Other uses
- Taungoo Mingaung, one of the Thirty Seven nats
Minkhaung (also spelled Mingaung or Minhkaung) was a Burmese royal title, and may refer to:

Mingyi Nyo was the founder of the Toungoo dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). Under his 45-year leadership (1485–1530), Toungoo (Taungoo), grew from a remote backwater vassal state of Ava Kingdom to a small but stable independent kingdom. In 1510, he declared Toungoo's independence from its nominal overlord Ava. He skillfully kept his small kingdom out of the chaotic warfare plaguing Upper Burma. Toungoo's stability continued to attract refugees from Ava fleeing the repeated raids of Ava by the Confederation of Shan States (1490s–1527). Nyo left a stable, confident kingdom that enabled his successor Tabinshwehti to contemplate taking on larger kingdoms on his way to founding the Toungoo Empire.
Minkhaung II was king of Ava from 1480 to 1501. His 20-year reign was the beginning of the decline of Ava's hold on Upper Burma. Yamethin, a region to the east of Ava, revolted upon Minkhaung's accession to the Ava throne and stayed independent throughout Minkhaung's reign. The southern regions of Prome and Tharrawaddy revolted in 1482, and also stayed independent. By the mid-1490s, the Shan states of Mohnyin, Mogaung, Momeik and Kale (Kalay) had also broken away, and begun raiding northern Ava territories. Minkhaung increasingly came to rely on Mingyi Nyo, the Viceroy of Toungoo, for military assistance. By the end of his reign, Toungoo was equally powerful as its nominal overlord Ava.
Mingyi Swa of Prome was viceroy of Prome from 1446 to 1482 during the reigns of kings Narapati I, Thihathura I and Minkhaung II of Ava.
Bayin Htwe was king of Prome (Pyay) from 1527 to 1532. His small kingdom, founded by his father Thado Minsaw in 1482, was conquered by the Confederation of Shan States in 1532, and he was taken prisoner to Upper Burma. He was later released, and returned to Prome only to be refused entry by his son Narapati. Bayin Htwe died at the outskirts of Prome (Pyay) in mid 1533.
Narapati of Prome was king of Prome from 1532 to 1539. He seized the throne after his father Bayin Htwe was taken captive by the Confederation of Shan States in 1532 back to Upper Burma. Bayin Htwe escaped after the Confederation's leader Sawlon was assassinated by his ministers, and returned to Prome (Pyay), c. May 1533. But Narapati shut the gates against his father, who soon died in the adjoining forests.
Minkhaung of Prome was the last king of Prome, who reigned three tumultuous years from 1539 to 1542. He succeeded his brother Narapati in 1539. Minkhaung frantically prepared to defend against another attack by Toungoo Kingdom. He reinforced his already heavily fortified city of Prome (Pyay), and hired foreign mercenaries. Although he knew his nominal overlords, the Confederation of Shan States, would assist him, he continued the alliance with King Min Bin of Mrauk U begun by his late brother. Min Bin was married to Minkhaung's and Narapati's sister.
The Prome Kingdom was a kingdom that existed for six decades between 1482 and 1542 in present-day central Burma (Myanmar). Based out of the city of Prome (Pyay), the minor kingdom was one of the several statelets that broke away from the dominant Ava Kingdom in the late 15th century. Throughout the 1520s, Prome was an ally of the Confederation of Shan States, and together they raided Avan territory. After Ava fell to the Confederation armies in 1527, Prome itself became a tributary of the Confederation in 1532. In the late 1530s, Prome became ensnarled in the Toungoo–Hanthawaddy War (1534–1541). Despite military assistance from the Confederation and the Mrauk U Kingdom, the small kingdom fell to the Toungoo (Taungoo) forces in 1542.
Thado Dhamma Yaza II was viceroy of Prome (Pyay) from 1551 to 1588, during the reigns of kings Bayinnaung and Nanda of Toungoo Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). Having begun his military career in the service of King Tabinshwehti, the youngest full brother of Bayinnaung was part of the small core group loyal to Bayinnaung, following the assassination of Tabinshwehti in 1550. Alongside his brothers Bayinnaung, Minye Sithu, Minkhaung II, Thado Minsaw and his nephew Nanda, he fought in nearly every campaign between 1550 and 1584 that rebuilt, expanded and defended the Toungoo Empire.
Minkhaung II of Toungoo was viceroy of Toungoo (Taungoo) from 1549 to 1551 and from 1552 to 1584 during the reigns of kings Tabinshwehti, Bayinnaung and Nanda of Toungoo Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). He briefly revolted against his eldest half-brother Bayinnaung from 1550 to 1551 but was pardoned by Bayinnaung. Alongside his brothers Bayinnaung, Minye Sithu, Thado Dhamma Yaza II, Thado Minsaw and his nephew Nanda, he fought in nearly every campaign between 1552 and 1584 that rebuilt, expanded and defended the Toungoo Empire.
