, killed between 9 and 13 civilians of German ethnic origin, wounding a further 60, during a protest in a city centre square. Estimates of casualties differ between Slovene and Austrian sources.

Marburg virus is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the Filoviridae family of viruses and a member of the species Marburg marburgvirus, genus Marburgvirus. Marburg virus (MARV) causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. The virus is considered to be extremely dangerous. The World Health Organization (WHO) rates it as a Risk Group 4 Pathogen. In the United States, the NIH/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases ranks it as a Category A Priority Pathogen and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lists it as a Category A Bioterrorism Agent. It is also listed as a biological agent for export control by the Australia Group.
Ravn virus is a close relative of Marburg virus (MARV). RAVV causes Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. RAVV is a Select agent, World Health Organization Risk Group 4 Pathogen, National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Category A Priority Pathogen, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Category A Bioterrorism Agent, and listed as a Biological Agent for Export Control by the Australia Group.
The Austro-Slovene conflict in Carinthia was a military engagement that ensued in the aftermath of World War I between forces loyal to the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs and later the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, and forces loyal to the Republic of German-Austria. The main theater of the conflict was the linguistically mixed region in southeastern Carinthia. The conflict was settled by the Treaty of Saint-Germain in 1919, which stipulated that the territorial dispute be resolved by a plebiscite.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Maribor, Slovenia.

The Drava Valley Railway is an east–west railway running along the Drava. It runs from Maribor to Innichen, where it merges into the Puster Valley Railway to Franzensfeste (Fortezza). It starts in northern Slovenia, crosses Carinthia and East Tyrol and ends in South Tyrol. The Klagenfurt–Bleiburg section has been rebuilt as part of the Koralm Railway, which follows the Jaun Valley Railway (Jauntalbahn) from Bleiburg. Like the rest of the line in Slovenia, this section of the line has one track and is unelectrified.