Salin Mibaya was the chief queen of Viceroy Thado Dhamma Yaza II of Prome.
Thado Minsaw was viceroy of Ava (Inwa) from 1555 to 1584 during the reigns of kings Bayinnaung and Nanda of Toungoo Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). He fought alongside his brothers Bayinnaung, Minye Sithu, Thado Dhamma Yaza II and Minkhaung II, and his nephew Nanda in nearly every campaign from the 1550s to 1570s that rebuilt, expanded and defended the Toungoo Empire. Two years after Bayinnaung's death, he raised the first serious rebellion against the rule of Nanda. Although his rebellion was defeated in April 1584, it had set in motion more rebellions elsewhere that ultimately led to the collapse of the empire in the next 15 years.
Anawrahta (1014–1077) was the founder of the Pagan Empire.
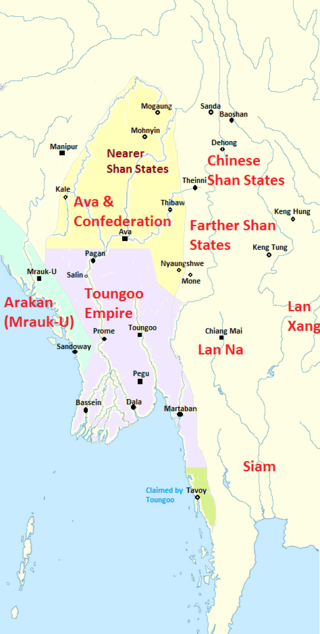
The Toungoo–Ava War (1538–1545) was a military conflict that took place in present-day Lower and Central Burma (Myanmar) between the Toungoo Dynasty, and the Ava-led Confederation of Shan States, Hanthawaddy Pegu, and Arakan (Mrauk-U). Toungoo's decisive victory gave the upstart kingdom control of all of central Burma, and cemented its emergence as the largest polity in Burma since the fall of Pagan Empire in 1287.
Atula Thiri Maha Yaza Dewi of Ava was the chief queen consort of King Narapati I of Ava from 1442 to 1468. She was the mother of King Thihathura of Ava and King Thado Minsaw of Prome, and a maternal aunt of King Leik Munhtaw of Hanthawaddy. King Alaungpaya, the founder of the Konbaung dynasty, was a tenth generation descendant of the queen.
Min Htwe was a principal queen consort of King Nanda of Toungoo Dynasty of Myanmar (Burma) from 1583 to 1599. The second daughter of Viceroy Minkhaung II of Toungoo, along with her two sisters Min Phyu and Min Pu, married her first cousin Nanda in 1583. The marriages of state solidified the ties between Minkhaung II and Nanda, the High King. At Pegu (Bago), she became the Queen of the Central Palace.
Thiri Yaza Dewi was a principal queen consort of King Nanda of Toungoo Dynasty of Myanmar (Burma) from 1583 to 1599. The youngest daughter of Viceroy Minkhaung II of Toungoo, along with her two sisters Min Phyu and Min Htwe, married her first cousin Nanda in 1583. The marriages of state solidified the ties between Minkhaung II and Nanda, the High King. At Pegu (Bago), she became the Queen of the Northern Palace.
Minye Kyawswa Saw Shwe Khet was governor of Prome (Pyay), a major vassal state of Ava, from 1417 to 1422, and from 1442 to 1446. He was the only governor or viceroy of Prome to serve more than one term. He also served as governor of districts of Prome: twice at Tharrawaddy (Thayawadi) (1422–1427) and (1446–1460) and at Paungde (1460–1470s).
Minkhaung Medaw was a principal queen of King Taka Yut Pi of Hanthawaddy (Ramanya) from c. 1535 to 1539, and of King Min Bin of Mrauk U (Arakan) from c. 1540 to 1554. A daughter of King Bayin Htwe of Prome, the queen is also referred to as Pegu Mibaya and Tanzaung Mibaya in the royal chronicles.
Tarabya I of Pakhan was a Burmese governor and military commander during the early Ava period. Between 1390 and 1413, Tarabya served as governor of Pakhan and as an officer in the Ava military in several campaigns, mostly against the southern Hanthawaddy forces in the Forty Years' War. In 1413, he lost his military command and was transferred to become governor of Pagan (Bagan), the ancient royal capital. He appeared to have ended his career there c. early 1430s.